The Resuscitation Team
Each team is composed of physicians, nurses, respiratory therapists, and pharmacists. Some centers also include security personnel, clergy, and social workers.
Key Takeaway
Team members must practice resuscitation procedures frequently. A commonly used strategy is just-in-time training, which includes simple training on a manikin in basic life support (BLS) with the use of a defibrillator. It can also be more advanced such as interdisciplinary ACLS in a simulation room. An expert physician typically supervises these training programs.
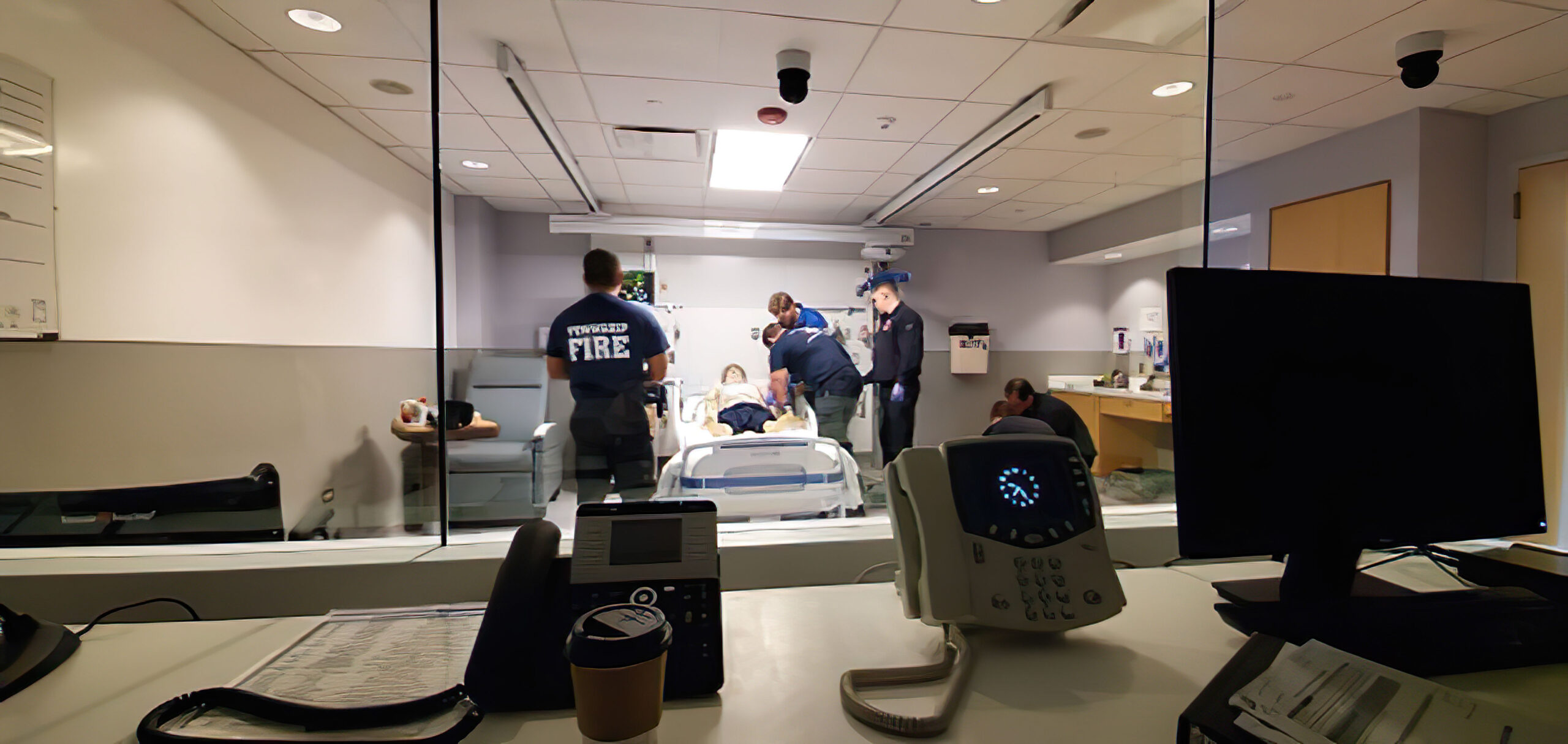

Clinicians monitoring the students in a high-fidelity ACLS simulation room.
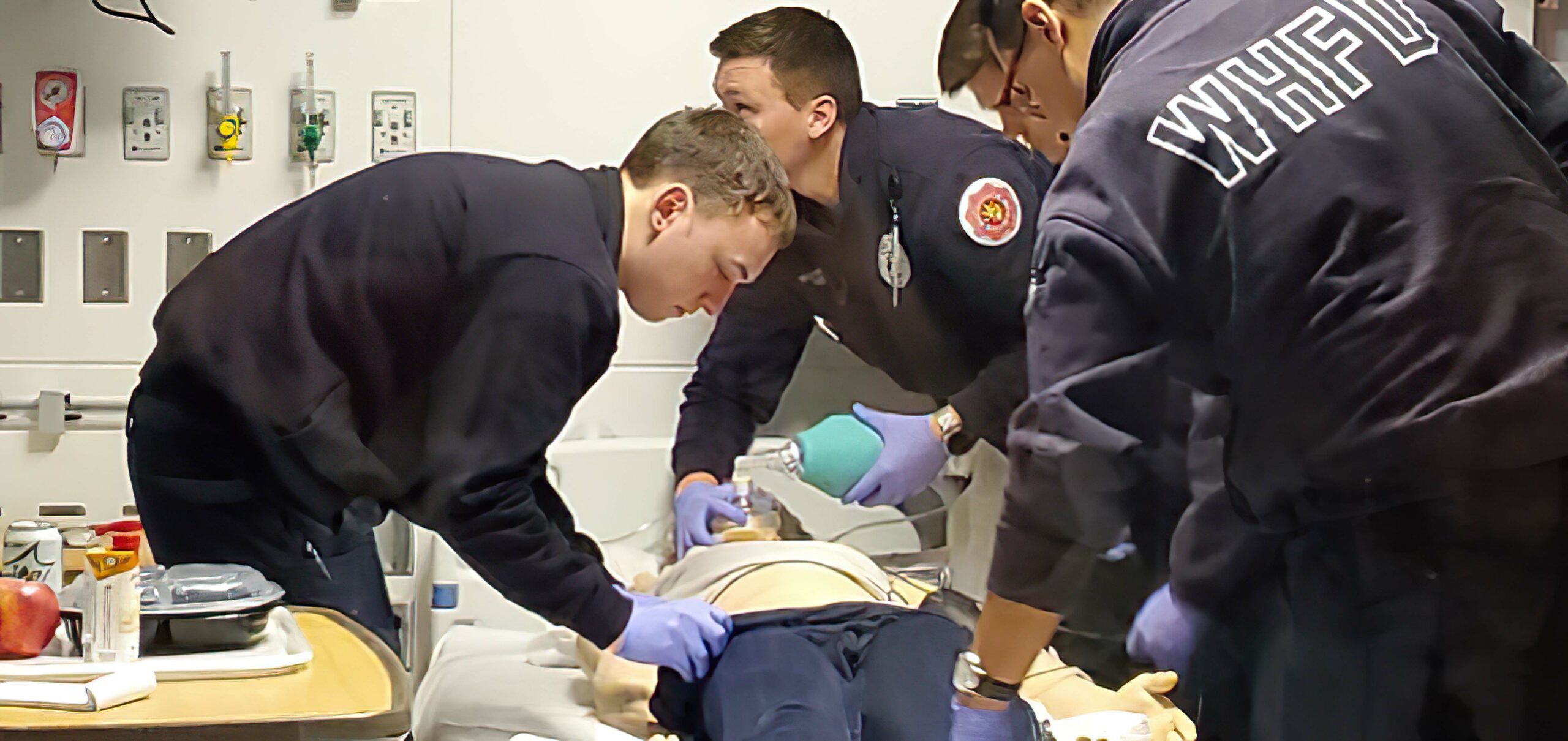
Students participating in a high-fidelity ACLS simulation.
The Acute Life-Threatening Events Recognition and Treatment (ALERT) Training Program
Although out of scope for this ACLS guide, the Acute Life-Threatening Events Recognition and Treatment (ALERT) training program aims to improve the early identification and treatment of prearrest patients. There is also an effort to identify if a patient is deteriorating further even after performing appropriate interventions. Data shows that the ALERT course reduces the number of IHCAs and improves the survival-to-discharge rate after IHCA.14
Key Takeaway
Debriefing following a resuscitation effort helps to improve care:
- Hot debriefings occur immediately after the resuscitation when details are fresh.
- Cold debriefings occur later and allow team members to prepare comprehensive reports of the incident.
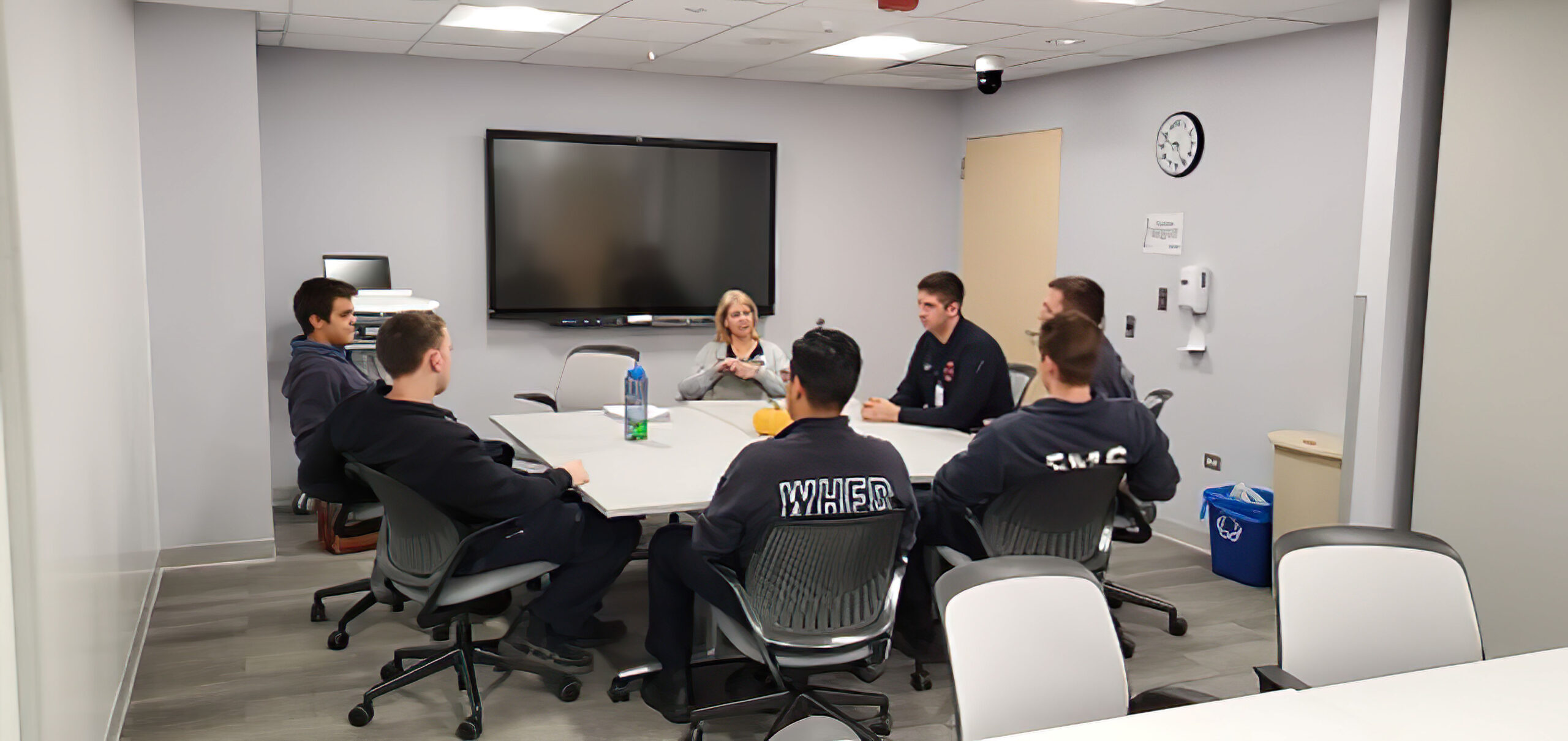

Students participating in debriefing.
14 Spearpoint KG, Gruber PC, Brett SJ. Impact of the Immediate Life Support course on the incidence and outcome of in-hospital cardiac arrest calls: an observational study over 6 years. Resuscitation. 2009;80(6):638–643.