Musculoskeletal Injuries
Definition
Musculoskeletal injuries are commonly caused by trauma. They include:
- Strains – caused by twisting or pulling that results in injury to a muscle or tendon.
- Sprains – caused by an abnormal motion of a joint that results in injury to a ligament.
- Dislocations – caused by an unexpected impact on a joint that results in a bone slipping out of its regular position in the joint.
- Fractures – caused by any type of injury that results in a break in any part of a bone. Open fractures are injuries where the broken bone has punctured through the skin.
Gross deformities of an extremity and swelling are common signs of musculoskeletal injuries.
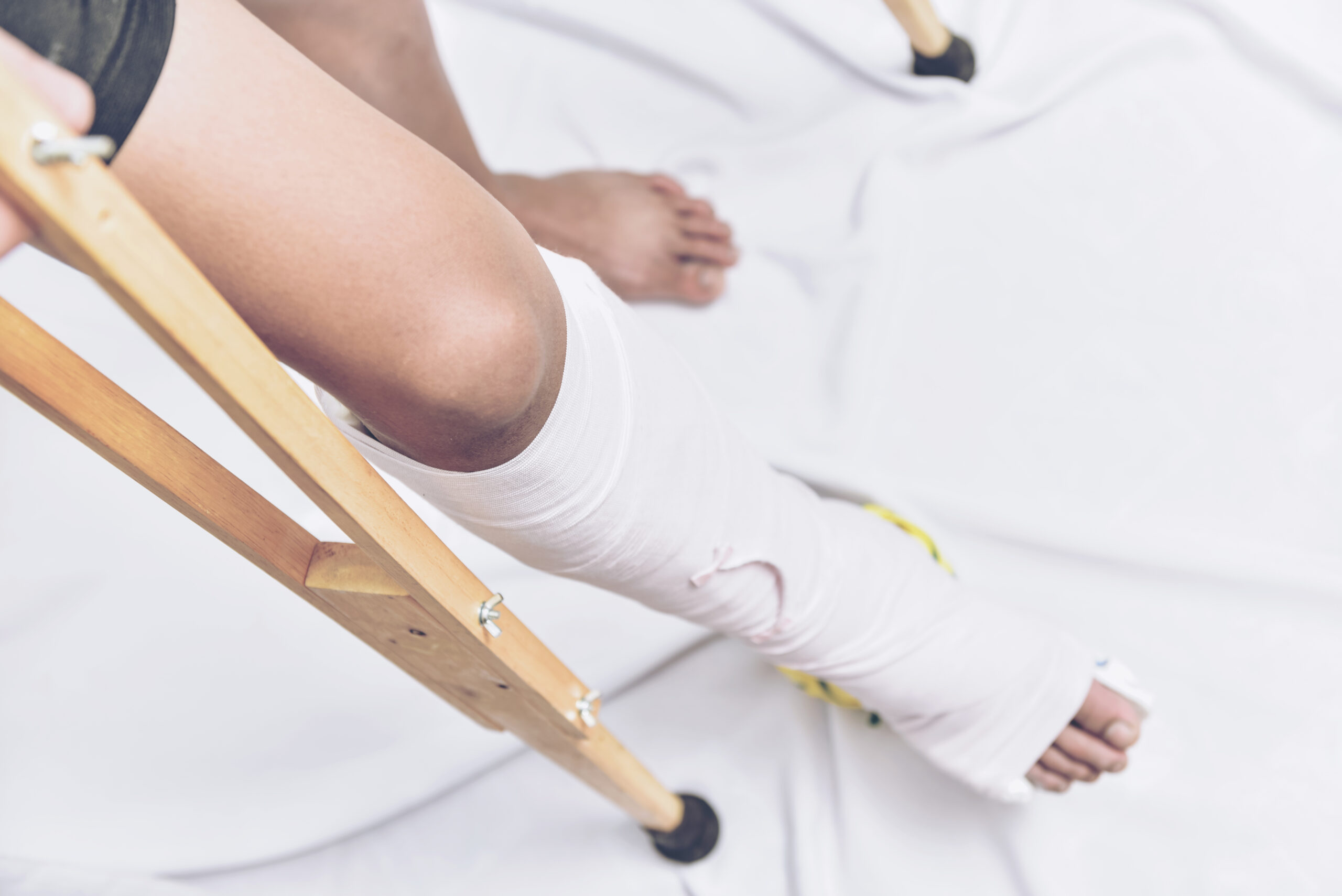

Fractured Lower Extremity in Splint
Symptoms of a Fracture
The symptoms of a fractured bone will depend on what bone is involved and the kind of break. Symptoms include:
- Pain, swelling or bruising over the affected area
- Gross deformity of the affected area:
- Looks abnormal
- Bent
- Not the usual shape
- Unable to put weight on or move the affected area
- Numbness in the area of the broken bone
Diagnosis of a Fracture
An X-ray of the affected area will usually reveal if there is a break in the bone or not. Sometimes, a normal-looking limb may have hairline fractures, which may not always be seen on the X-ray at the time of the injury.
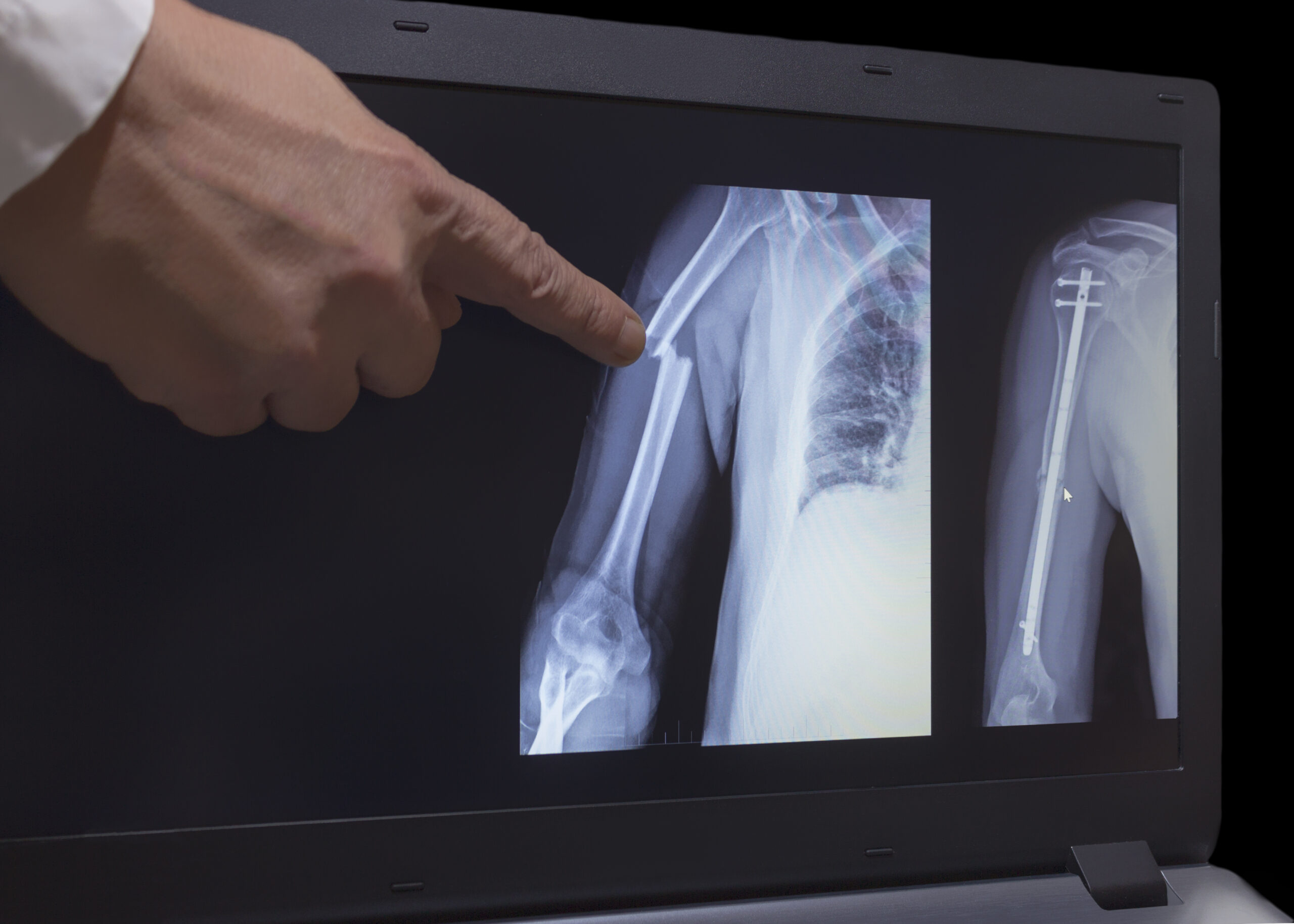
Examining Upper Arm Fracture X-Ray
First Aid Interventions for Musculoskeletal Injuries
Before treating a person with musculoskeletal injuries, the first aid responder activates the emergency response system. If there has been significant trauma, responders need to remember to go back to the systematic approach’s basics. If the patient is conscious, they should follow the primary assessment, and if unconscious, they follow the BLS assessment.
If there are more significant injuries, such as active bleeding, these should be addressed first. It is best to assume that spinal injuries are present in these situations and avoid moving the patient, asking them not to move their head and neck. Injured persons tend to position their affected limb comfortably, and it is generally fine for them to do so.
A key skill in providing first aid for musculoskeletal injuries includes immobilizing the injured extremity by applying a splint. Immobilization will decrease the pain, bleeding, and risk of further injuries to the surrounding tissues, blood vessels, or nerves.
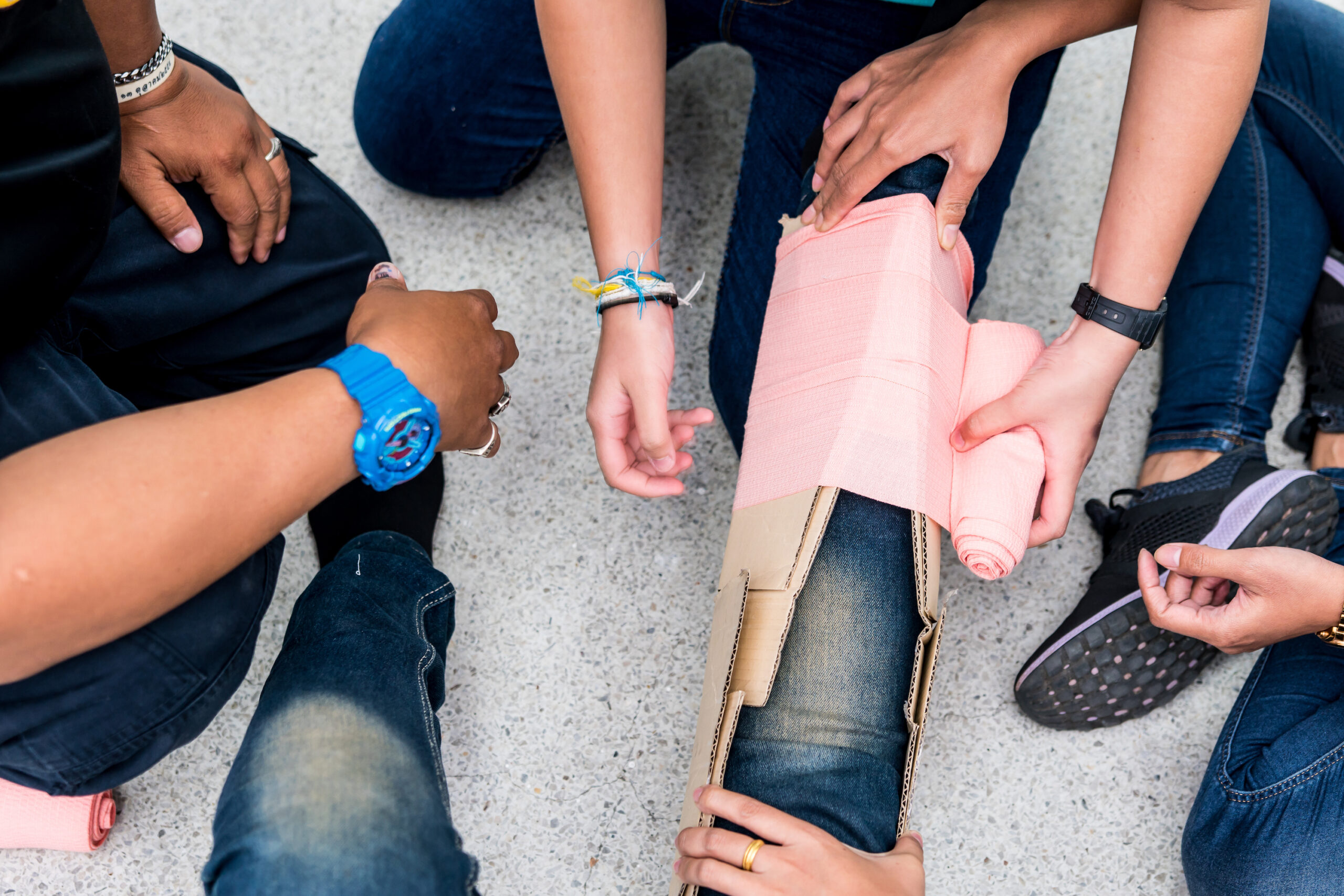

Applying a splint to the injured limb minimizes the risk of further injury and decreases pain
After stabilizing the patient, over-the-counter pain relievers may be given if available and ONLY if EMS will be delayed for more than an hour. Otherwise, it is best NOT TO GIVE THE PATIENT ANYTHING BY MOUTH.
When the patient is stabilized or sent home for recovery, emergency physicians or orthopedic specialists advise the following (they “use the RICE” and “avoid the HARM” mnemonics) for fast recovery:
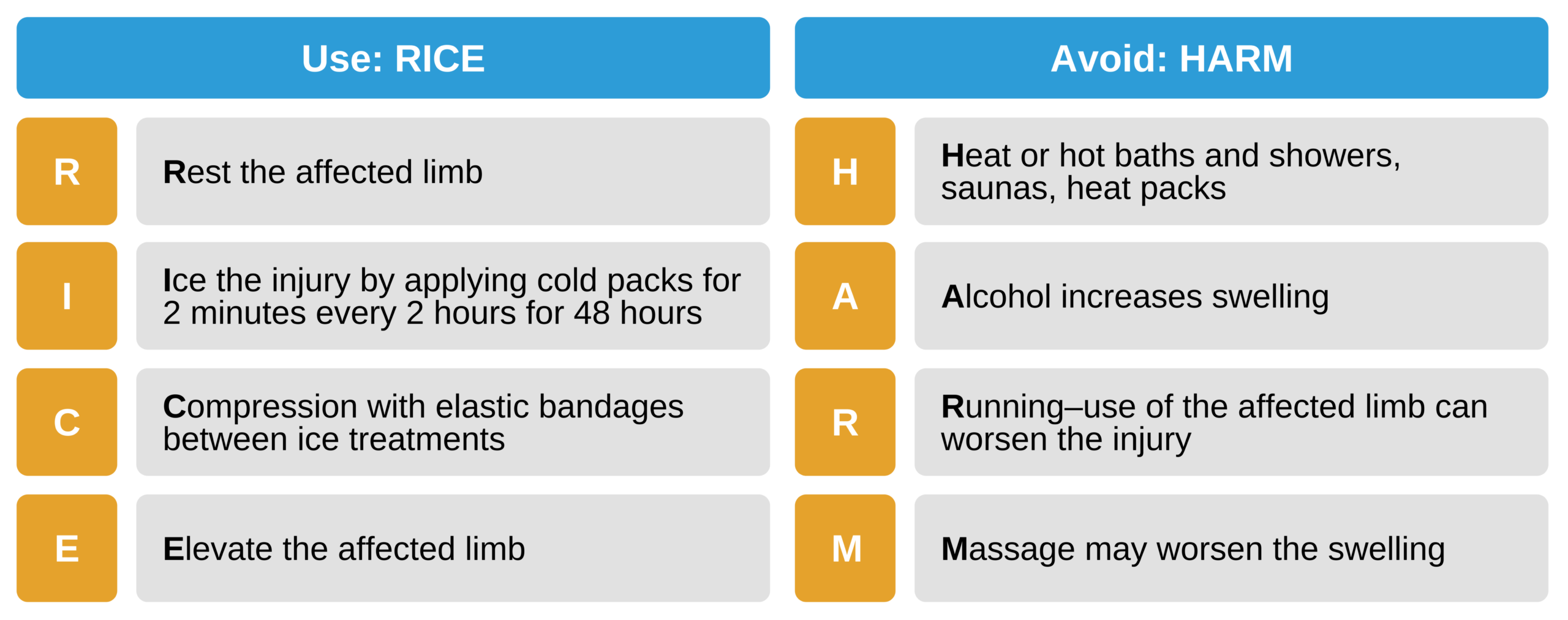
Use RICE, Avoid HARM

RICE stands for rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
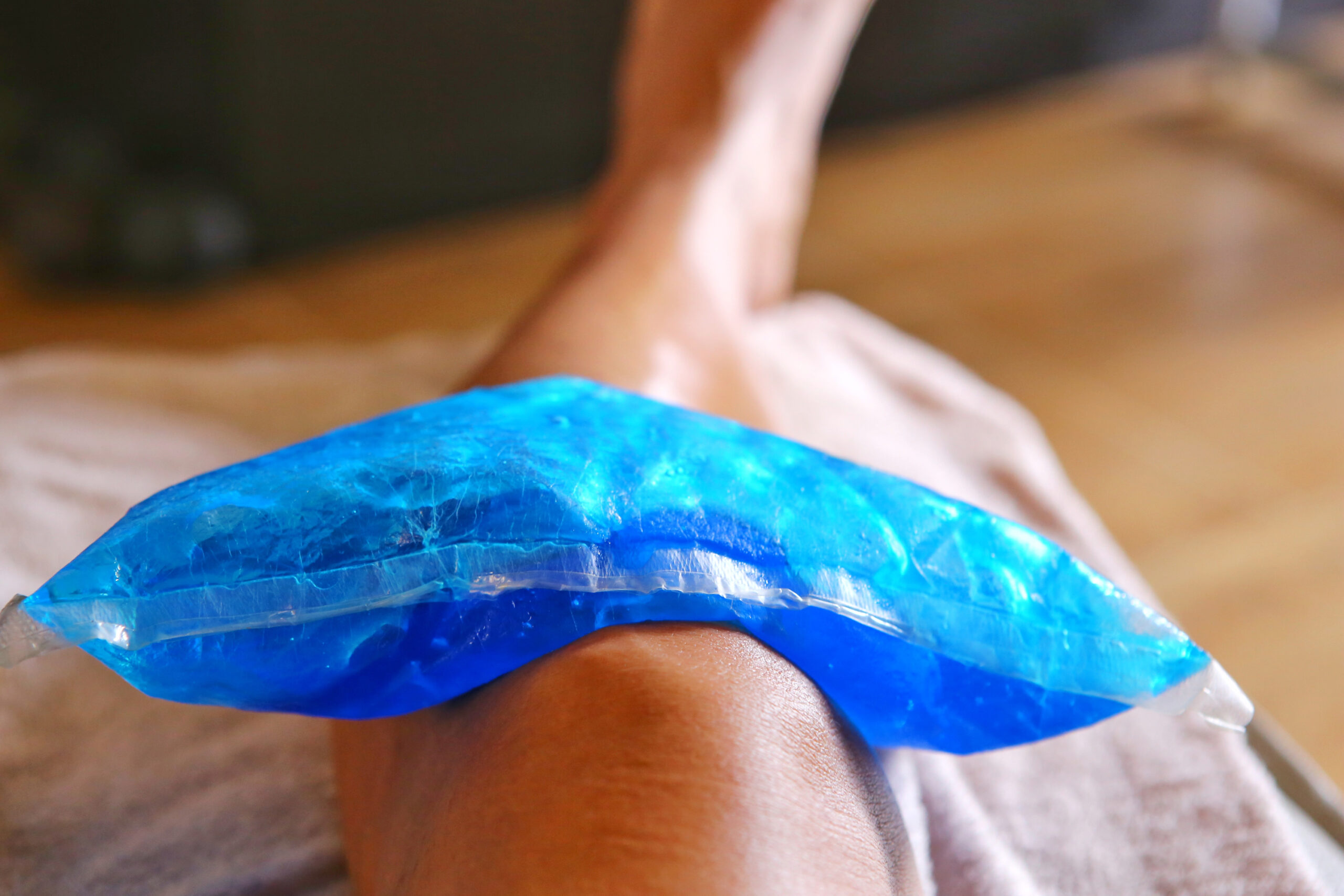
A cold pack helps to reduce swelling