Chapter Progress
0% Complete
Get 12-Lead ECG Certified Today
Left Anterior Fascicular Block
The most striking ECG characteristics of left anterior fascicular block are (see Figure 2):
- Left axis deviation in the frontal QRS axis between −30° and −90° in 90% of cases
- A single R wave in leads I and aVL
- A small q wave may be present, but an s wave is rare
- Slurring of the R wave
- An rS complex with a positive and asymmetric T wave in leads II, III, and aVF
- A negative T wave in aVR
- A positive, flat, or negative T wave in leads I and aVL
Other ECG characteristics in left anterior fascicular block:
- A smooth QRS transition zone with an RS configuration in precordial leads V1 through V6
- May have an rS complex in V1 through V6
- R and S amplitude may be equal in V2 and V3 and in V4 through V6
- R rarely higher than S in V2 and V3 or in V5 and V6
- A small s wave in lead I and a mirror image of an R wave in lead III
- Positive and asymmetric T wave in all precordial leads
- Small q wave in V3 through V6 is a rare finding
Left axis deviation is seen in 90% of patients with left anterior fascicular block. The remaining 10% of patients may have anterior fascicular block due to inferior wall infarction, LVH, and anatomical anomalies in the thorax.
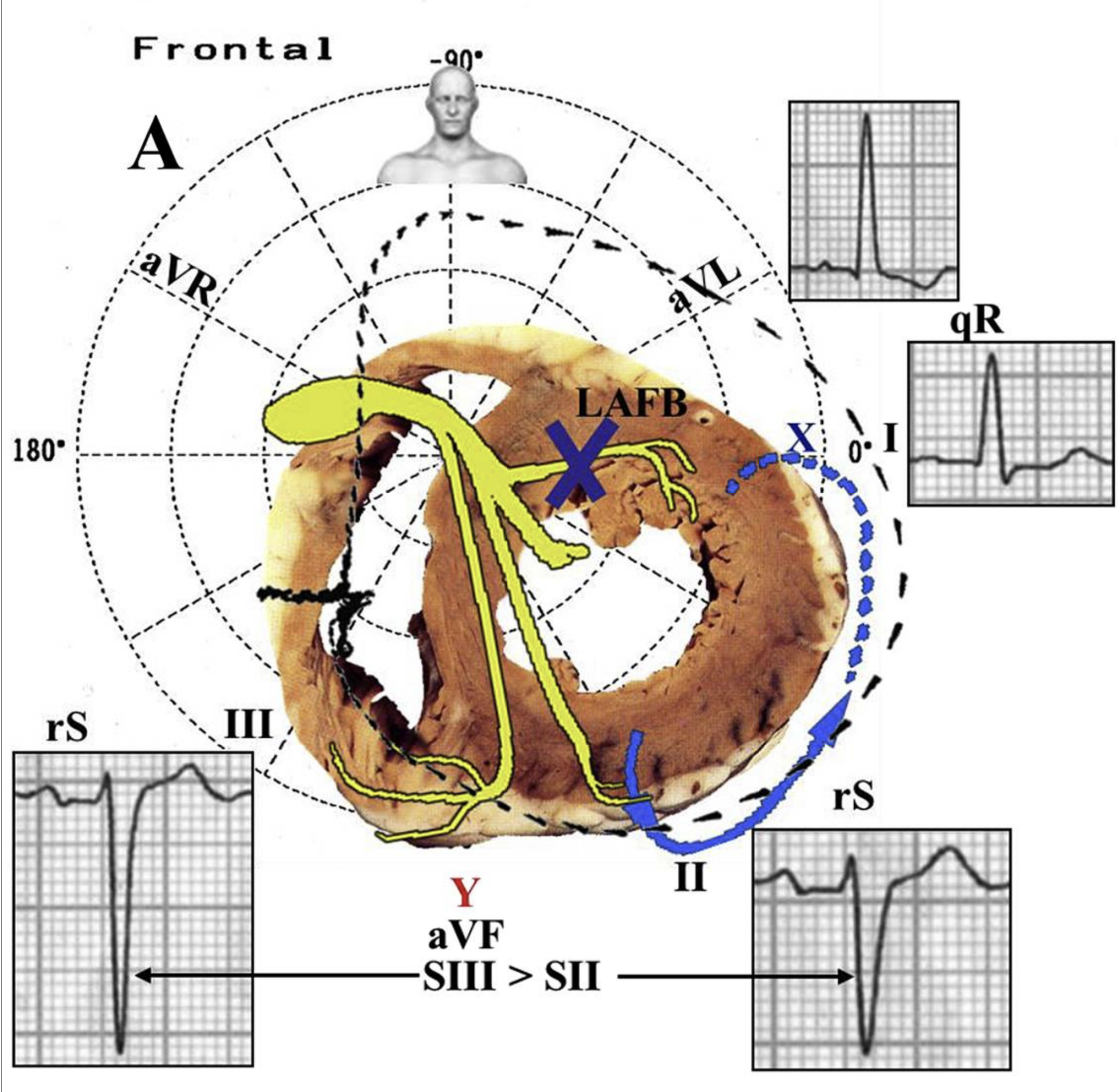
Left Anterior Fascicular Block With Vectors and Corresponding ECG Tracing 11
11 Pérez-Riera AR, Barbosa-Barros R, Daminello-Raimundo R, de Abreu LC, Tonussi Mendes JE, Nikus K. Left posterior fascicular block, state-of-the-art review: a 2018 update. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2018;18(6):217–230.