Normal ECG Variants Quiz
Quiz Summary
0 of 8 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
The results of your practice test are waiting! Just fill in your email address in the box below, and we will share your results. You’ll only need to enter your email one time. After taking your next practice exam, you’ll receive your results as soon as you click on “Submit.”
Once you pass five practice tests, a 20% discount coupon will immediately be sent to the email address you provided.
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Time has elapsed
Try Again. You didn’t get a passing score.Congratulations! You Passed.
You got 0 out of 0 correct and scored 0. Review your incorrect answers and try again.
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
Earn a 20% Discount on Your Next Certification Course!
ACLScertification.org is proud to offer a 20% discount to students who successfully pass 5 of our practice tests in one sitting. Currently, you have passed 0 of the 5 required tests. Start testing your skills and earning your discount now in our Practice Exam Section.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 8
1. Question
1. A group of rhythms originating outside of the sinoatrial node but still within the conduction system that represents an IRRITABILITY in the conduction system is known as which of the following arrhythmias?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 8
2. Question
2. An ECG tracing represents a heart rate of 48 bpm, regular R-R interval, an upward deflection of the P wave, an R-R interval of 0.12 seconds, and a QRS complex < 0.12 seconds. What ECG pattern does this describe?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 8
3. Question
3. Patients with a junctional rhythm have junctional P waves that may occur in which segment of the ECG tracing?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 8
4. Question
4. When analyzing a patient’s ECG, you notice a deep Q wave in frontal lead II and inverted T wave morphology in frontal lead III. What can you conclude?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 8
5. Question
5. Which characteristic of a premature ventricular contraction is caused by a refractory state of the T wave of the core rhythm when an irritable ventricular focus causes a strong ventricular depolarization?
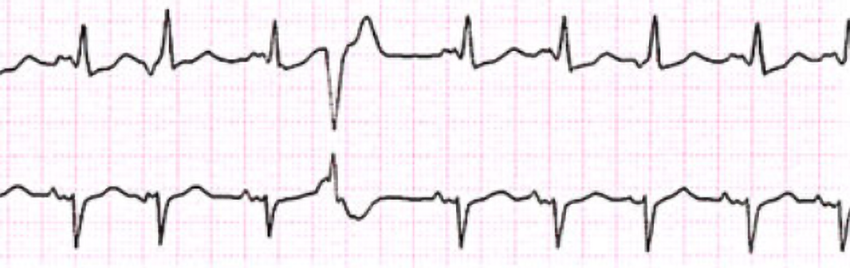 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 8
6. Question
6. Which one of the following ECG examples is likely a pathologic Q wave?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 8
7. Question
7. Which one of the following frontal leads may have nonpathologic or normal variant deep Q waves?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 8
8. Question
8. While measuring the PR interval, you notice that not all P waves are conducted throughout the long lead ECG tracing. What is the most probable conclusion?
CorrectIncorrect