Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal protective equipment provides the user with a barrier for protection against the transmission of bloodborne pathogens.
Personal Protective Equipment
Gloves
Gloves should be worn by the healthcare provider before touching the patient in circumstances that might expose the hands to body fluids or blood. Gloves give an extra layer of protection, creating a barrier for contact between the rescuer and the patient.
Related Video – Understanding Medical Gloves Procedures
Gloves also reduce the likelihood of transmission of microorganisms from a patient who is colonized or infected with pathogenic organisms. Wearing gloves does not replace the need for hand hygiene because they may have microtears, and the hands can become contaminated during glove removal.
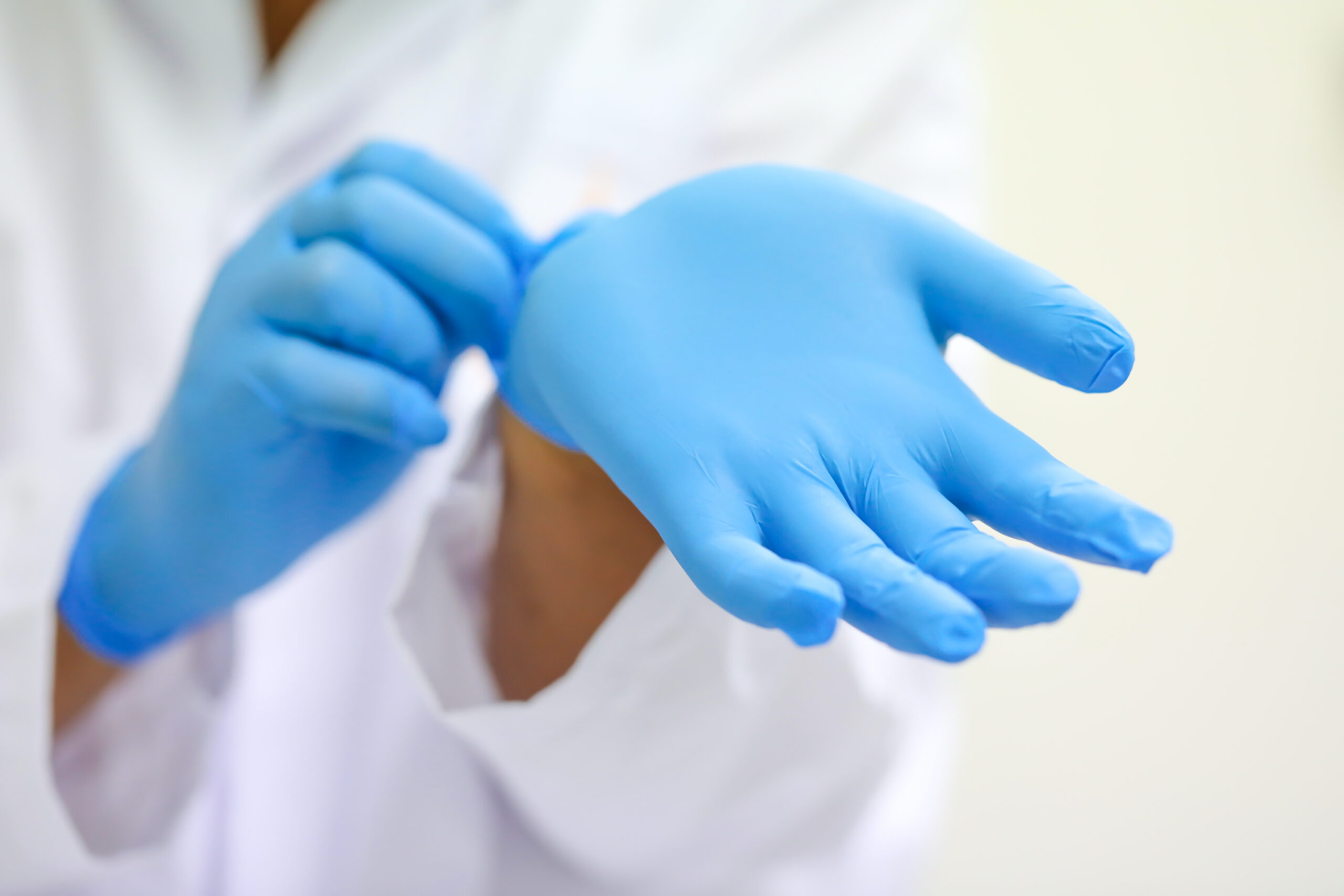
Gloves should be changed between patient encounters and not reused.
Gloves should always be changed between patient encounters. Sometimes, it is also necessary to change heavily contaminated gloves while working with a particular patient to prevent cross-contamination of body sites or medical equipment.
These gloves should not be reused and must be disposed of right away.
Related Video – How to Properly Remove Gloves and Wash Your Hands
Masks
Masks should be worn by healthcare providers who will likely contact patients with respiratory secretions to protect them from infectious materials such as aerosols containing blood or body fluids. Masks cover the nose and mouth. Providers tend to uncover the nose because mask material can be irritating. This practice should be avoided because it defeats the purpose of wearing the mask, allowing a passage into the airway through the nose.
Medical-Grade Mask
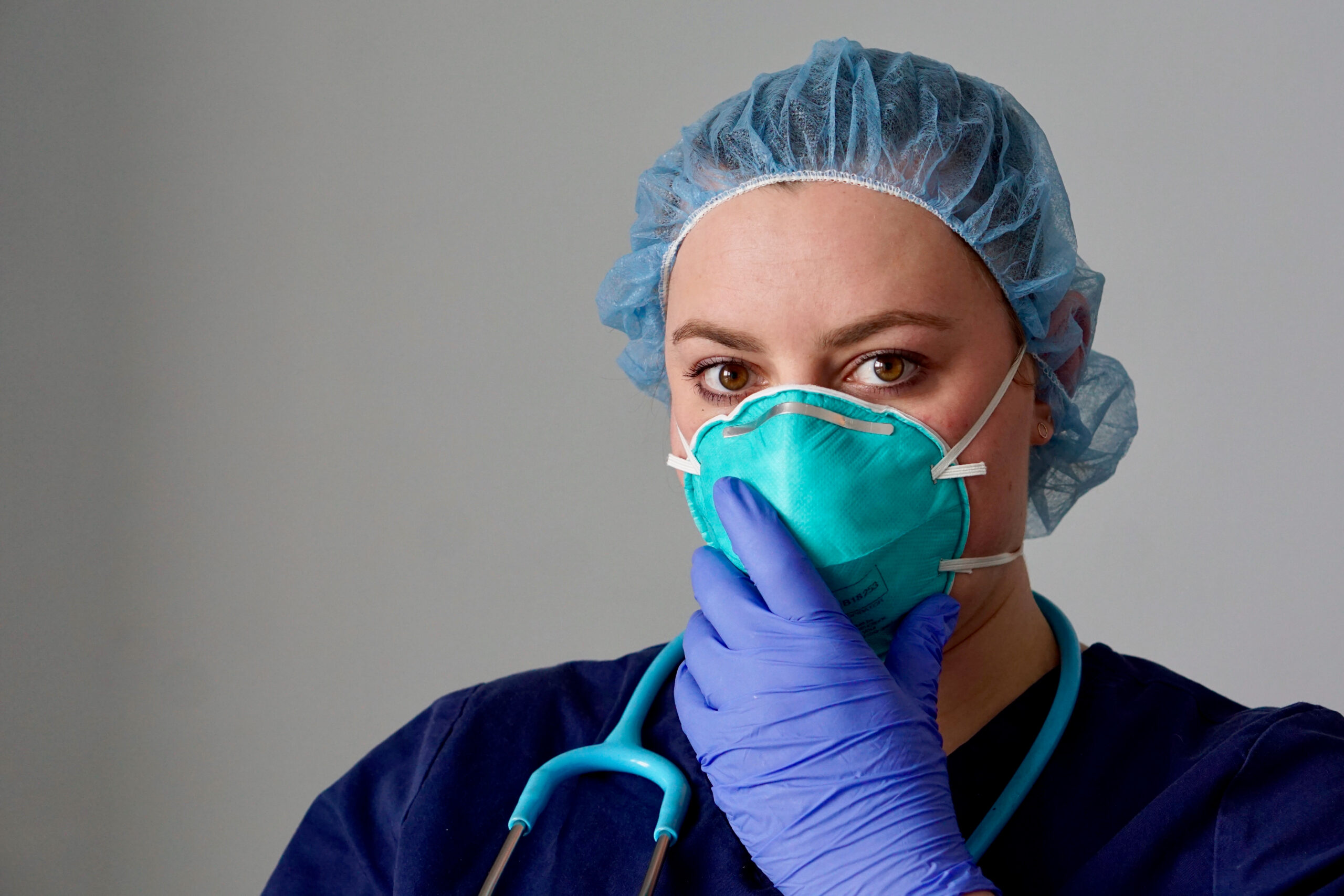

N95 Mask, Glove, and Cap
Goggles
The sclera of the eyes can be a route of transmission of bloodborne pathogens because of its thin layer. Protective eyewear is designed to enclose the eyes so that pathogens from body secretions and blood do not enter.
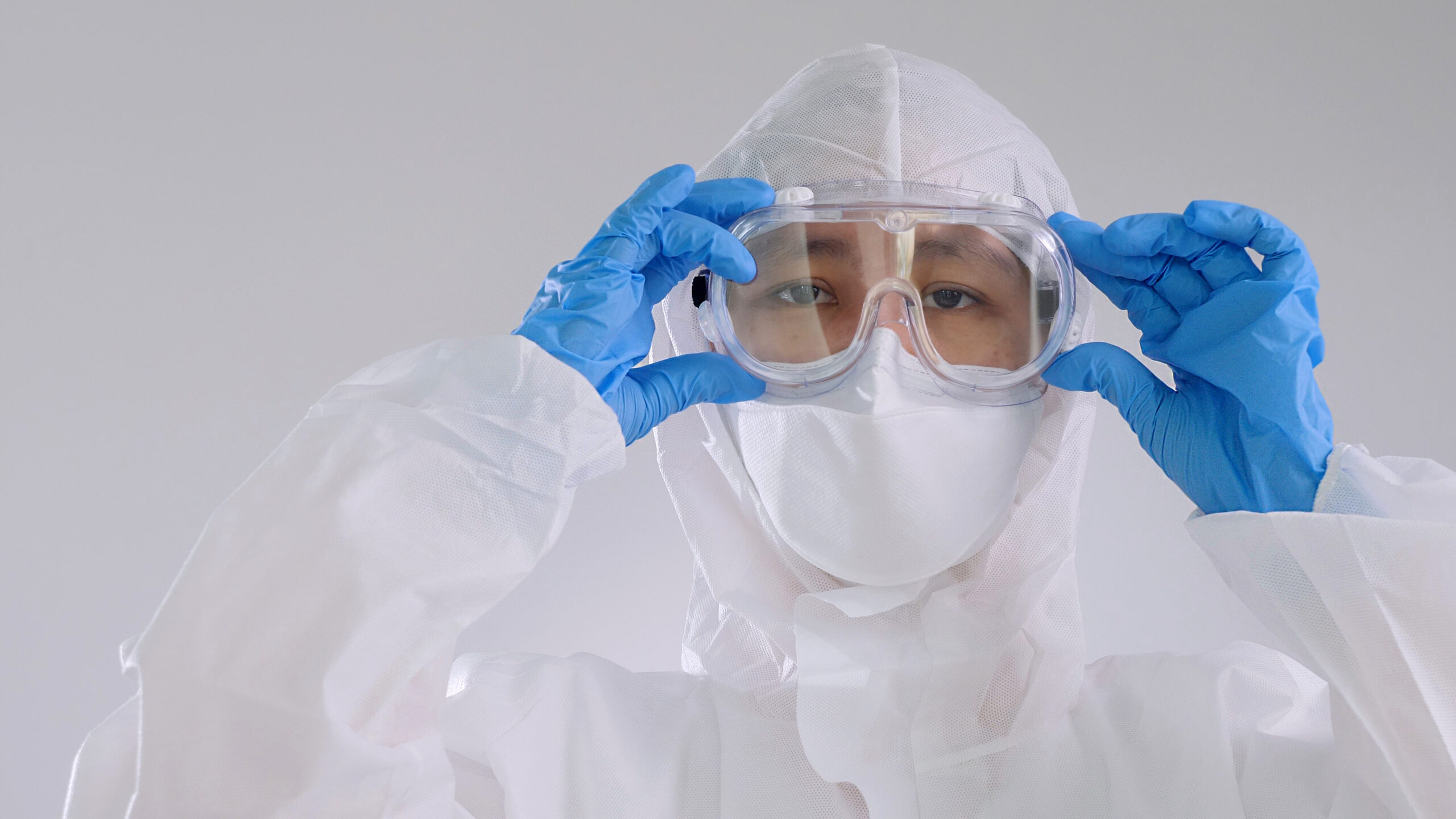

Goggles, Mask, Gloves, Gown, and Hood
Gowns
Gowns add another layer of protection to the whole body of the healthcare provider. They are nonabsorbent and designed to protect the provider.
Shoe covers
Designed to be worn over the shoes, shoe covers protect the underside of the shoes when walking in a hazardous area so as not to track waste into clean areas upon leaving. They also provide some protection for the tops of the shoes from anything that may be dropped from above.
Caps and hoods
Hair coverings may be found in the form of hoods or caps. These protect the hair from spatters of infectious material while working with patients or cleaning. They also serve to keep hair away from the face, so the wearer will not need to use a contaminated hand to move it.

Gown
Face Shields
Face shields protect the healthcare provider’s face from the forehead and wrap around to the sides of the face, extending below the chin. The eyes, mouth, nose, and face should be well covered.

Face Shield