Exercise
EXERCISE 1. A patient in the emergency department presents with dyspnea at rest, distended jugular veins, and chest pain. You suspect an acute myocardial infarction and obtain a 12-lead ECG: 10
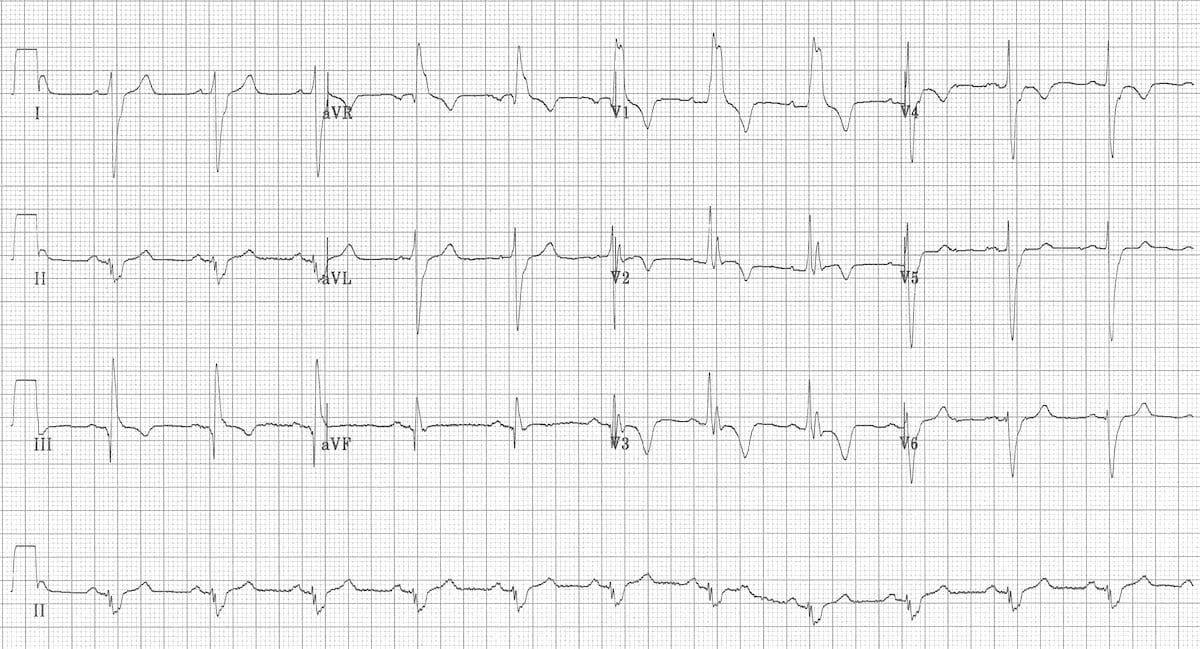
ECG Suggesting Acute Pulmonary Embolism
The pattern suggests acute pulmonary embolism. Diagnosis is confirmed by a spiral CT scan of the chest that shows a massive saddle PE in the right and left main pulmonary arteries.
List the ECG criteria for pulmonary embolism that are seen in the ECG tracing above.

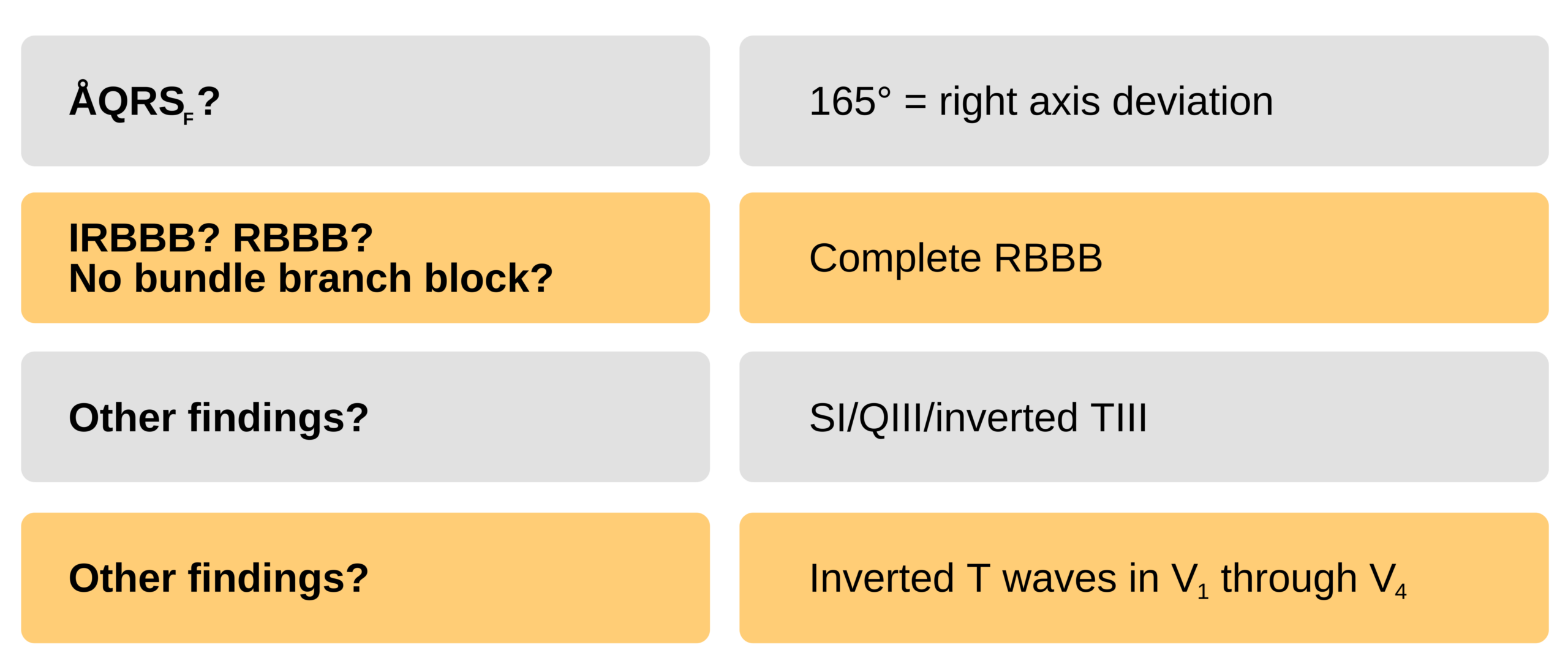
RATIONALE:
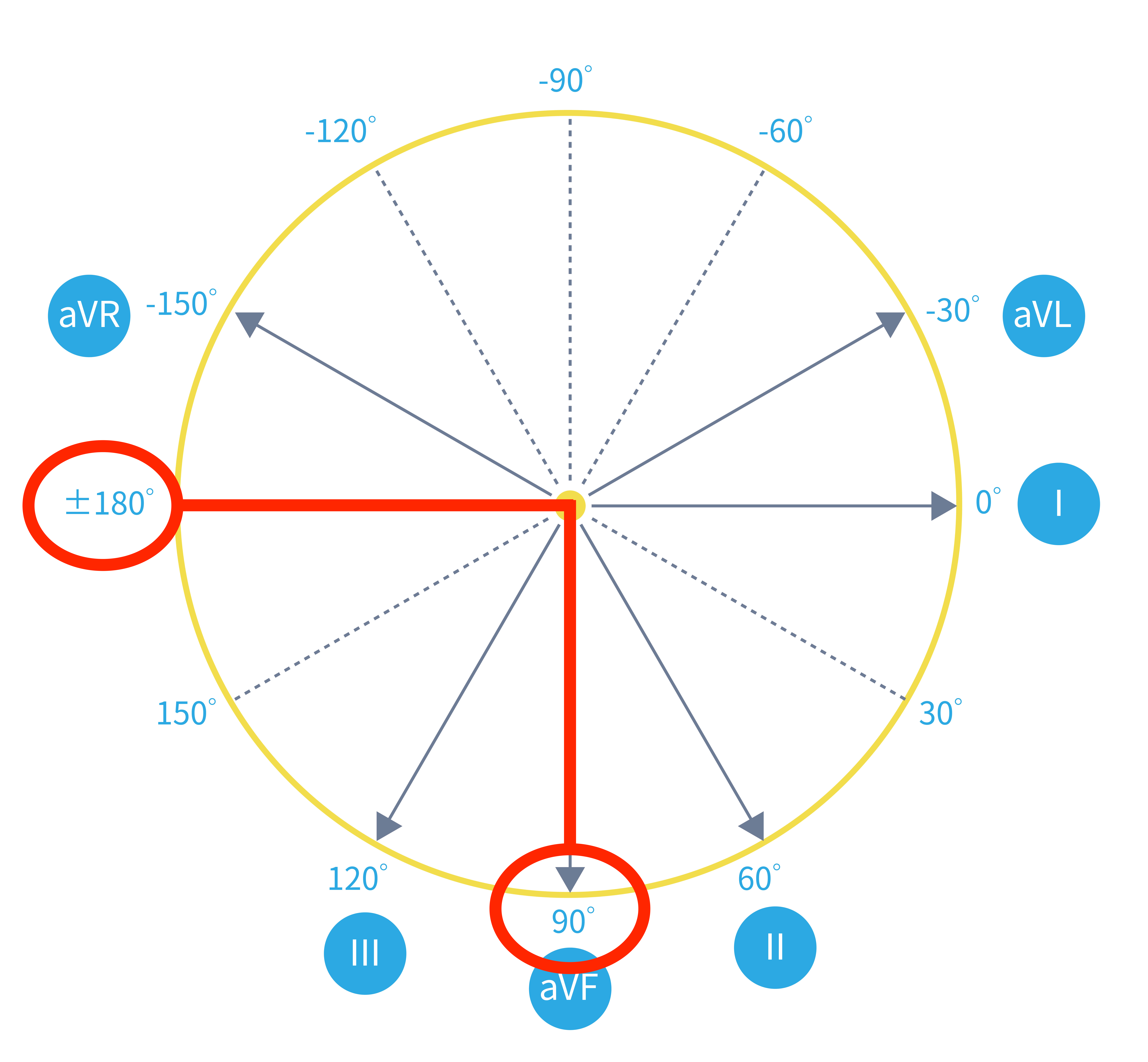
ÅQRSF 165°: aVF is the isoelectric lead, and lead I has a negative deflection. The axis is rotated 15° toward aVF because aVF is more positive than negative −180° − 15° = 165°. Negative deflections of lead II and aVR and positive deflections in lead aVL and III further confirm this evaluation of the cardiac axis.
Rationale Answer Infograph
The ECS suggests a complete RBBB because of the RSR pattern in leads V1 through V3.
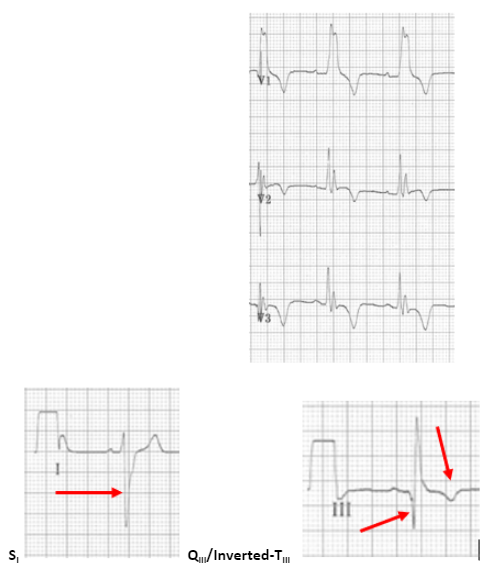
- Presence of SI QIII inverted-TIII
- Inverted T waves in V1–V4 (see 12-lead ECG above)
- Clockwise rotation
10 Burns E. Massive pulmonary embolism. Life in the fastlane website. Accessed May 8, 2021.
https://litfl.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/ECG-Massive-bilateral-pulmonary-embolus-2.jpeg