Treatment of AVNRT
Vagal maneuvers, intravenous adenosine, and intravenous calcium channel blockers or beta-blockers are treatment options for AVNRT.
If a patient is hemodynamically unstable, synchronized electrical cardioversion almost always terminates AVNRT in conjunction with the other treatments mentioned above.
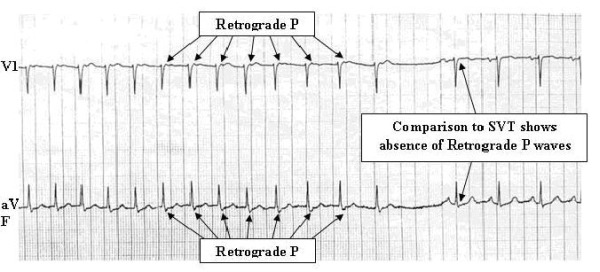
Typical AVNRT Terminated by Carotid Sinus Massage 50
Figure 2 shows AVNRT that is terminated with carotid sinus massage. The short RP-interval (< 0.1 seconds) suggests this patient has the more common “slow-fast” AVNRT. A retrograde P wave is immediately seen after the QRS complex and could be easily misconstrued as a broad S wave in frontal lead aVF.
After performing the vagal maneuver, the patient has achieved normal sinus rhythm. The retrograde P waves are absent in the sinus rhythm tracing, proving that these were not broad S waves but rather retrograde P waves in typical “slow-fast” AVNRT.
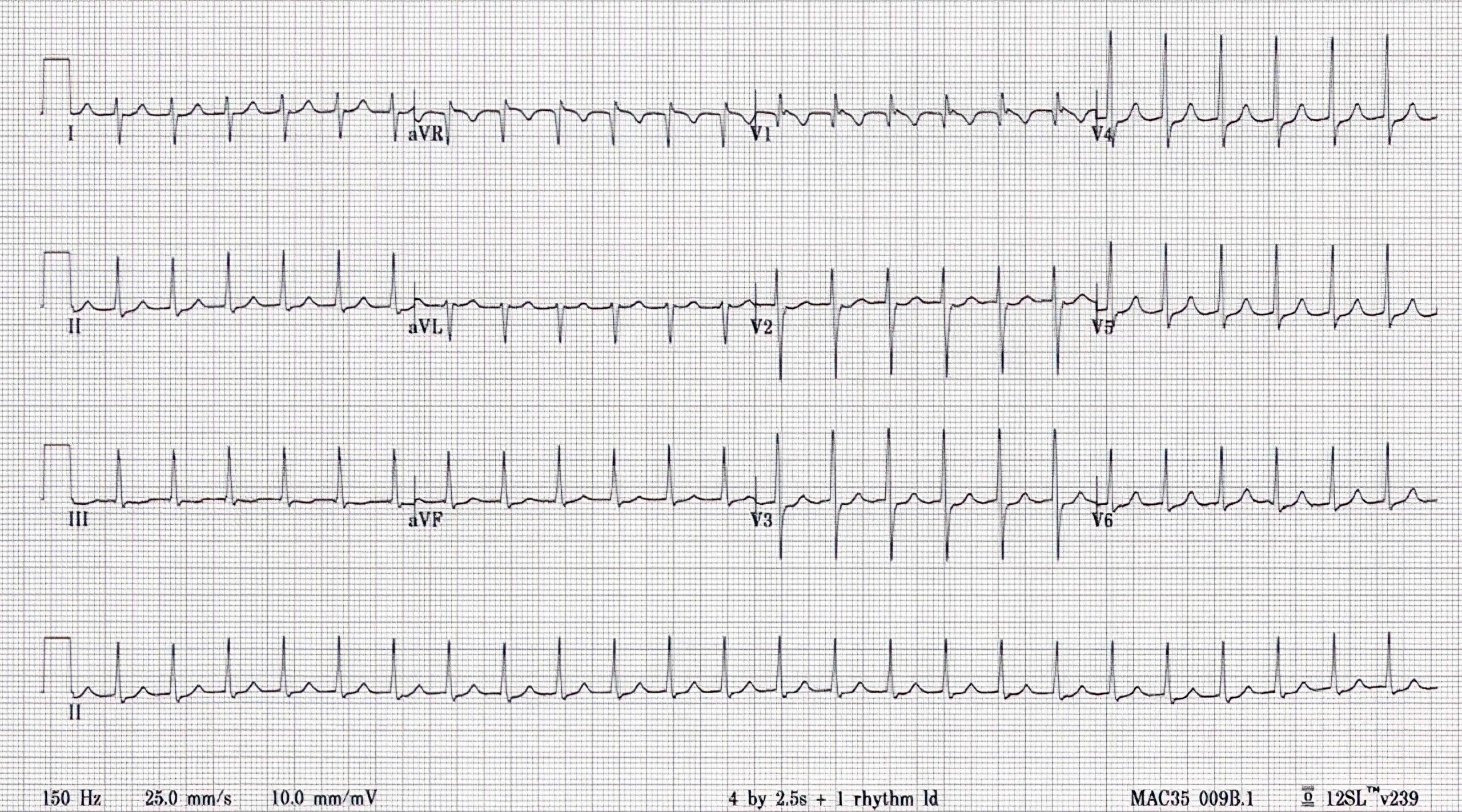
Typical AVNRT ECG (Left) and ECG After 6 mg Adenosine (Right)
The two ECGs above are from a patient with typical AVNRT (on the left) who was treated with adenosine (follow-up ECG on the right). The broad S waves disappear after the patient has achieved normal sinus rhythm (indicated by the arrow), a finding that confirms this is likely a retrograde P wave.
50 Mani BC, Pavri BB. Dual atrioventricular nodal pathways physiology: a review of relevant anatomy, electrophysiology, and electrocardiographic manifestations. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2014;14(1):12–25.