Vasopressors Following ROSC
Vasopressors Following ROSC
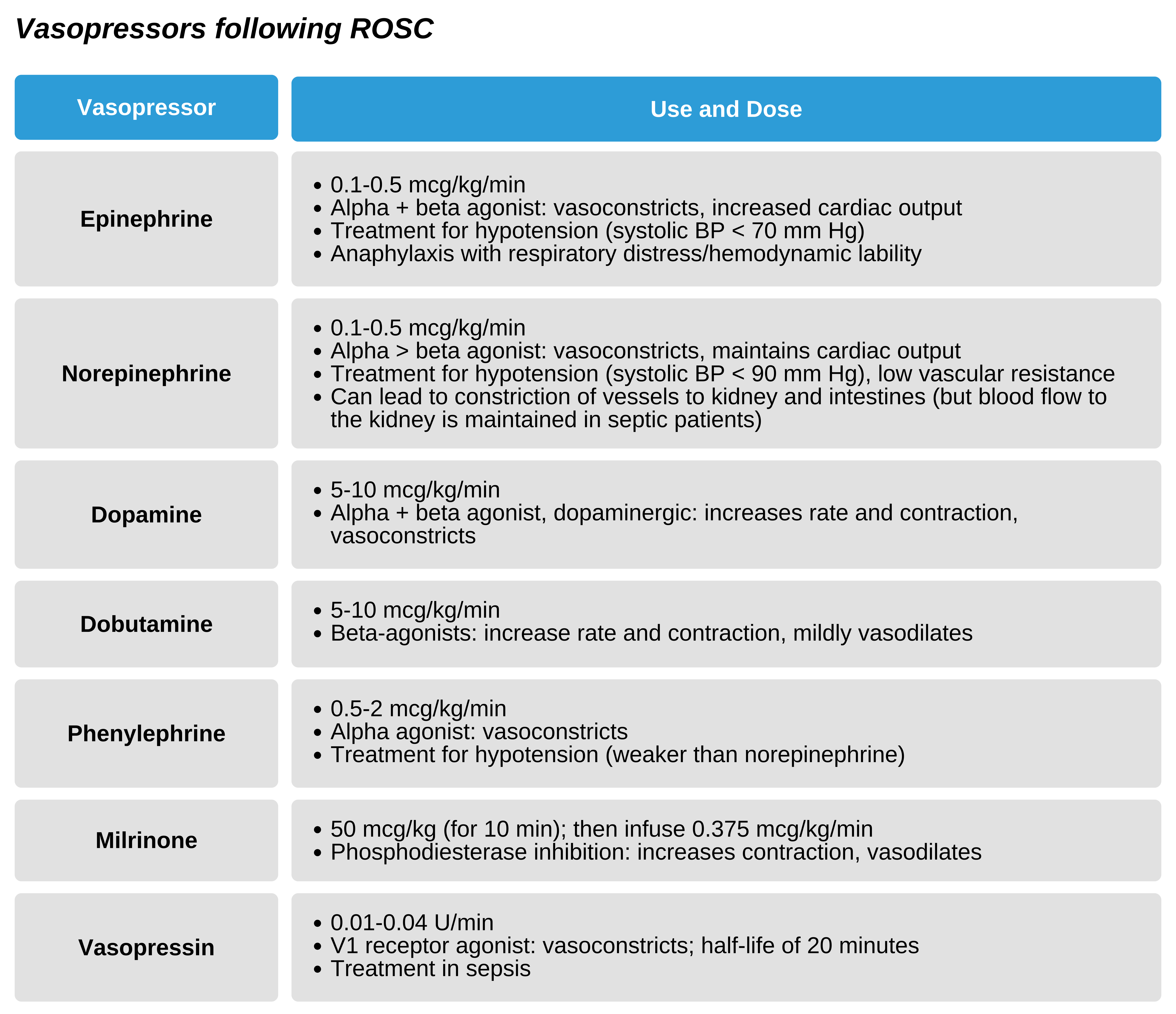
Vasopressors are used in this period to manage hemodynamics, cardiac output, and to ensure good perfusion of the brain and heart. During early ROSC, patients usually experience hemodynamic instability as well as a stunned myocardium following inadequate perfusion, reperfusion, and defibrillation injury that can persist for hours. Echocardiograms can help assess these conditions during this time.
Vasopressor medications, and their doses, are specific for contractility, rates, and systemic vascular effects and can reverse these effects. The goal should be to avoid hypotension using a combination of fluids and medications as needed. These medications do have adverse effects, and therefore the dose should be titrated to the best effect. Typically, administer via central line as they can cause necrosis in peripheral lines during extravasation. Do not administer these medications with alkaline solutions like sodium bicarbonate, which can inactive them.