Morphology and Origin
PVCs can be monomorphic or polymorphic. All monomorphic PVCs exhibit the same morphology. Polymorphic beats exhibit more than one morphology, meaning they look different.
Monomorphic PVCs are all generated by the same focus. This is also called unifocal. Polymorphic PVCs may have impulses that are unifocal but are coming from varying levels of ventricular activation with equal coupling intervals. Polymorphic PVCs may also be multifocal, in which case they display varying coupling intervals.
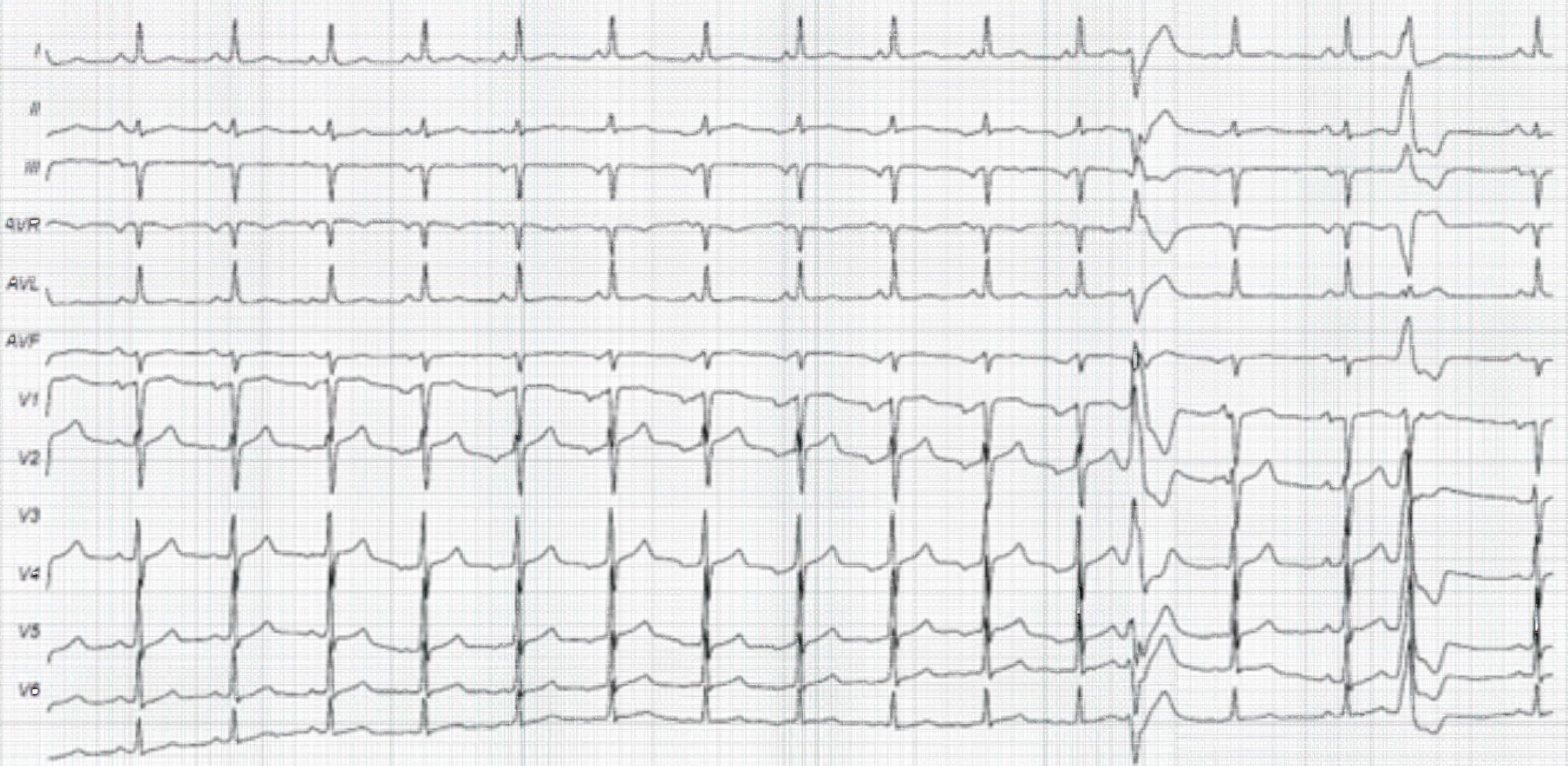
Polymorphic Premature Ventricular Complexes ECG
Some PVCs that originate from the left ventricle have an RBBB pattern. PVCs that originate from the right ventricle present with an LBBB pattern. This is mostly seen in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia. These patients present with PVCs or ventricular tachycardia with a left bundle-branch pattern.
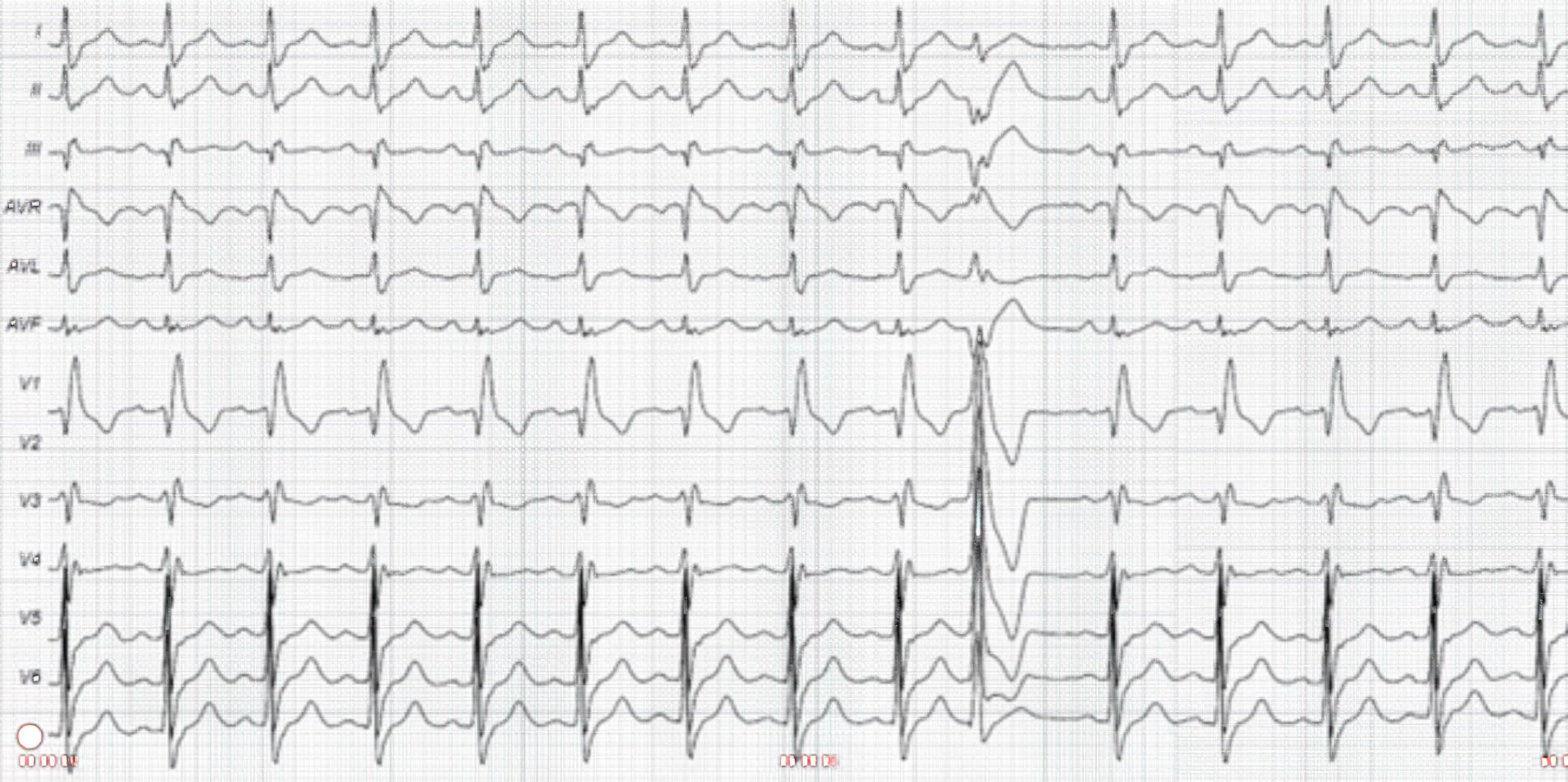
Premature Ventricular Contraction With RBBB Pattern
Since most heart diseases affect the left ventricle, one might expect patients with PVCs and RBBB pattern to outnumber those with LBBB pattern. However, this is not the case. Other mechanisms that alter the QRS complexes must play a role, such as the location of the electrical impulse breakthrough.
PVCs in the superior QRS axis reflect an impulse from either the left posterior fascicle or the base of either ventricle. A PVC in the vertical QRS axis reflects an impulse from either the left anterior fascicle or the right ventricular outflow tract. If the PVC has a narrow QRS complex (which is not common), the site of origin is the septum, and the impulse is conducted over the right bundle-branch and the left fascicles.