Ventricular Rhythms Flashcard 1
Rationale
B. Rationale: Ventricular fibrillation is an extremely irritable ventricular focus that makes the impulses fire chaotically, causing the ventricles to quiver and leading to a fatal arrhythmia because no sufficient cardiac output is produced. In ventricular fibrillation, there are no waves or complexes to identify. This is represented by a grossly chaotic fibrillatory pattern on ECG.
Question
A ventricular focus that fires in a chaotic manner is caused by which of the following ECG phenomena?
a. Torsade’s de pointes
b. Ventricular fibrillation
c. Ventricular tachycardia
d. Atrial flutter
Answer
a. Torsade’s de pointes
Rationale
B. Rationale: A PVC followed by two sinus beats is known as trigeminy. A PVC between every other beat is known as bigeminy. A PVC that follows after three sinus beats is known as quadrigeminy. A PVC that follows five sinus beats is known as tetrageminy.
Question
A premature ventricular contraction that is followed by two sinus rhythm beats and then another PVC is known as which one of the following?
a. Bigeminy
b. Trigeminy
c. Quadrigeminy
d. Tetrageminy
Answer
d. Tetrageminy
Rationale
B. Rationale: An extremely irritable focus in the ventricles can override the heart’s pacemaker cells and cause a sustained run of PVCs. This is known as ventricular tachycardia. It has a rate of 150 to 250 bpm. The R-R interval has a slightly irregular appearance, but the intervals are generally uniform. Ventricular tachycardia presents with bizarre-looking QRS complexes that are > 0.12 seconds and a T wave that deflects opposite the R wave.
Question
A sustained run of premature ventricular contractions is known as which of the following?
a. R on T phenomenon
b. Ventricular tachycardia
c. AV-nodal re-entrant tachycardia
d. Supraventricular tachycardia
Answer
b. Ventricular tachycardia
Rationale
B. Rationale: The appearance of three or more consecutive PVCs is considered ventricular tachycardia.
Answer choice A – A sawtooth appearance within the isoelectric line represents atrial flutter.
Answer choice C – A variation in the amplitude of the QRS complex is not representative of ventricular tachycardia.
Answer choice D – A narrow QRS interval is usually characteristic of supraventricular tachycardia.
“
Question
An ECG with PVCs is renamed to ventricular tachycardia in which of the following situations?
a. When there is a concomitant sawtooth appearance within the isoelectric line
b. When there are three or more consecutive PVCs
c. When the amplitude of the QRS complex varies widely
d. When there is a narrow QRS interval
Answer
b. When there are three or more consecutive PVCs
Rationale
A. Rationale: This is an ECG of a patient in renal failure that progressed into torsade’s de pointes after being diagnosed with severe hyperkalemia. Torsade’s de pointes is a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in which the wide QRS complexes have varying amplitudes that “twist” along the isoelectric line.
Question
Refer to the ECG finding below. What is your diagnosis?
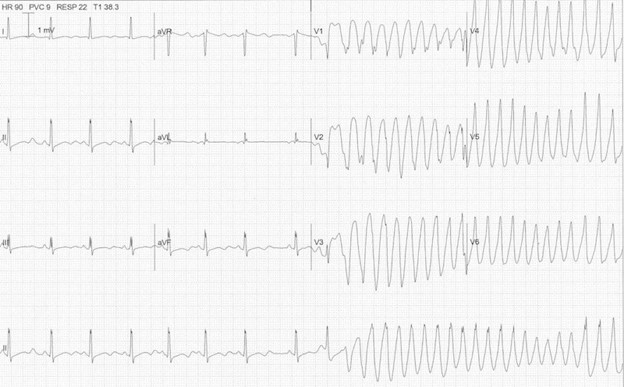
a. Torsade’s de pointes
b. Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
c. Ventricular fibrillation
d. Atrial fibrillation
Answer
a. Torsade’s de pointes
Rationale
C. Rationale: Accelerated idioventricular rhythm generates impulses that assume control because they overcome the impulses from the sinus node. It occurs at a rate of 60–100 bpm. Atrioventricular dissociation may be present in which the atrial rate is slower than the ventricular rate. The P-P intervals are longer than the R-R intervals.
Question
Refer to the ECG tracing below. This patient has a heart rate of 78 bpm, broad QRS complexes, and dissociated P waves (in the blue circle). What is your conclusion?
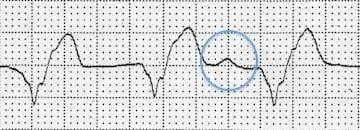
a. AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
b. First-degree AV block
c. Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
d. Sick sinus syndrome
Answer
c. Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
Rationale
C. Rationale: The term “bigeminy” refers to a premature ventricular beat that occurs right after a normal beat.
Answer choice A – “Quadrigeminy” refers to a normal beat followed by 3 consecutive ventricular premature beats.
Answer choice B – The term “trigeminy” refers to a premature ventricular beat that occurs after two normal beats.
Answer choice D – A run of 7 or more premature ventricular beats is a risk factor for the development of ventricular tachycardia.
Question
The term bigeminy with premature ventricular beats refers to which of the following definitions?
a. A premature ventricular beat that occurs after three normal beats
b. A premature ventricular beat that occurs after two normal beats
c. A premature ventricular beat that occurs after a normal beat
d. A “run” of at least 7 premature ventricular beats
Answer
c. A premature ventricular beat that occurs after a normal beat
Rationale
D. Rationale: A idioventricular rhythm is a ventricular escape rhythm that occurs due to the failure of higher pacemaker sites. There are no P waves because its origin is in the ventricles. It has a slower inherent rate of 20–40 bpm. Likewise, it has a QRS complex of 0.12 seconds and longer.
Question
What ECG diagnosis is caused by a ventricular escape beat characterized by the absence of P waves and slow QRS complexes (> 0.12 seconds) but with a regular rhythm at a rate of 20–40 bpm?
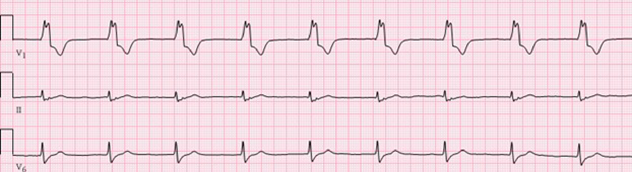
a. Junctional rhythm
b. Complete heart block
c. Premature ventricular contraction
d. Idioventricular rhythm
Answer
d. Idioventricular rhythm
Rationale
A. Rationale: A PVC that occurs early on top of the T wave is called an R-on-T phenomenon. This can induce ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation and is common in patients with an ischemic myocardium.
Answer choice B – Torsades de pointes is a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia usually induced by hypomagnesemia.
Answer choice C – AVNRT is a type of supraventricular tachycardia caused by a reentrant circuit within or close to the AV node.
Answer choice D – A delta wave is the characteristic finding of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
Question
What is the diagnosis when you find a premature ventricular beat on top of the T wave in an ECG tracing?
a. R-on-T phenomenon
b. Torsade’s de pointes
c. AVNRT
d. Delta wave
Answer
a. R-on-T phenomenon
Rationale
A. Rationale: Polymorphic PVCs may have impulses that are unifocal but coming from varying ventricular activation, which will show equal coupling intervals. Polymorphic PVCs may also be multifocal where there are varying coupling intervals.
Answer choice B – A bundle branch block is represented by a wide QRS complex > 0.12 seconds.
Answer choice C – An escape rhythm is a slow rhythm that is initiated by and causes contraction of the ventricles.
Answer choice D – Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is represented by a strain pattern with an increased amplitude of the QRS complex.
“
Question
When PVCs have a polymorphic configuration on ECG, what can you conclude?
a. There are different foci of impulses in the ventricles
b. A bundle branch block has disrupted the flow of impulses in one fascicle but not the other
c. There is fibrosis in the sinoatrial node in which an escape rhythm is formed
d. Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
Answer
a. There are different foci of impulses in the ventricles