Chapter 1: Theories in ECG Interpretation
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Chapter 2: Systematic Approach to ECG Interpretation
2 Topics | 1 Quiz
Chapter 5: Abnormalities of the P Wave
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
Chapter 6: Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
Chapter 8: Biventricular Hypertrophy
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
Chapter 9: Acute Pulmonary Embolism
7 Topics | 1 Quiz
Chapter 10: Fascicular Blocks
7 Topics | 1 Quiz
Chapter 11: Complete and Incomplete Bundle-Branch Blocks
5 Topics | 1 Quiz
Chapter 14: Myocardial Infarction
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Chapter 16: Pericarditis
6 Topics
Chapter 19: Atrial Arrhythmias
5 Topics | 1 Quiz
Chapter 20: Sick Sinus Syndrome
10 Topics | 1 Quiz
Chapter 22: Atrioventricular Junctional Tachycardias
5 Topics | 1 Quiz
Chapter 23: Premature Ventricular Contractions
7 Topics | 1 Quiz
Chapter 24: Ventricular Tachycardia
3 Topics
Chapter Progress
0% Complete
Get 12-Lead ECG Certified Today
Introduction
An acute pulmonary embolism (PE) obstructs the pulmonary vasculature. It occurs when a thrombus migrates into the pulmonary circulation. PE is one of the major causes of reversible cardiac arrest.
A PE can be fatal during the first 48 hours without medical intervention. Common diagnostic tools for detecting a pulmonary embolism are a nuclear medicine procedure known as a ventilation-perfusion scan and CT-angiography of the lungs. These two imaging modalities combined with serum D-dimer tests are the best diagnostic modalities for pulmonary embolism.
Related Video – Hs and Ts – Pulmonary Embolism
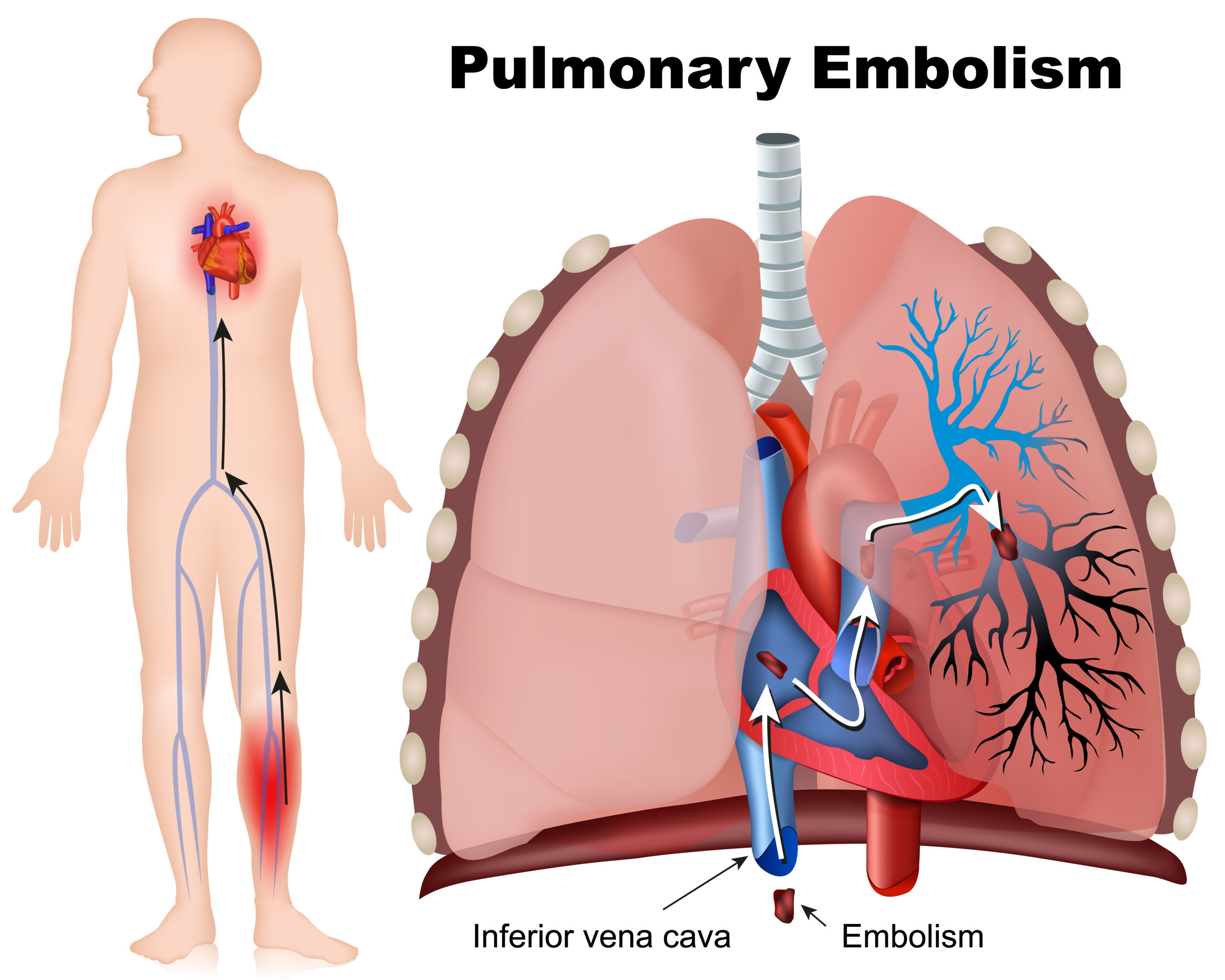
Pulmonary embolism is one of the major causes of reversible cardiac arrest.