Atrial Rhythms – Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation occurs when the atria are so irritable that they are no longer beating but are merely quivering. During atrial fibrillation, there are no discernible P waves. An ECG shows barely visible waves along the isoelectric line; these fibrillatory waves are known as f waves.
The quivering atria have impulse rates > 350 bpm. The presence of a reasonable ventricular rate, exemplified by an irregular R-R interval, is due to the AV node blocking the rapid impulses from the irritable atria.
Atrial fibrillation is easily recognized by two characteristic findings: the absence of P waves and an irregular rhythm demonstrated by irregular R-R intervals (see Figure 4.7). The absence of the P wave makes the PR interval unmeasurable. Since atrial fibrillation is a supraventricular rhythm, the QRS complex is < 120 milliseconds.
A ventricular rate > 100 bpm may cause symptoms. A rapid ventricular rate is referred to as atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response (AF with RVR).
Figure 4.7. Atrial Fibrillation
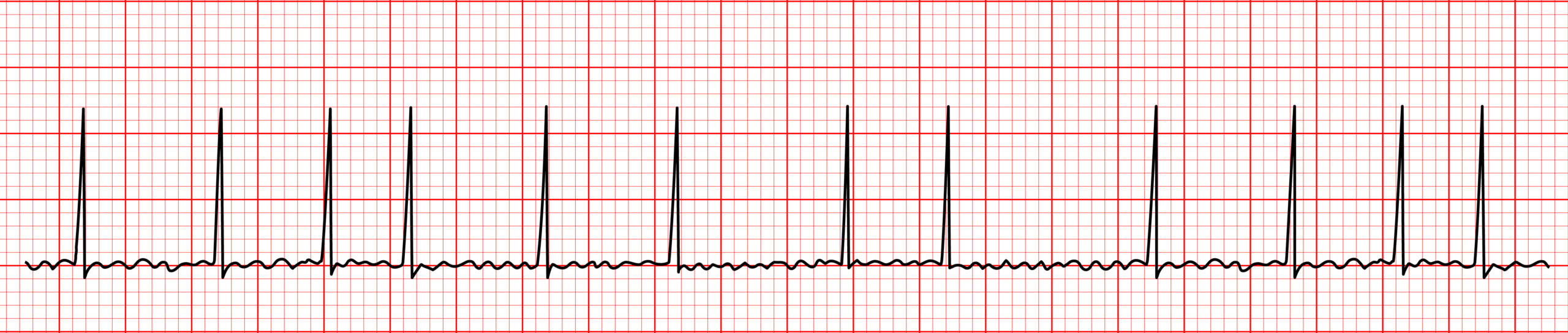
Atrial Fibrillation ECG Reading
Characteristics of Atrial Fibrillation
- Irregularly irregular rhythm
- Atrial rate > 350 bpm
- Ventricular rate varies
- No discernible P waves
- PR interval is unmeasurable
- QRS complex normal: < 120 milliseconds