Cardiac Arrest Flashcard 1
Rationale
C. Rationale: The patient is in cardiac arrest demonstrated by the absence of a pulse and the absence of breathing. Thus, the interpretation of this ECG finding is pulseless electrical activity (PEA). PEA has an organized rhythm on ECG but with no palpable pulse. It can present as a slow, normal, or fast rhythm. Agonal PEA has a very slow rate. PEA can also show low or high amplitude T waves, prolonged PR and QT intervals, atrioventricular dissociation, complete heart block, or ventricular complexes without P waves.
Question
A 4-year-old patient in the intensive care unit with septic shock is unresponsive. You notice multiple petechiae on the patient’s skin. You check the breathing and pulse, but you find none. You immediately activate the emergency response system, and the code team arrives. An ECG monitor shows the following tracing:

What is your interpretation of this ECG result?
a. Ventricular fibrillation
b. Sinus bradycardia
c. Pulseless electrical activity
d. Asystole
Answer
c. Pulseless electrical activity
Rationale
B. Rationale: If anaphylaxis causes cardiac arrest, the provider prioritizes high-quality CPR with attention to maintaining a patent airway and administering fluid therapy. Epinephrine is the drug of choice for treating anaphylaxis. The goal of high-quality CPR is to maintain adequate oxygen delivery until the anaphylactic reaction resolves. Steroid therapy can be of value in the management of anaphylaxis upon resolution of the cardiac arrest. If return of spontaneous circulation has been achieved, methylprednisolone can be given at a dose of 1 to 2 mg/kg IV or IO as part of post-cardiac arrest care.
Question
A 7-year-old girl presents with angioedema and difficulty breathing after eating peanuts. You suspect anaphylaxis. The patient goes into cardiac arrest after a few minutes. The drug of choice for treating anaphylaxis in this case is:
a. Methylprednisolone
b. Epinephrine
c. Lidocaine
d. Diphenhydramine
Answer
b. Epinephrine
Rationale
C. Rationale: When a pediatric patient goes into cardiac arrest, the PALS resuscitation team’s primary goal is to achieve an organized and perfusing cardiac rhythm evidenced by a return of a palpable pulse and spontaneous breathing. This is termed return of spontaneous circulation. Clinically, the patient’s color and breathing returns to normal. The treatment of cardiac arrest with PALS involves establishing intravascular access, rhythm assessment for shockable and non shockable rhythms, early defibrillation if indicated, medical therapy, and advanced airway management.
Question
After a successful cardiac life support intervention, the pediatric patient in cardiac arrest achieves an organized cardiac rhythm with a palpable pulse. This is known as:
a. Normal sinus rhythm
b. Post-cardiac arrest care
c. Return of spontaneous circulation
d. Cardioversion
Answer
c. Return of spontaneous circulation
Rationale
A. Rationale: A rhythm that does not record any electrical activity from the heart is known as asystole. Asystole is a non shockable rhythm. In this case, following the American Heart Association pediatric cardiac arrest guidelines, the next step is to immediately perform high-quality CPR for 5 cycles, administer epinephrine IV every 3 to 5 minutes, and perform another rhythm check.
Question
After giving a shock of 50 J to a 6-year-old girl in cardiac arrest, you resume 5 cycles of CPR. A rhythm check reveals the following tracing:
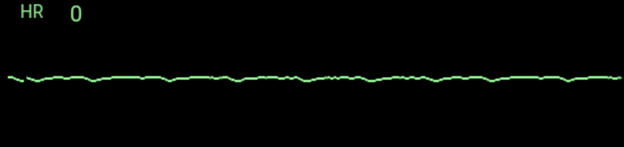
What is your next course of action?
a. Immediately resume CPR
b. Give another shock at 50 J
c. Give another shock at 75 J
d. Administer epinephrine
Answer
a. Immediately resume CPR
Rationale
B. Rationale: To prevent interruptions in chest compressions, rhythm and pulse checks must be performed within 10 seconds. If the team is unsure or the arrhythmia persists after the 10-second check, CPR must resume at once.
Question
After giving a shock, the team is now in the rhythm check stage of CPR. The team leader requests you to perform a rhythm check to see if the shock was successful. How much time is allotted to analyze and perform a rhythm check during CPR in a pediatric cardiac arrest patient in ventricular fibrillation?
a. 5 seconds
b. 10 seconds
c. 30 seconds
d. 1 minute
Answer
b. 10 seconds
Rationale
B. Rationale: If after the rhythm check, the VF or pVT persists, then a higher dose of 4 J/kg or 100 J may be given in this case. If the arrhythmia persists in the next rhythm check, a much higher dose between 5 and 10 J/kg should then be delivered. The maximum adult dose for a pediatric patient should not be exceeded.
Question
After providing the first shock and performing a rhythm check, the pediatric cardiac arrest patient continues with pulseless ventricular tachycardia. What energy setting is best for the next shock to be given?
a. The same dose
b. A higher dose
c. The highest setting of the defibrillator
d. Perform conventional CPR with medications instead
Answer
b. A higher dose
Rationale
D. Rationale: Respiratory failure and shock are the most common causes of cardiac arrest in pediatric patients.
Question
Aside from respiratory failure, the most common cause of cardiac arrest in pediatric patients is:
a. DIC
b. Head trauma
c. Infection
d. Shock
Answer
d. Shock
Rationale
A. Rationale: The first shock dose for infants must be calculated at 2 J per kg. Therefore, the rescuer must administer 20 J for the first shock in this case. The second dose is calculated at 4 J per kg.
Question
Calculate the first shock dose for a 10 kg infant. How much should you administer in this case?
a. 20 J
b. 30 J
c. 40 J
d. 50 J
Answer
a. 20 J
Rationale
B. Rationale: The most common cause of cardiac arrest in infants and children is respiratory failure and shock, also described as a hypoxic arrest. Hypoxic arrest in infants and children may be due to an underlying disease. It is vital for healthcare providers to reverse respiratory failure and shock so that it does not progress into cardiac arrest.
Question
Cardiac arrest in infants and children from respiratory failure and shock is also known as which one of the following medical conditions?
a. Acute respiratory distress syndrome
b. Hypoxic arrest
c. Acute myocardial infarction
d. Hypoventilation syndrome
Answer
b. Hypoxic arrest
Rationale
D. Rationale: Intraosseous canalization provides non collapsible vascular access for intravenous medications and fluid resuscitation. However, in PALS, it is a priority to use the IV route for all medical therapies and fluid resuscitation techniques. If the intravenous route is not possible, the next recommended route is intraosseous.
Question
Drug administration through non collapsible vascular access can be gained through which of the following routes?
a. Intravenous route
b. Subcutaneous route
c. Intramuscular route
d. Intraosseous route
Answer
d. Intraosseous route