Sinus Rhythms Explained: A Comprehensive Guide to ECG Interpretation
Understanding sinus rhythms is fundamental to mastering ECG interpretation. In this guide, “Sinus Rhythms Explained,” we explore the electrical impulses originating from the sinoatrial (SA) node—the heart’s natural pacemaker. We will cover the criteria for Normal Sinus Rhythm, identify common variations like Sinus Bradycardia and Sinus Tachycardia, and distinguish between benign irregularities and those requiring clinical intervention.
ACLS Certification Association videos have been peer-reviewed for medical accuracy by the ACA medical review board.
Article at a Glance
- Four rhythms originate from the sinus node.
- A normal sinus rhythm is the normal rhythm of a healthy heart.
- Clinicians should know normal sinus rhythm characteristics to identify abnormalities, and also be able to distinguish them from other rhythms, such as the junctional escape rhythm, which originates from the AV junction.
The following rhythms originate from the sinus node, the pacemaker of the heart: (1) normal sinus rhythm, (2) sinus bradycardia, (3) sinus tachycardia, and (4) sinus arrhythmia.
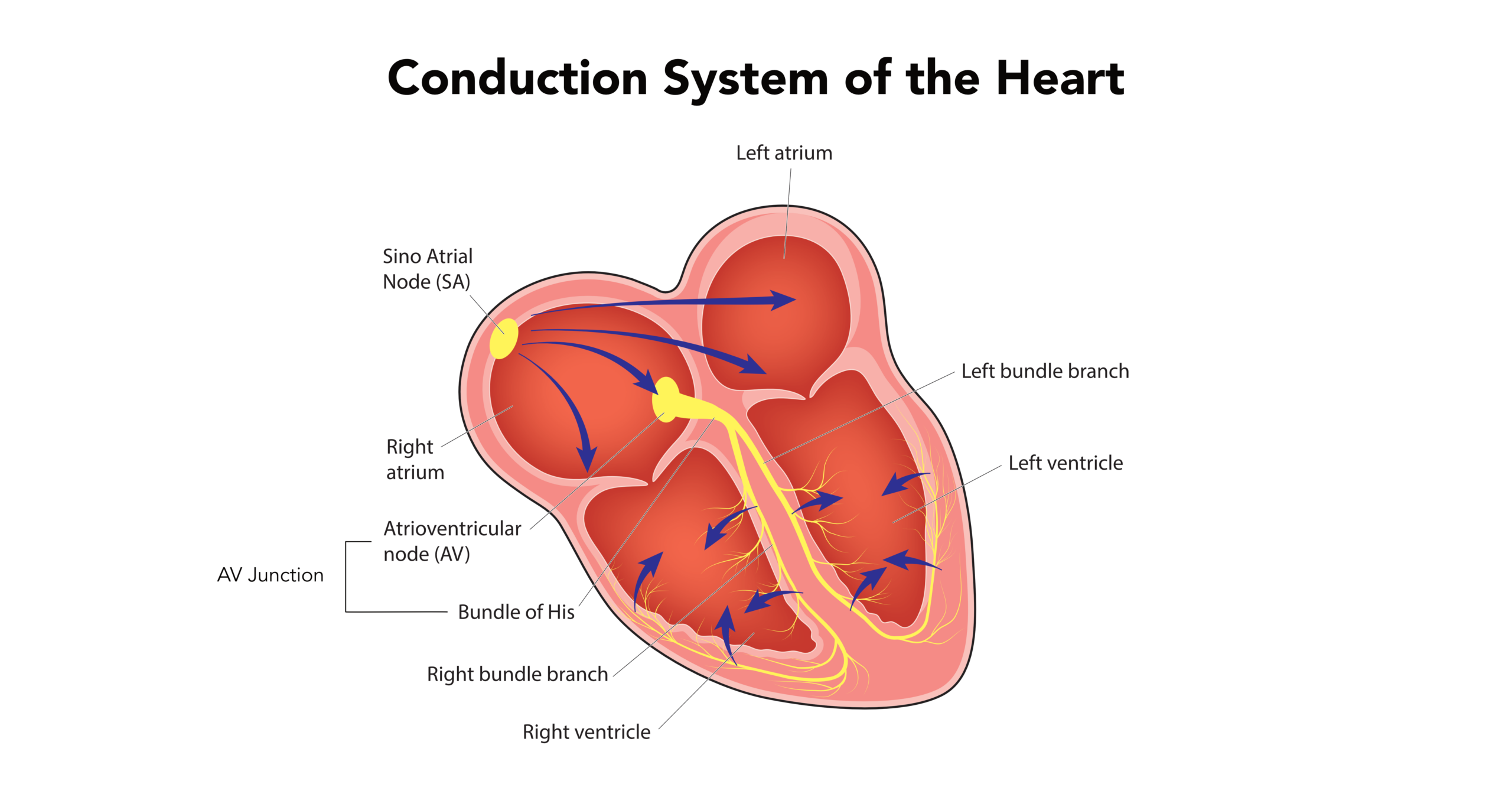
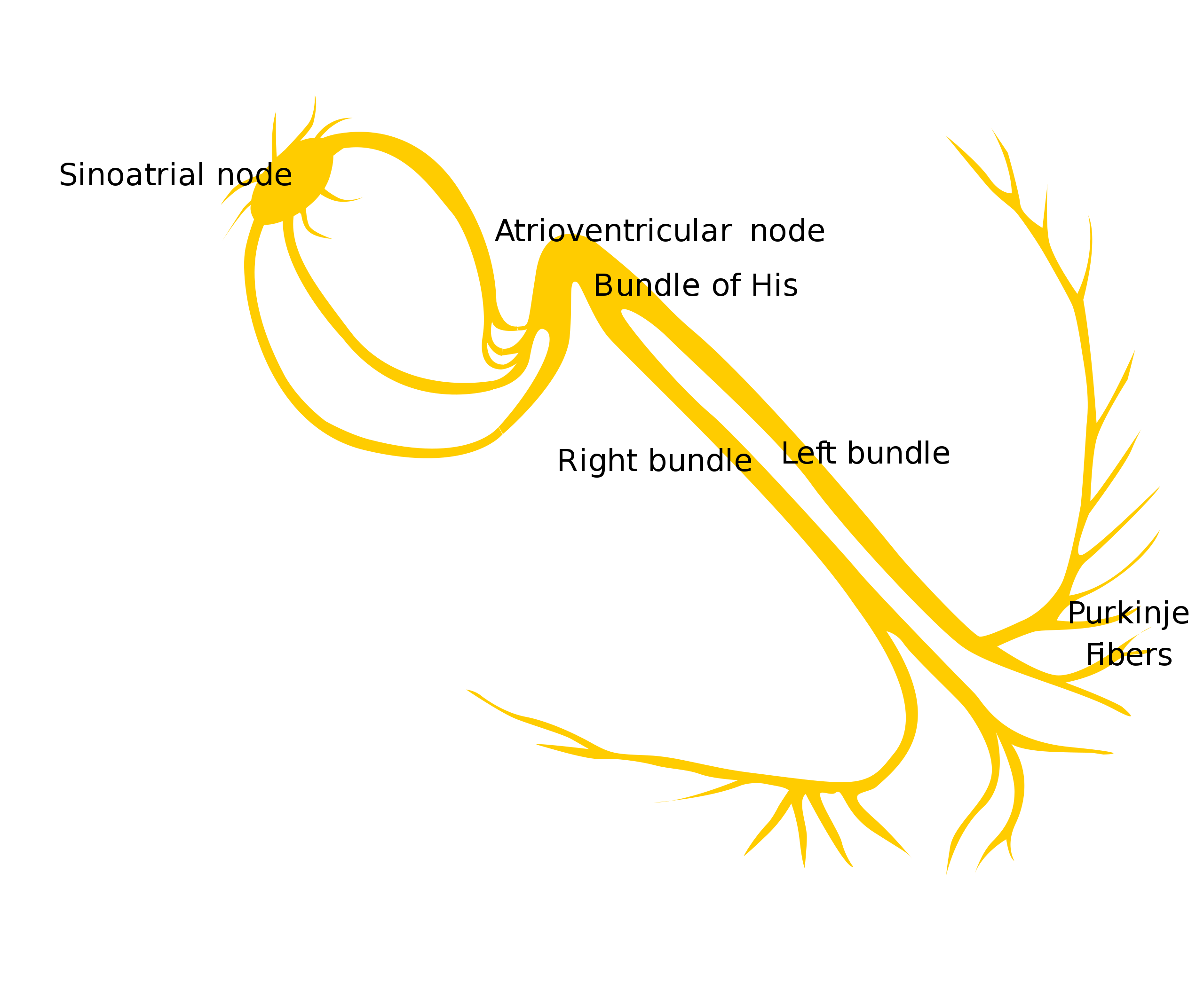
The right atrium’s sinus node is the heart’s pacemaker.
Normal Sinus Rhythm
Normal sinus rhythm is the standard rhythmic pattern of a healthy heart, reflecting normal electrical activity where the impulse originates in the SA node and travels down the normal conduction pathway.1
Clinical Implications: Normal Sinus Rhythm indicates the heart is beating effectively with appropriate timing, ensuring optimal cardiac output for the body’s demands. No treatment is required.
On a six-second strip of LEAD II, the following characteristics define normal sinus rhythm:
- RATE: 60–100 beats per minute (bpm).
- RHYTHM: regular R-R interval. The presence of a dropped beat or an ectopic beat means the rhythm is not a normal sinus rhythm.
- P WAVE: the atria depolarizes first, followed by the ventricles. The impulse travels towards LEAD II, so the P wave has an upward deflection. The P wave is followed by the QRS complex.
- PR INTERVAL: the PR interval is 0.12– 0.20 seconds and is consistent throughout the ECG strip. Varying PR intervals within the 6-second ECG strip is not a normal sinus rhythm.
- QRS COMPLEX: the QRS complex is less than 0.12 seconds. If the QRS complex is prolonged, the rhythm is not a normal sinus rhythm.
ECG Rhythm Review – Normal Sinus Rhythm
In this video, we review the foundational criteria for identifying Normal Sinus Rhythm on a 6-second strip, focusing on rate, regularity, and wave morphology.
Read: Rhythms Originating from the Atrium
Sinus Bradycardia
Sinus bradycardia is a sinus rhythm with a rate less than 60 bpm.2
Clinical Implications & Treatment: This rhythm is common in well-conditioned athletes or during sleep. However, it can also result from vagal stimulation, hypothermia, or medications (like beta-blockers).
- Asymptomatic: Usually requires monitoring but no intervention.
- Symptomatic: If the patient shows signs of poor perfusion (dizziness, hypotension, chest pain), treatment is necessary. This may include Atropine or transcutaneous pacing as per ACLS algorithms, since sinus bradycardia is classified among bradyarrhythmias.
- RATE: less than 60 bpm.
- RHYTHM: regular R-R interval; a discrepancy of one small square is acceptable.
- P WAVE: upward deflection followed by a QRS complex.
- PR INTERVAL: 0.12–0.20 seconds, and consistent throughout the 6-second LEAD II strip.
- QRS COMPLEX: less than 0.12 seconds.
ECG Rhythm Review – Sinus Bradycardia
Watch this brief overview to learn how to identify Sinus Bradycardia, characterized by a regular rhythm but a rate falling below 60 beats per minute.
Sinus Tachycardia
Sinus tachycardia is a sinus rhythm with a rate more than 100 bpm.
Clinical Implications & Treatment: Sinus tachycardia is usually a compensatory response to the body’s increased demand for oxygen.
- Common Causes: Fever, pain, anxiety, dehydration (hypovolemia), or exercise.
- Treatment: The goal is to treat the underlying cause (e.g., administering fluids for dehydration, antipyretics for fever, or analgesics for pain) rather than trying to slow the heart rate directly with cardiac medications.
- RATE: more than 100 bpm.
- RHYTHM: regular R-R interval.
- P WAVE: upward deflection followed by a QRS complex.
- PR INTERVAL: 0.12–0.20 seconds and consistent throughout the 6-second LEAD II strip.
- QRS COMPLEX: less than 0.12 seconds.
ECG Rhythm Review – Sinus Tachycardia
This video breaks down Sinus Tachycardia, explaining how to distinguish this rapid rate (over 100 bpm) from other tachyarrhythmias.
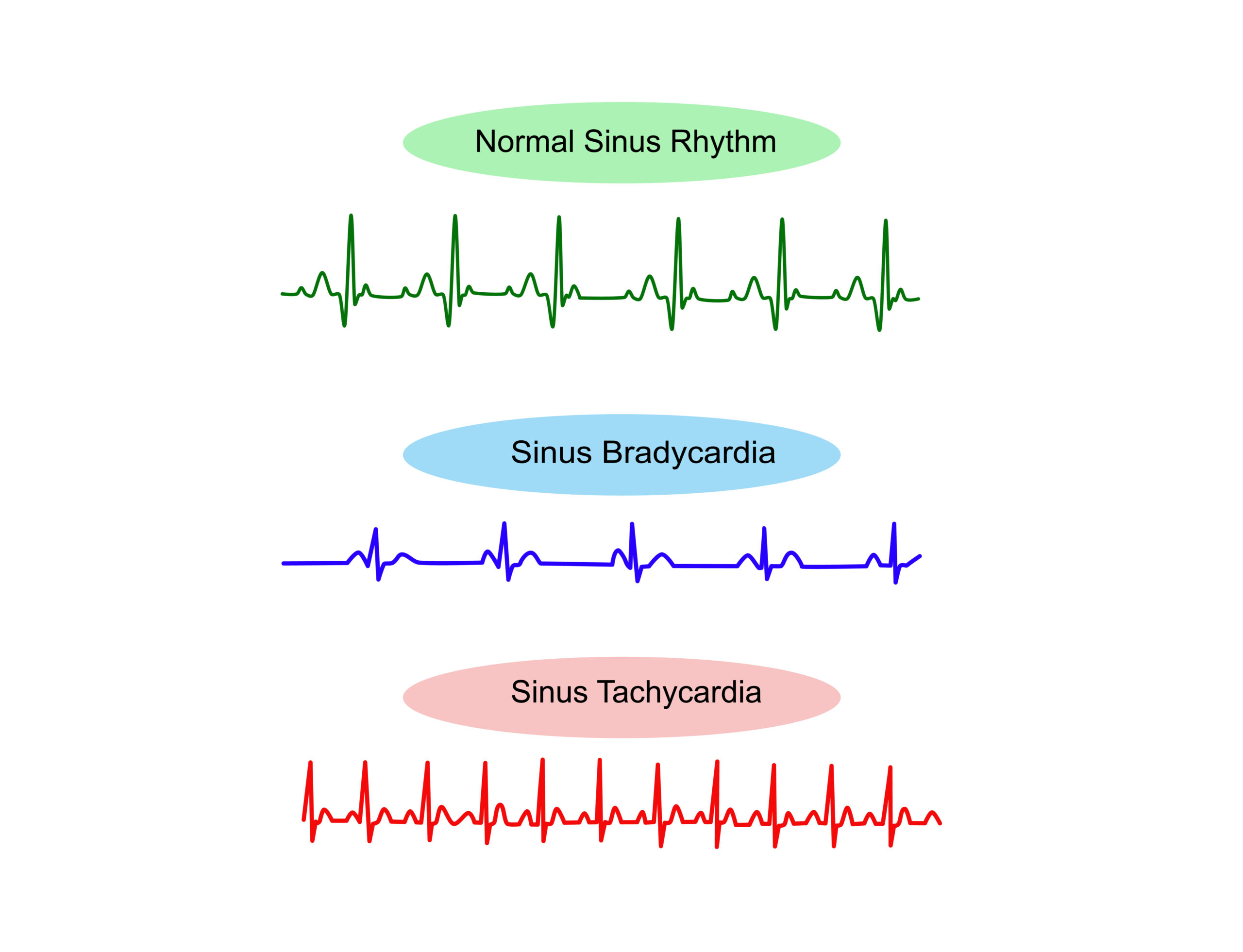
Sinus bradycardia is a sinus rhythm less than 60 bpm, while sinus tachycardia is a sinus rhythm greater than 100 bpm.
Sinus Arrhythmia
Sinus arrhythmia is a variation of normal sinus rhythm that correlates with the respiratory cycle.3
Respiratory Mechanism: This condition is a normal physiological phenomenon, often seen in children and young adults. During inspiration (breathing in), intrathoracic pressure decreases, venous return increases, and the heart rate speeds up. During expiration (breathing out), the heart rate slows down.
The same characteristics are present in sinus arrhythmia as normal sinus rhythm, but there is an R-R interval irregularity.
- RATE: 60–100 bpm (varies with respiration).
- RHYTHM: irregular R-R interval (phasic with breathing).
- P WAVE: upward deflection followed by a QRS complex.
- PR INTERVAL: 0.12–0.20 seconds, and consistent throughout the 6-second LEAD II strip.
- QRS COMPLEX: less than 0.12 seconds.
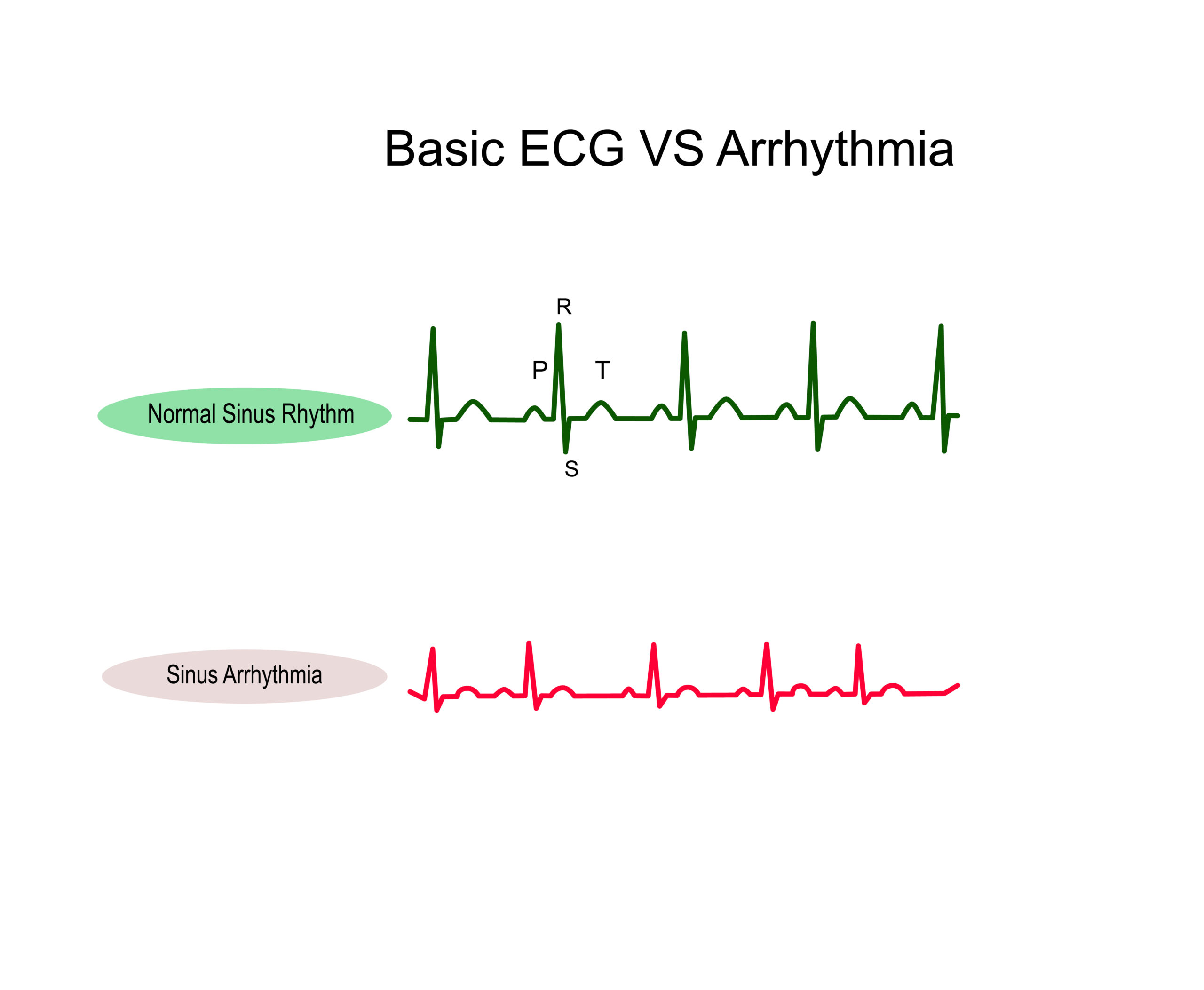
Compared to a normal rhythm, sinus arrhythmia presents with a variation in the R-R interval.
Sinus Pause, Arrest, and Exit Block
Sometimes the Sinus Node fails to initiate an impulse (disorder of automaticity) or the impulse is blocked from exiting the node (disorder of conductivity). These result in pauses on the ECG strip.
Sinus Pause
A sinus pause (or sinus block) is a transient failure of the SA node to initiate a heart beat. On the ECG, this appears as a pause where a P-QRS-T complex is missing. The duration of the pause is not a multiple of the previous P-P interval, meaning the rhythm resumes “out of step” with the underlying cadence.
Sinus Arrest
Sinus arrest is a more significant failure of the SA node, often resulting in a longer pause (typically defined as > 3 seconds, though definitions vary). Like a sinus pause, the rhythm resumes at a random point, disrupting the timing of the next beat. Clinical symptoms such as syncope (fainting) or dizziness are more common here due to the extended lack of cardiac output.
Sinus Exit Block
In a sinus exit block, the SA node fires correctly, but the electrical impulse is blocked from exiting the node to depolarize the atria. The distinguishing feature on an ECG is that the pause is an exact multiple of the P-P interval (e.g., exactly two or three missed beats). When the rhythm resumes, it falls perfectly back in step with the previous rhythm.
There are four rhythms originating from the sinus node, including normal sinus rhythm, sinus bradycardia, sinus tachycardia, and sinus arrhythmia. They all have different rates, rhythms, P wave ECG placement, PR intervals, and QRS complexes. Clinicians should know the different values to effectively diagnose and treat patients, including differentiating supraventricular tachycardias in SVT vs ST discussions. Pediatric cases are guided by the PALS bradycardia algorithm.Summary
More Free Resources to Keep You at Your Best
Editorial Sources
ACLS Certification Association (ACA) uses only high-quality medical resources and peer-reviewed studies to support the facts within our articles. Explore our editorial process to learn how our content reflects clinical accuracy and the latest best practices in medicine. As an ACA Authorized Training Center, all content is reviewed for medical accuracy by the ACA Medical Review Board.
1. Jill Seladi-Schulman, Ph.D. Understanding Sinus Rhythm. Healthline. 2021.
2. Cleveland Clinic. Sinus Bradycardia. 2022.
3. Michael P. Soos; David McComb. Sinus Arrhythmia. National Library of Medicine. 2021.