Conduction in Sinus Rhythm
Conduction in Sinus Rhythm
Impulses from the SA node are conducted over the fast and slow pathways in an antegrade direction. The slower impulse is blocked at the inferior aspect of the AV nodal tissue because the faster impulse has already activated it and the tissue reached the refractory state before the slower impulse conduction from the SA node reached it (see figure 1).
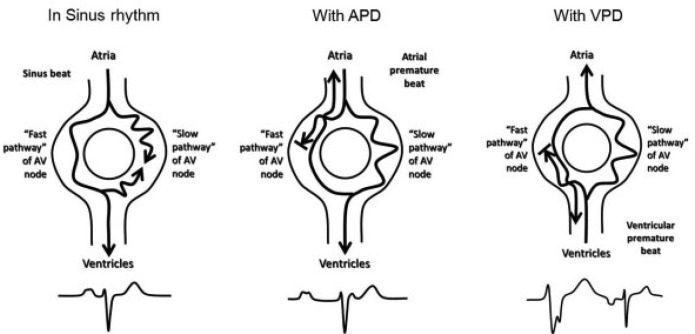
Dual AV Nodal Pathway Physiology in Sinus Rhythm 46
The figure above depicts the physiology of the AV nodal pathways during sinus rhythm, with a PAC (which initiates the common “slow-fast” type of AVNRT), and with a PVC (which initiates the rarer “fast-slow” type of AVNRT).
46 Mani BC, Pavri BB. Dual atrioventricular nodal pathways physiology: a review of relevant anatomy, electrophysiology, and electrocardiographic manifestations. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2014;14(1):12–25.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0972629216307112