ECG Basic Principles Flashcard 1
Rationale
D. Rationale: The standard complete ECG study makes use of 12 leads. These leads represent the following leads: I, II, III, aVR, aVL, aVF, and V1 to V6.
Question
A complete ECG procedure measures using how many leads?
a. 1 lead
b. 3 leads
c. 5 leads
d. 12 leads
Answer
d. 12 leads
Rationale
D. Rationale: The normal PR interval is about 0.12–0.2 seconds if the impulse is generated in the SA node. But since junctional rhythms are in close proximity to the ventricles, the PR interval is expected to be shorter than 0.12–0.2 seconds.
Question
Due to the close proximity of the junctional pacemaker to the ventricles, the PR interval is expected to be how long?
a. 0.2 seconds
b. 0.15 seconds
c. 0.12 seconds
d. 0.10 seconds
Answer
d. 0.10 seconds
Rationale
C. Rationale: Electrical signals that flow away from the positive electrode of the ECG device cause a downward deflection in the tracing generated by the ECG device.
Question
Electrical impulses that flow away from the positive electrode of the ECG device cause the measured amplitude of the ECG tracing to deflect in which direction?
a. Flat
b. Upward
c. Downward
d. Both upward and then downward
Answer
c. Downward
Rationale
C. Rationale: The sinoatrial node is the anatomical structure where normal impulse generation originates.
Answer choice A – The Bundle of His transmits impulses from the atrioventricular (AV) node.
Answer choice B – The Purkinje fibers are specialized cardiac muscle fibers that form a network in the ventricular walls that conducts the impulses responsible for ventricular contractions.
Answer choice D – The intraventricular septum separates the left and right ventricles and does not generate electrical impulses.
Question
Impulse generation originates in which one of the following anatomical structures of the heart?
a. Bundle of His
b. Purkinje fibers
c. Sinoatrial node
d. Intraventricular septum
Answer
c. Sinoatrial node
Rationale
A. Rationale: Calipers can measure equidistant R-R intervals throughout the ECG printout, representing R-R wave regularity that demonstrates the overall regularity of the patient’s ECG.
Question
In an ECG printout, regularity is best measured with which of the following tools?
a. Vernier calipers
b. Ruler
c. Protractor
d. Visual estimation
Answer
a. Vernier calipers
Rationale
C. Rationale: This action potential pattern refers to the electrical measurements in the working heart cell.
Answer choices A & B – The conduction cell and sinus node cell have similar patterns distinct from working heart cells. The only difference between them is that the action potential within a single conduction cell has a slower and more gradual depolarizing phase.
Answer choice D – Myocytes do not conduct electrical activity.
Question
Refer to the graph below. This plot pattern depicts the electrical measurement of a:
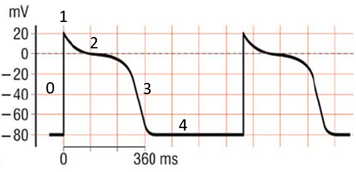
a. Conduction cell
b. Sinus node cell
c. Working heart cell
d. Myocyte cell
Answer
c. Working heart cell
Rationale
D. Rationale: One small square measured horizontally is 0.04 seconds, and thus 5 small squares measured horizontally is 0.2 seconds. One small square measured vertically is 0.1 millivolt, and 5 small squares measured vertically is 0.5 millivolts.
Question
The ECG strip is divided into small squares and big squares. The border around the 5 small squares is weighted heavily when printed. When the ECG machine is set to its default settings, 5 small squares on the horizontal axis indicate which of the following measurements?
a. 0.1 millivolt
b. 0.5 millivolt
c. 0.5 seconds
d. 0.2 seconds
Answer
d. 0.2 seconds
Rationale
D. Rationale: The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization. When impulses are generated from the ventricles, they will show a widened QRS complex on an ECG tracing (i.e., longer than 0.12 seconds). Sometimes, a supraventricular rhythm may also present with widened QRS complexes when there is a delay in impulse conduction from the supraventricular focus to the ventricles.
Question
The QRS complex represents which segment of the cardiac conduction system?
a. Atrial repolarization
b. Atrial depolarization
c. Ventricular repolarization
d. Ventricular depolarization
Answer
d. Ventricular depolarization
Rationale
C. Rationale: The heart is a muscle working as a pump system that ejects blood into the systemic circulation by the action of myocytes. When stimulated by electrical impulses, the myocytes contract. The ECG measures the function of the heart’s conduction system as it generates impulses causing the myocardium to contract.
Question
What function of the heart is measured by an electrocardiogram?
a. Ventricular contraction
b. Cardiac output
c. Conduction system
d. Wall-motion abnormalities
Answer
c. Conduction system
Rationale
B. Rationale: The normal PR interval is 120–200 milliseconds.
Answer choice A – The normal QRS interval is 70–100 milliseconds.
Answer choice D – The normal QT interval is 360–440 milliseconds.
Question
What is the normal PR interval?
a. 70–100 ms
b. 120–200 ms
c. 210–310 ms
d. 360–440 ms
Answer
b. 120–200 ms