Arrhythmia
Normal variant arrhythmias are the ECG findings of an arrhythmia in a patient without any heart disease. To be considered a normal variant arrhythmia, three conditions must be present:
- Absence of heart disease
- The arrhythmia does not represent any normal variants
- The arrhythmia occurs only in rare instances, and its occurrence is unrelated to very low or very high rates.
A healthy individual may feel the symptoms of a normal variant arrhythmia.
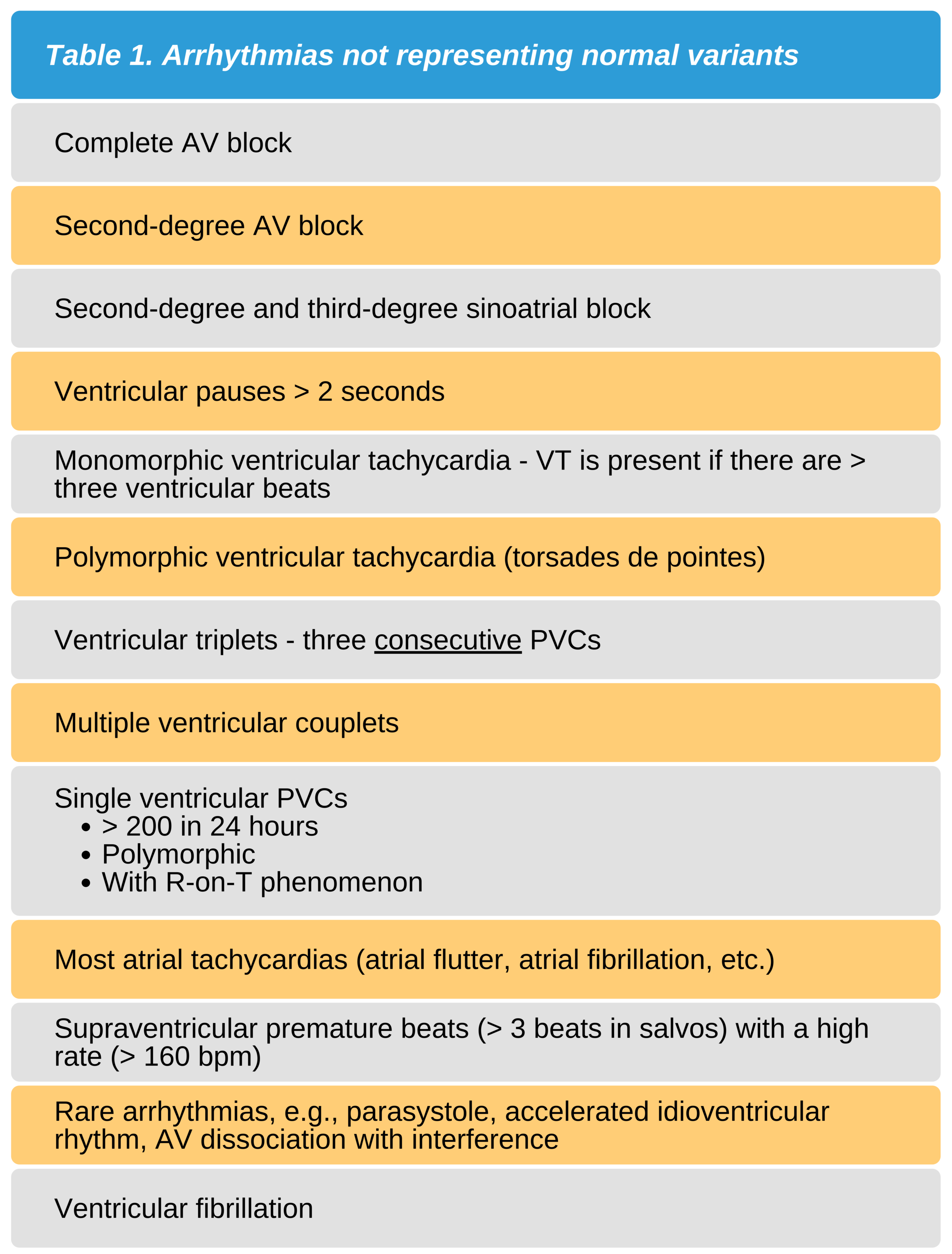
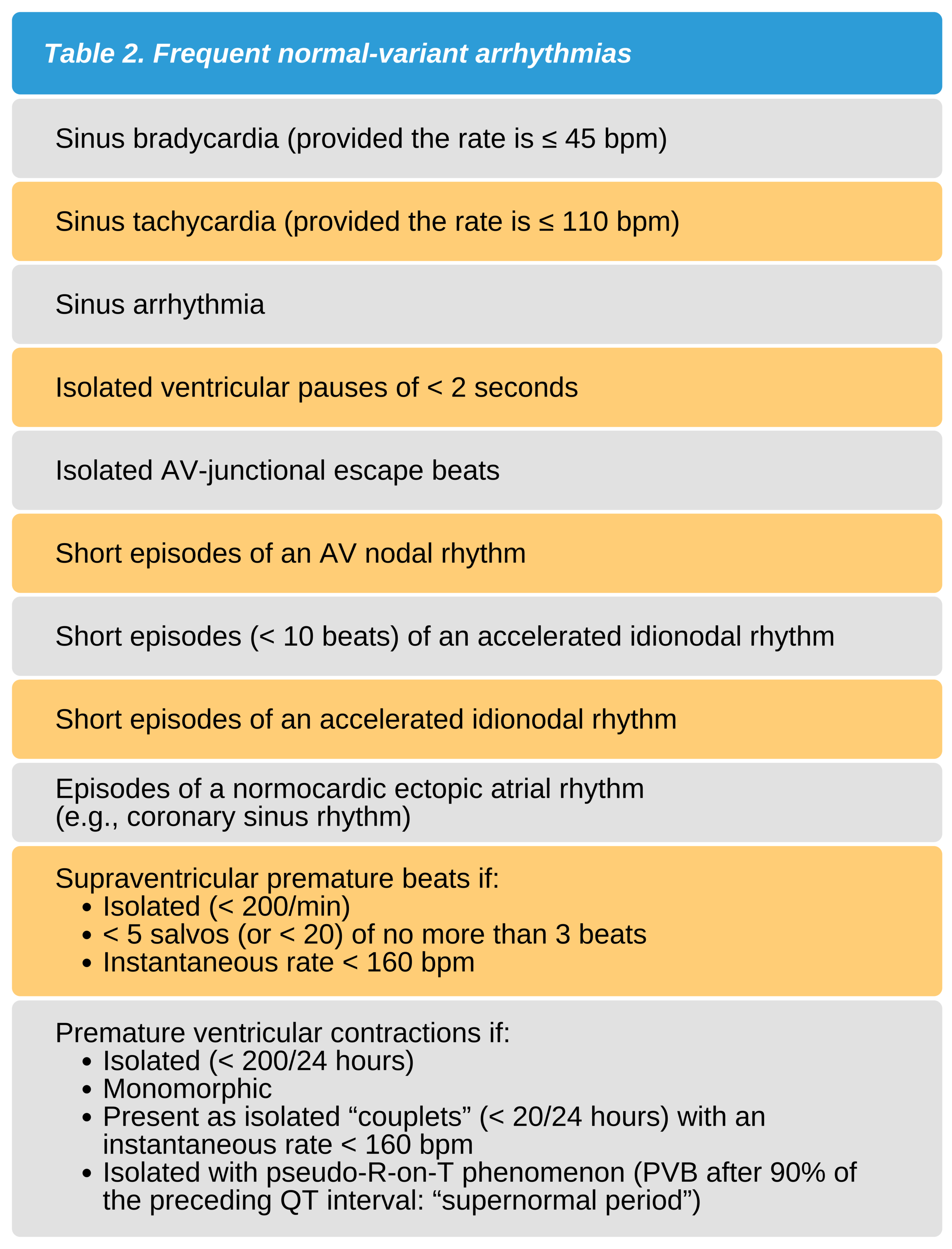
Table 1 lists the arrhythmias that do not represent normal variants. Table 2 lists the frequent normal-variant arrhythmias.
Given the list above, it is difficult to distinguish pathologic arrhythmias from normal variant arrhythmias. Younger athletic patients, for example, may present with a slow ventricular escape rhythm. Ventricular tachycardia in these types of patients may also be a normal variant. However, these findings must not be overlooked as they can represent serious cardiac conditions.
ECG interpreters must not only look for patterns in the ECG morphology of each patient. ECG interpretation and diagnosis must take into consideration the patient’s clinical presentation, demographics, and other ancillary findings.