How to Calculate Injectables
ACLS Certification Association videos have been peer-reviewed for medical accuracy by the ACA medical review board.
Article at a Glance
- Providers should know the calculation of one-time injectable medications.
- The formula is: (Drug dose ordered/Amount in vial) X # mLs in vial = #mLs to give the patient.
Some studies suggest around 100,000 patients die yearly from medication errors, which falls on us. We must continue to improve. In this lesson, we’re going to review simple injectables calculations. First, look at the container to see any pertinent calculation information. The container will tell you the name of the drug, the total amount of the drug in the container, the total amount of fluid in the container, and the concentration, or the amount of drug per mL, in the container. Drug label information to make calculations. Here is a simple formula for drug calculations: Give/Have × CC‘s in the vial = CC‘s administered to the patient “Give” connotes the total amount of the drug administered to the patient. It usually is measured in milligrams or micrograms. “Have” means the total amount of the drug in the container. If a vial contains 5 mg total, 5 mg is its “have.” For the equation, how much you “give” is divided by how much drug you “have”. Multiply by the CC’s in the vial, which is the total amount of fluid in that container. Remember, 1 CC is the same as 1 mL. Overall, the equation will equal how many CC’s you draw to administer a dose of medication. Read: General Stroke CareA Simple Formula for Drug Calculations
Related Video – What is the Dosage Calculation?

In this example, we’ll be administering fentanyl for pain management. The black arrows point to key pieces of drug information for our calculations. The container informs you the drug’s name is fentanyl citrate. There are a total of 500 mcg of drug in the container. It says there is a total of 10 mL within that container, and the concentration is 50 mcg/mL. First, figure how much drug to administer to the patient. Fentanyl is weight-based and dosed at 1 mcg/kg. Let’s say the patient weighs 86 kilograms. Therefore, you want to administer 86 mcg of fentanyl in total. Next, take 86 mcg and divide that by 500 mcg, then multiply by 10 mL, which is 1.72 mL. That is the amount of fluid you need to draw out of the container to administer 86 mcg of fentanyl (dosed at 1 mcg/kg). Example calculation for fentanyl.Example Calculation
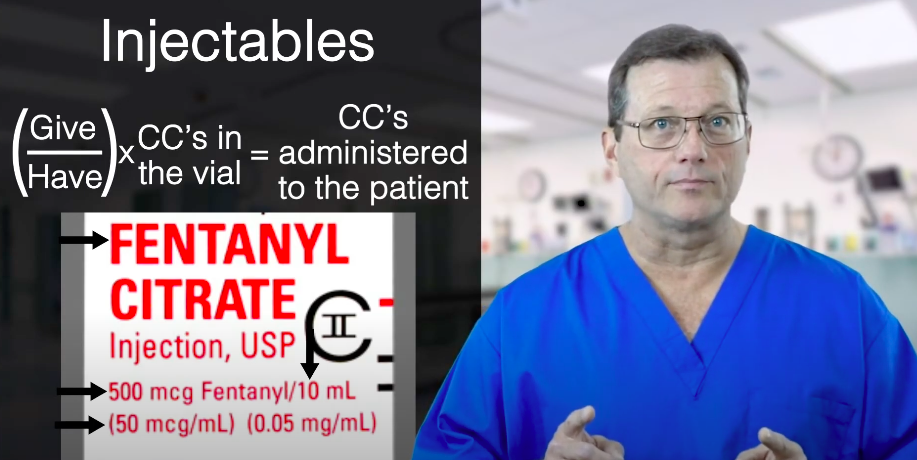

To calculate drug administration, start with “give,” or the total amount of drug you want to administer. Divide by “have,” the total amount of drug you have on hand. Finally, multiply by the total amount of mL in the vial. That equates to how many mL you will draw to administer to the patient. Remember, if the drug dosing is weight-based, you’re going to have to calculate the dose first.Summary
More Free Resources to Keep You at Your Best
Editorial Note
ACLS Certification Association (ACA) uses only high-quality medical resources and peer-reviewed studies to support the facts within our articles. Explore our editorial process to learn how our content reflects clinical accuracy and the latest best practices in medicine. As an ACA Authorized Training Center, all content is reviewed for medical accuracy by the ACA Medical Review Board.