Assessment Flashcard 2
Rationale
C. Rationale: The patient’s signs and symptoms are most likely secondary to hypoglycemia (normal blood glucose level is > 70 mg/dL). The patient has type 1 diabetes, which is insulin-dependent, and iatrogenic hypoglycemia from insulin may cause this stroke-like condition.
Question
A 54-year-old patient with type 1 diabetes mellitus is brought to the emergency department for loss of consciousness. Vital signs are as follows: HR = 100 bpm, BP = 100/80 mm Hg, RR = 12/min, T = 36.8°C, oxygen saturation = 100%. Glucometer reading is 45 mg/dL. The patient cannot be aroused. What is your next course of action?
a. Perform neurologic screening
b. Order a CT scan of the head
c. Treat hypoglycemia
d. Give fibrinolytic therapy
Answer
c. Treat hypoglycemia
Rationale
D. Rationale: The patient’s heart and respiratory rates are normal. There is no indication to initiate rescue breathing, give naloxone, or to start chest compressions. Monitoring the patient until EMS arrives is the proper response.
Question
A 55-year-old man is found down and unresponsive to verbal commands when you tap on both of his shoulders. His respiratory rate is 16 breaths/minute, and his heart rate is 65 bpm. What should you do?
a. Initiate rescue breathing
b. Administer naloxone
c. Start chest compressions and attach AED pads
d. Monitor until emergency responders arrive
Answer
d. Monitor until emergency responders arrive
Rationale
A. Rationale: Healthcare providers must recognize the classic signs of pulmonary embolism, which is a reversible cause of cardiac arrest. Orthopedic patients are at risk because of their inability to ambulate post-surgery. In the absence of cardiac tamponade, arrhythmia, pneumothorax, or myocardial infarction, pulmonary thromboembolism should be suspected if there is a sudden drop in blood pressure and elevated central venous pressure that can be assessed by noting distended neck veins on examination.
Question
A 59-year-old inpatient is post-op day 3 from an open reduction internal fixation of a compound femur fracture. He reports pleuritic chest pain and difficulty breathing. You record his vital signs and note a sudden drop in blood pressure. You also notice that his neck veins are distended. After 5 minutes, he loses consciousness and goes into cardiac arrest. Out of the following causes, which is your primary consideration?
a. Pulmonary embolism
b. Cardiac tamponade
c. Atelectasis
d. Tension pneumothorax
Answer
a. Pulmonary embolism
Rationale
A. Rationale: Severe hypoglycemia can mimic stroke symptoms (also known as neuroglycopenic symptoms). D50 glucose is the appropriate treatment, and when it is given in a hypoglycemic patient with stroke-like findings, the patient immediately regains consciousness. The healthcare provider must know how to recognize neuroglycopenic symptoms versus those of acute stroke.
Question
A 60-year-old man is brought to the emergency department unresponsive. He has the following vital signs: HR = 100 bpm, BP = 100/80 mm Hg, RR = 12/min, T = 36.8°C, oxygen saturation = 100%. Blood sugar level = 30 mg/dL. A 12-lead ECG records the following tracing:
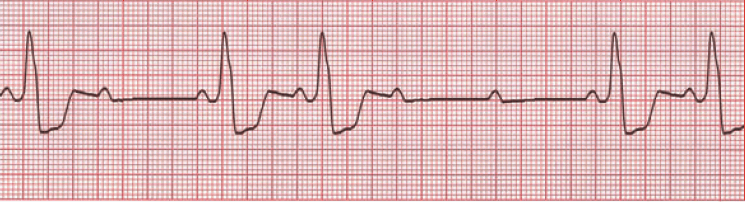
What is the treatment of choice for this patient?
a. D50 glucose
b. Nicardipine
c. Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator
d. Nitroprusside
Answer
a. D50 glucose
Rationale
B. Rationale: Older individuals are susceptible to pulmonary thrombosis, particularly after undergoing surgical procedures that cause immobility for days into recovery. In this patient, the diagnosis is confirmed with a ventilation/perfusion scan. Immediate fibrinolysis is recommended but should only be given after consulting an expert.
Question
A 71-year-old woman undergoes hip replacement surgery. On the third hospital day, she suddenly develops chest pain and difficulty breathing. A ventilation/perfusion scan reveals two segmental mismatched defects in the right middle lobe. After the test, the patient goes into cardiac arrest and expires. What is the likely cause of the patient’s demise?
a. Myocardial infarction
b. Pulmonary thrombosis
c. Hypovolemic shock
d. Tension pneumothorax
Answer
b. Pulmonary thrombosis
Rationale
D. Rationale: A marked reduction of the GWR obtained from a brain CT scan taken within 2 hours after cardiac arrest predicts a poor neurologic outcome.
Question
A cardiac arrest patient has achieved a return of spontaneous circulation after 25 minutes of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. He is presently comatose. The neurologist wants to assess the patient’s prognosis and orders a CT scan of the brain. If the CT scan taken within 2 hours after cardiac arrest shows a marked reduction of the gray-white ratio, what can the neurosurgeon conclude of this finding?
a. It is a normal finding.
b. It is not significant, and the CT must be repeated after 6 hours.
c. It is an indication of good survivability to hospital discharge.
d. It predicts a poor neurologic outcome.
Answer
d. It predicts a poor neurologic outcome.
Rationale
D. Rationale: Brain edema is represented by the gray-white ratio (GWR) in a CT scan of the brain. The normal GRW is 1.3, and this value decreases with brain edema.
Question
A comatose patient was revived after an unwitnessed cardiac arrest. After reviewing the patient’s brain CT scan, the neurosurgeon concludes that this patient’s neurologic outcome is poor. The patient has a gray-white ratio of 0.5 on a CT scan of the brain. What can you conclude in this finding?
a. A normal GWR
b. Parkinson’s disease
c. Brain tumor
d. Brain edema
Answer
d. Brain edema
Rationale
A. Rationale: Dilated pupils, the presence of myoclonus, and high blood levels of neuron-specific enolase are predictors of poor neurologic outcomes following cardiac arrest. An electroencephalogram exhibiting reactivity to external stimuli is the sign of a functioning brain, indicating a more favorable neurologic outcome.
Question
A neurologist is projecting the likely outcome of a 72-year-old man that has been revived 15 minutes after cardiac arrest. Which of the following are clinical findings or tools that can help to conclude that this patient has a good prognosis?
a. Dilated pupils in response to light
b. Status myoclonus during the first 120 hours
c. Electroencephalogram reactivity to external stimuli
d. High blood levels of neuron-specific enolase
Answer
a. Dilated pupils in response to light
Rationale
C. Rationale: Targeted temperature management and sedation can skew the data gathered from prognosticating tests. Therefore, it is recommended for clinicians to wait another 72 hours after the patient has returned to normal core temperature before performing prognosticating tests.
Question
A patient has achieved a return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) after 15 minutes of ACLS. She is comatose and is admitted to the ICU with targeted temperature management. When is the most appropriate time to perform prognosticating tests in this situation?
a. 24 hours after ROSC
b. 72 hours after ROSC
c. 72 hours after the patient returns to normal temperature
d. 24 hours after the patient returns to normal temperature
Answer
c. 72 hours after the patient returns to normal temperature
Rationale
A. Rationale: Waveform capnography is an indicator of CPR quality. End-tidal CO2 pressures should be maintained between 10 and 20 mm Hg when providing CPR. If this value drops to 10 mm Hg and below, it should signify that CPR needs improvement. Methods for improving CPR are as follows: compression rate of 100–120/minute, compression depth of 2 inches, allow full chest recoil, ensure that the ET tube is not obstructed, and ensure visible chest rise after each breath.
Question
A patient in cardiac arrest is successfully intubated in the ED. While performing 2 cycles of CPR, waveform capnography measures pressures at 9 mm Hg. What is your next course of action?
a. Improve the quality of CPR.
b. Give epinephrine via the endotracheal route.
c. Insert an IV and infuse packed RBCs properly typed and cross-matched.
d. Discontinue CPR and call the time of death.
Answer
a. Improve the quality of CPR.