Chapter Progress
0% Complete
Get Arrhythmia Interpretation Certified Today
Atrioventricular Block – First-Degree Atrioventricular Block
The conduction time between the atria and ventricles is represented by the PR interval. A PR interval > 200 milliseconds (0.20 seconds) is considered a first-degree AV block (see Figure 5.4).
Causes of First-degree AV Blocks
- Structural abnormalities within the AV node
- An increase in vagal tone
- Drugs that slow down conduction, including digoxin, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers
It is important to note that no physical blockage occurs in first-degree AV block.
Related Video – One Quick Question: What are the First-Degree Heart Block Criteria?
Figure 5.4. First-Degree Atrioventricular Block
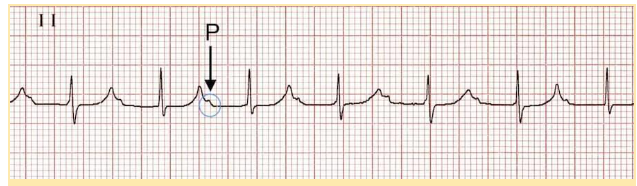
First-Degree Atrioventricular Block with P Waves Buried Within T Waves
Characteristics of a First-Degree Atrioventricular Block
- Underlying rhythm determines the regularity
- Underlying rhythm determines the rate
- Upright and uniform P waves
- Each P wave is followed by a QRS complex
- Prolonged PR interval ( > 200 milliseconds)
- PR interval consistent across the ECG strip
- QRS complex < 120 milliseconds