Conduction in Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia
AVNRT production is influenced by a premature atrial beat with a first-degree AV block. When the condition allows, the two pathways can be used as a reentry circuit in which one is conducted antegrade while the other is conducted in a retrograde direction. The rate in this circuit is fast, between 130 bpm and 220 bpm.
Common Form of AVNRT
AVNRT is paroxysmal; it occurs suddenly and spontaneously resolves. In the common form of AVNRT, the slow pathway traverses the antegrade direction while the fast pathway traverses retrograde. The atria and ventricles are activated at approximately the same time because the atria are on the receiving end of the retrograde impulse, and the ventricles are on the receiving end of the antegrade impulse.
In the frontal plane, P waves are produced in opposite directions. Visible P waves are negative in leads II, III, and aVF. The P wave is hidden within the QRS complex 70% of the time.
Ten percent of the time, P waves are superimposed at the end of the QRS complex. These can be described as pseudo-S waves in the inferior leads III and aVF. The P waves may also be superimposed in precordial lead V1, which produces pseudo-R’ waves. These characteristics have similar morphologies with an incomplete RBBB.
In 20% of patients, a P wave immediately follows the QRS complex, either somewhere in the ST segment or just before the T wave. This RP interval is relatively shorter than the PR interval.
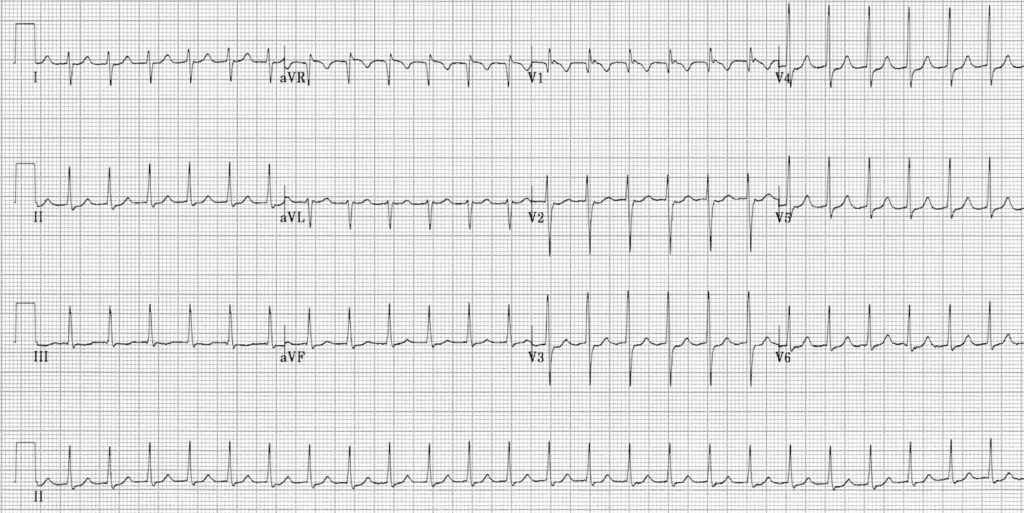
ECG Representing Typical Slow-Fast AVNRT 47
Atypical AVNRT
Paroxysmal AVNRT is most common, but AVNRT can be incessant, lasting for hours to days.
Of the patients diagnosed with AVNRT, 5% have the rare type. In rare AVNRT, the fast conduction circuit moves in an antegrade direction, while the slower circuit moves in a retrograde direction. The atria are activated last.
Negative P waves appear in the inferior leads III and aVF. The P waves appear late, after the QRS complex. The RP interval is longer than the PR interval.
The incessant form of rare AVNRT is resistant to pharmacologic therapies. Heart failure may ensue after days or months.
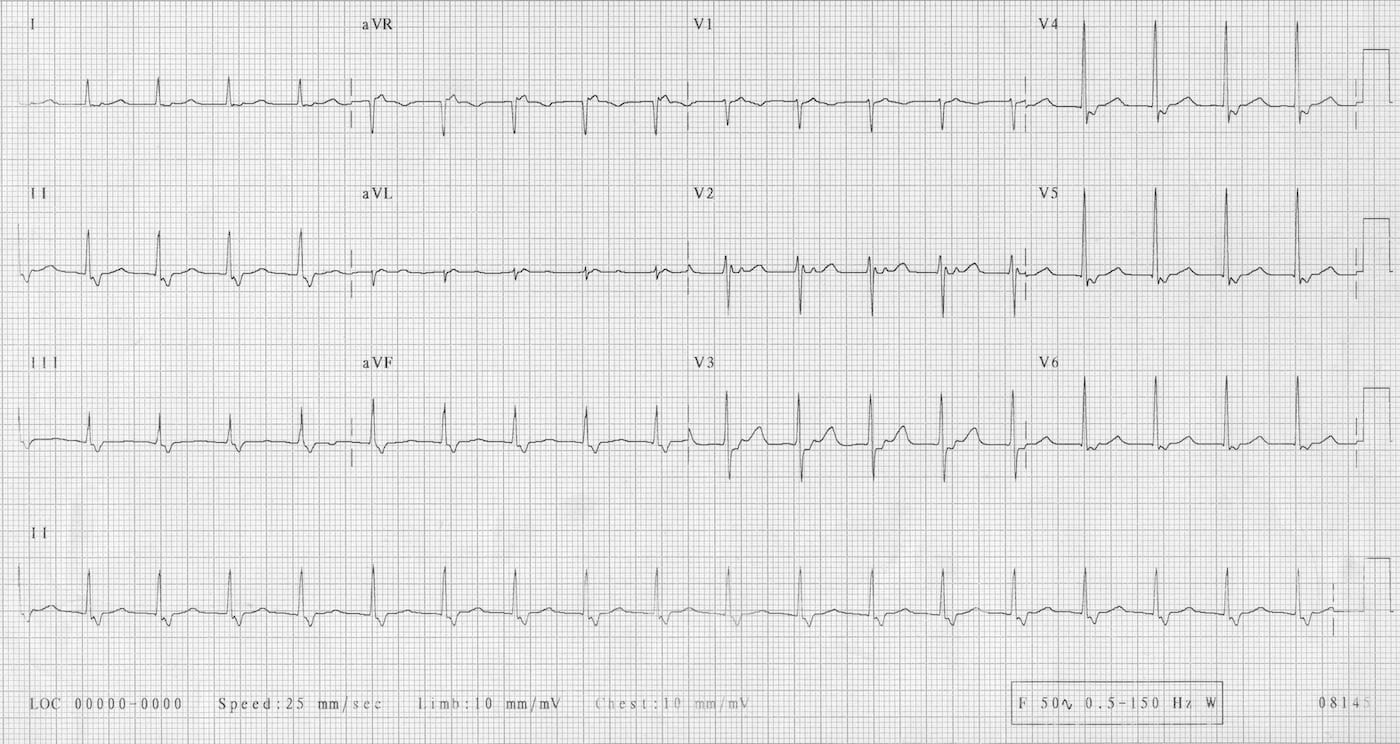
ECG Representing Atypical Fast-Slow AVNRT 48
47 Burns E. Supraventricular tachycardia. Life in the fastlane website. Accessed September 28, 2020.
https://litfl.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/Slow-Fast-Typical-AVNRT-1024×513.jpg
48 Cadogan M. AVNRT for two. Life in the fastlane website. Accessed September 28, 2020.
https://litfl.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/AVNRT-ECG-Library-03.jpeg