Stroke Flashcard 1
Rationale
D. Rationale: The Rationale for treating malignant hypertension in acute ischemic stroke patients that will undergo fibrinolytic therapy is to prevent intracerebral hemorrhage after the administration of the recombinant tissue plasminogen activator drug.
Question
What is the pharmacologic management for malignant hypertension in patients with acute stroke who are candidates for recombinant tissue plasminogen activator therapy?
a. Procainamide
b. Dopamine
c. Lidocaine
d. Labetalol
Answer
d. Labetalol
Rationale
A. Rationale: Once it has been established that the patient is a candidate for fibrinolytic therapy, the provider must then determine if he is eligible. The healthcare provider must know the inclusion criteria, exclusion criteria, and relative exclusion criteria for fibrinolytic therapy. Multilobar infarctions is one of the exclusion criteria.
Question
A 48-year-old man is diagnosed with ischemic stroke and is being considered for fibrinolytic therapy. Which of the following is an exclusion criterion for fibrinolytic therapy?
a. CT scan demonstrates multi lobar infarctions
b. Diagnosis of ischemic stroke causing measurable neurologic deficit
c. Onset of symptoms < 3 hours before beginning the treatment
d. Patient’s age is 18 years old or above
Answer
a. CT scan demonstrates multi lobar infarctions
Rationale
A. Rationale: Ischemic stroke is the most common type of stroke (87%). The second most common is hemorrhagic stroke. (ACLS Case: Acute Stroke)
Question
A 57-year-old man developed facial drooping, slurred speech, and weakness on the left side. You suspect the patient had a stroke and are determining whether surgical or pharmacologic treatment is needed for this patient, depending on the type of stroke. Which of the following is the most common type of stroke?
a. Ischemic
b. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
c. Intracranial hemorrhage
d. Subdural hemorrhage
Answer
a. Ischemic
Rationale
A. Rationale: Ischemic stroke is the most common type of stroke (87%). The second most common type of stroke is hemorrhagic stroke.
Question
A 57-year-old man has developed facial drooping, slurred speech, and weakness on the left side. Suspecting the patient has had a stroke, you need to determine whether he needs surgical or pharmacologic treatment, and this depends on the type of stroke. Which of the following is the most common type of stroke?
a. Ischemic
b. Subarachnoid Hemorrhagic
c. Intracranial Hemorrhagic
d. Subdural Hemorrhagic
Answer
a. Ischemic
Rationale
D. Rationale: Recent surgery within the previous 14 days is a relative contraindication to fibrinolytic therapy. The risk of bleeding would need to be weighed carefully in this patient.
Question
A patient is being assessed as a potential candidate for fibrinolytic therapy. Which of the following is a relative contraindication to fibrinolytic therapy in this patient?
A. The patient’s symptoms started 30 minutes ago.
B. The patient is 58 years of age.
C. The patient had a heart attack 5 years ago.
D. The patient had a hernia repair 1 week ago.
Answer
D. The patient had a hernia repair 1 week ago.
Rationale
D. Rationale: Admission to a stroke unit or a critical care unit should be within 3 hours from presentation to the ED. (ACLS Case: Stroke)
Question
A patient with a stroke should be admitted to a stroke unit or critical care unit within how many hours of being brought to the ED?
a. 12 hours
b. 8 hours
c. 6 hours
d. 3 hours
Answer
d. 3 hours
Rationale
A. Rationale: Aspirin is not a time-critical intervention. The patient should be admitted to the stroke unit per protocol. Anticoagulants or antiplatelet treatment should not be administered for 24 hours after rtPA.
Question
A patient with suspected stoke has no evidence of hemorrhage on a CT scan and is a candidate for fibrinolytic therapy. Which one of the following is correct?
a. Review the risks and benefits with the patient and/or family.
b. Aspirin is a time-critical intervention.
c. The patient may be discharged home.
d. Start heparin.
Answer
a. Review the risks and benefits with the patient and/or family.
Rationale
A. Rationale: Time is of the essence for the successful treatment of acute ischemic stroke. The American Heart Association recommends that the CT scan be ready for interpretation within 25 minutes of the patient’s arrival in the emergency department.
Question
A patient with suspected stroke is brought to the emergency department. Within what timeframe from the patient’s arrival should the CT scan be completed and ready for interpretation?

a. 15 minutes
b. 25 minutes
c. 45 minutes
d. 1 hour
Answer
a. 15 minutes
Rationale
C. Rationale: This is an ischemic stroke. Acute ischemic changes are seen (encircled). Since the onset of symptoms was < 3 hours ago, fibrinolytic therapy is indicated.
Question
A patient’s stroke symptoms began 2 hours ago. In the emergency department, she has the following CT scan of the head:
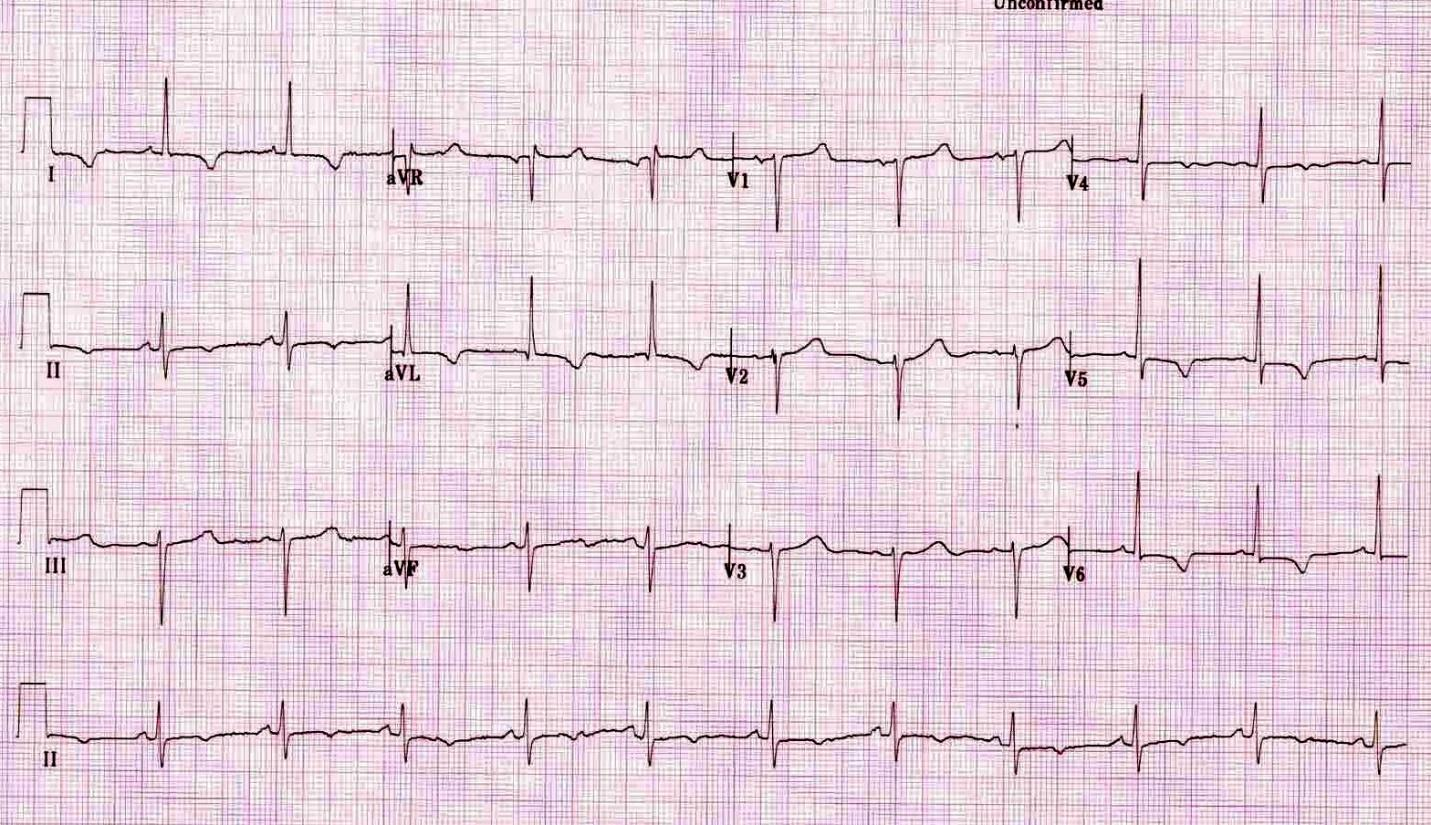
What is the next most appropriate step?
a. Observe the patient as there are no signs of stroke in this CT scan.
b. Consult a neurosurgeon and transfer the patient for appropriate care.
c. Consider fibrinolytic therapy.
d. Refer the patient to stroke rehabilitation.
Answer
c. Consider fibrinolytic therapy.
Rationale
B. Rationale: Endovascular therapy shows clinical efficacy in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke and can be performed within 6 hours of the onset of acute stroke symptoms.
Question
According to AHA recommendations, what other management of acute stroke increases the treatment window time to 6 hours from the onset of symptoms?
a. Ultrasound-enhanced thrombolysis
b. Endovascular therapy
c. Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists
d. Intravenous ancrod
Answer
b. Endovascular therapy