Pharmacology Flashcard 1
Rationale
D. Rationale: Naloxone is the antidote for opioid toxicity.
Question
A 24-year-old man is believed to have taken a heroin overdose. Heroin is a synthetic opioid and has become an epidemic of abuse in the United States. What is the pharmacologic treatment of choice for opioid toxicity?
a. Epinephrine
b. Activated charcoal
c. Ferrous sulfate
d. Naloxone
Answer
d. Naloxone
Rationale
C. Rationale: This woman has persistent ventricular fibrillation. She has been given standard therapy with CPR, defibrillation, and epinephrine. In this case, amiodarone is the recommended medication following VF refractory to standard management. It has a 40% success rate in nonarrest cases of VT and fewer side effects than other antiarrhythmic medications. Epinephrine can be tried again, but because it has failed multiple times in this patient, it is appropriate to use another medication. Resuscitation efforts should not be terminated until all appropriate options have been exhausted. Lidocaine is an alternative to amiodarone but is considered inferior.
Question
A 37-year-old woman is in cardiac arrest. CPR is started within 1 minute of collapse, and defibrillation is provided at about 4 minutes following the arrest. Her initial rhythm is shown below.
She has been treated with increasing doses of biphasic defibrillation without success. Three doses of epinephrine 1 mg have been administered. What is the next step in management?
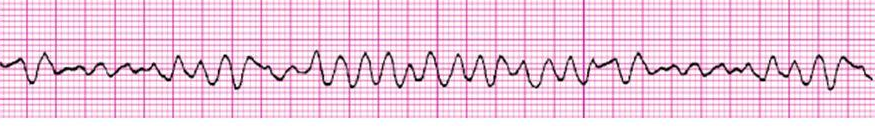
a. 1 mg IV epinephrine
b. Terminating the resuscitation
c. 300 mg IV amiodarone
d. 1.5 mg/kg IV lidocaine
Answer
c. 300 mg IV amiodarone
Rationale
C. Rationale: Atropine is given at a dose of 1.0 mg IV every 3 to 5 minutes until a total dose of 3 mg is administered.
Question
Atropine is given at a dose of 1.0 mg IV every 3 to 5 minutes to a maximum dose of:
a. 1 mg
b. 2 mg
c. 3 mg
d. 4 mg
Answer
c. 3 mg
Rationale
D. Rationale: Epinephrine to treat cardiac arrest is recommended to be given IV or IO with a solution of 1:10,000 dilution, 1 mg every 3 to 5 minutes. Studies have shown that this standard dose was responsible for improved survival and ROSC.
Question
Epinephrine is given IV to treat cardiac arrest in a dilution of:
a. 1:10
b. 1:100
c. 1:1,000
d. 1:10,000
Answer
d. 1:10,000
Rationale
D. Rationale: Along with delivery by trained medical personnel, bystander-administered naloxone for opioid-associated life-threatening emergencies is also recommended.
Question
Naloxone can be administered in opioid-associated life-threatening emergencies by:
a. trained EMS personnel
b. emergency physicians
c. bystanders at the scene
d. all of the above
Answer
d. all of the above
Rationale
B. Rationale: Tricyclic antidepressant toxicity is characterized by sinus tachycardia, wide QRS tachycardias, and supraventricular tachycardia.
Question
Signs of tricyclic antidepressant toxicity include all of the following EXCEPT:
a. altered mental status
b. sinus bradycardia
c. hypertension
d. urinary retention
Answer
b. sinus bradycardia
Rationale
A. Rationale: Epinephrine is a vasopressive medication that leads to increases in both alpha- and beta-adrenergic activity. The alpha-adrenergic actions lead to increased vasoconstriction and increased central perfusion pressure. The beta-adrenergic actions lead to ionotropic and chronotropic effects on the heart that will increase cardiac output while increasing the myocardial oxygen requirement. Consequently, while epinephrine is useful for improving perfusion and cardiac output, it can have the adverse event of causing myocardial ischemia.
Question
What are the physiologic effects of epinephrine?
a. Increased central perfusion pressure, increased cardiac output, increased myocardial oxygen requirement
b. Decreased central perfusion pressure, increased cardiac output, increased myocardial oxygen requirement
c. Increased central perfusion pressure, decreased cardiac output, increased myocardial oxygen requirement
d. Increased central perfusion pressure, decreased cardiac output, decreased myocardial oxygen requirement
Answer
a. Increased central perfusion pressure, increased cardiac output, increased myocardial oxygen requirement
Rationale
D. Rationale: Vasopressin and epinephrine, when used alone, are effective drugs for cardiac arrest and improve the chance of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC). The combination of the two drugs, however, shows no significant advantage compared to using epinephrine alone. In the interest of simplifying the adult cardiac arrest algorithm, vasopressin was removed.
Question
Which one of the following statements is true?
a. The administration of vasopressin alone is more effective than giving epinephrine and vasopressin as combination therapy.
b. There is a significant advantage to giving vasopressin and epinephrine together compared to using epinephrine alone in the treatment of cardiac arrest.
c. There is no significant advantage to giving vasopressin and epinephrine together compared to using vasopressin alone in the treatment of cardiac arrest.
d. There is no significant advantage to giving vasopressin and epinephrine together compared to using epinephrine alone in the treatment of cardiac arrest.
Answer
d. There is no significant advantage to giving vasopressin and epinephrine together compared to using epinephrine alone in the treatment of cardiac arrest.
Rationale
C. Rationale: Vasopressors are used to improve cardiac output and blood perfusion to the heart and brain.
Question
You are assigned by your team leader to give vasopressors intravenously while attempting to revive a cardiac arrest patient secondary to status asthmaticus. Vasopressors are used to:
a. decrease perfusion to the brain
b. increase ventilation to the lungs
c. improve cardiac output
d. improve oxygenation of the blood
Answer
c. improve cardiac output
Rationale
B. Rationale: Naloxone can be administered to the patient via intramuscular injection or intranasal delivery.
Question
You are to administer naloxone to a patient with a drug overdose. How is naloxone administered?
a. transdermal patch
b. intranasal or intramuscular
c. intravenous
d. subcutaneous injection
Answer
b. intranasal or intramuscular