Acquired Valvular Heart Diseases
ECG changes in patients with documented acquired valvular heart diseases assist in evaluating their severity. However, not all anatomical changes from acquired valvular heart diseases can be detected on ECG.
Valvular Aortic Stenosis
Of patients with valvular aortic stenosis, 60% present with detectable LVH on ECG. Slightly prolonged QRS complexes appear with discordant asymmetric T waves that have a negative deflection in limb leads I and aVL and precordial leads V5 and V6. These characteristics indicate systolic overload. The frontal QRS axis is normal (between +30° and +60°) because the nature of the anatomical changes in valvular aortic stenosis is concentric LVH.
Valvular Aortic Incompetence
In patients with valvular aortic incompetence, the ECG changes include tall R waves with deep Q waves in precordial leads V4 through V6. Slight ST wave elevation and tall symmetrical T waves appear in the same leads. The QRS complex is normal. A left ventricular diastolic overload pattern is not seen in valvular aortic incompetence. The frontal QRS axis is between +30° and −10°.
In general, the ECG pattern of valvular aortic incompetence resembles valvular aortic stenosis. T wave inversion in the lateral leads V5 and V6 may represent severe aortic incompetence.
Mitral Stenosis
In mitral stenosis, “twin-peaked” P waves indicate left atrial enlargement or “p mitrale.” The peak-to-peak interval between the P waves is > 0.04 seconds. RVH caused by mitral stenosis results in a vertical frontal QRS axis with an incomplete RBBB or a tall R wave in V1. Atrial fibrillation is common in patients with advanced mitral stenosis.
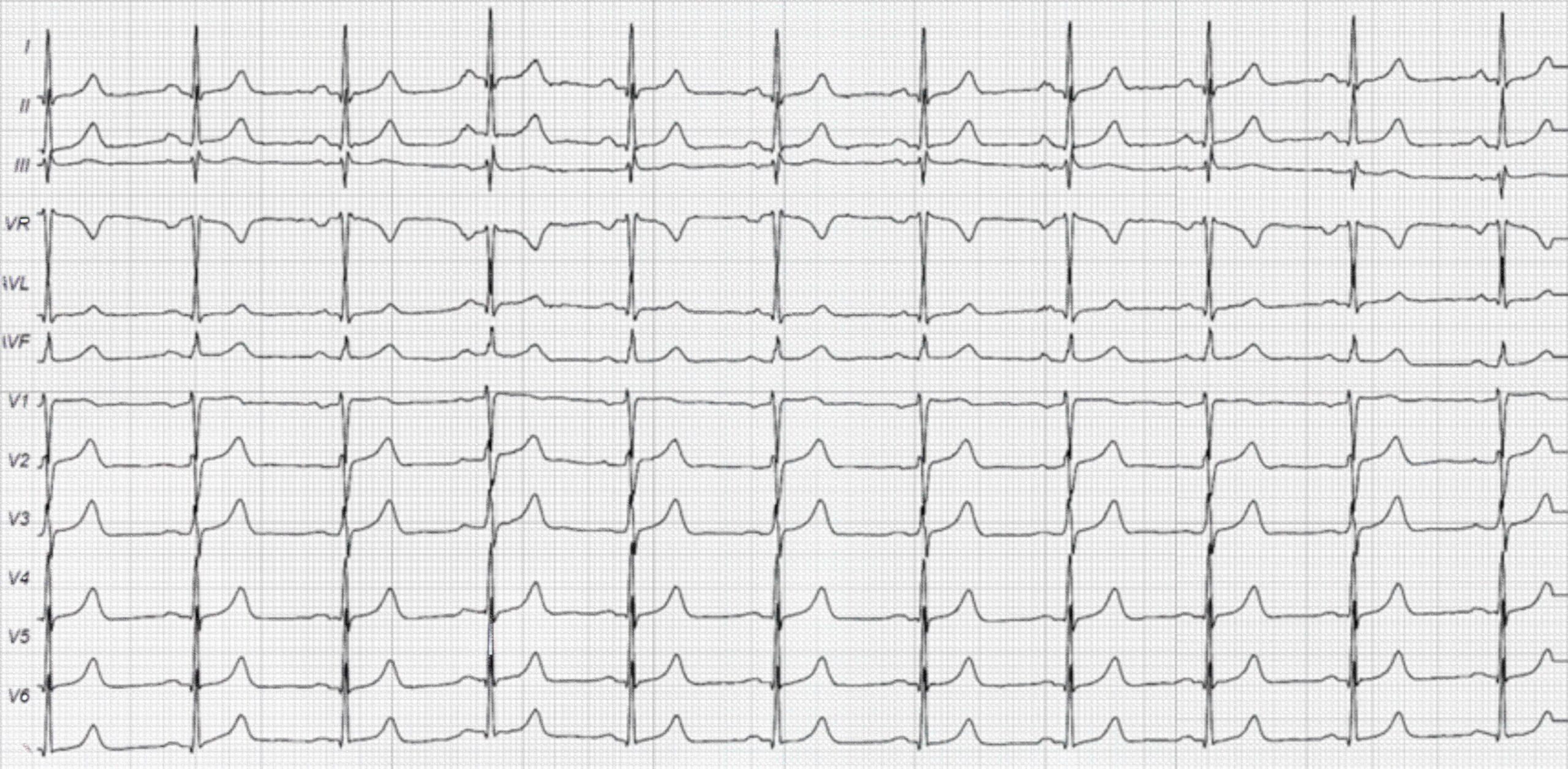
43-Year-Old Woman With a History of Mitral Stenosis ECG
The ECG above was taken from a 43-year-old woman with mitral stenosis that has caused left atrial enlargement. Twin-peaked P waves are noted with a duration of 0.12 seconds. The rest of the ECG findings are unremarkable.
Related Video – Aortic Stenosis – Part 1 (Heart Murmur Series)
Related Video – Aortic Stenosis – Part 2 (Heart Murmur Series)
Mitral Incompetence
Severe mitral incompetence causes left atrial enlargement and LVH in 30% of diagnosed patients. Sometimes a counterclockwise QRS rotation is seen with left ventricular dilatation instead of the expected clockwise rotation.

Foxglove AKA the Digitalis Plant