ACLS Principles Flashcard 2
Rationale
A. Rationale: Unlike other causes of cardiac arrest, a witnessed drowning event should prompt immediate rescue breathing. There is no benefit to trying to remove water in the airway using the Heimlich (abdominal thrust) maneuver.
Question
A witnessed drowning event should prompt immediate rescue breathing rather than compressions.
a. True
b. False
Answer
a. True
Rationale
B. Rationale: After the AED announces that the shock has been delivered, CPR must be resumed as soon as possible for 2 minutes before performing the next rhythm check.
Question
After an AED delivers a shock to the patient, the next rhythm check is performed after:
a. 1 minute
b. 2 minutes
c. 3 minutes
d. 5 minutes
Answer
b. 2 minutes
Rationale
C. Rationale: This woman was found unresponsive for an unknown amount of time. Typically, a patient who has been in cardiac arrest for a short period will be in the first stage: the electric stage, when defibrillation is still quite successful due to minimal ischemia. As time progresses, the patient enters the hemodynamic stage, during which chest compressions can still provide a perfusing cardiac output even as ischemia progresses. During the final metabolic stage, there is widespread ischemia and energy failure. In this stage, defibrillated shockable rhythms are less likely to result in spontaneous contractions after the shock due to the lack of ATP to support muscular contractions. Rather, there is a higher risk of persistent asystole. There is no inflammatory stage in the three-stage model of cardiac arrest.
Question
An older woman is found down and unresponsive. No bystanders are present. She is not breathing, and no pulse is palpable. Chest compressions are started immediately with rescue breaths. An AED is found, the pads are placed, and it detects a shockable rhythm, which is quickly delivered. Immediate resumption of chest compressions is started. However, upon the next pulse check, there is no palpable pulse. Repeat AED evaluation no longer detects a shockable rhythm. What stage of arrest is the patient most likely in at this time?
a. electric stage
b. hemodynamic stage
c. metabolic stage
d. inflammatory stage
Answer
c. metabolic stage
Rationale
C. Rationale: Asynchronous ventilations help decrease interruptions in chest compressions by providing ventilations while chest compressions are simultaneously being performed. Intubated patients are given one breath every 6 seconds.
Question
How does a rescuer provide ventilations on an intubated patient in a multiple rescuer scenario?
a. gives 2 breaths after every 30 chest compressions
b. gives 2 breaths after every 15 chest compressions
c. gives one breath every 6 seconds with continuous compressions
d. there is no difference in providing ventilations in single-rescuer and team scenarios
Answer
c. gives one breath every 6 seconds with continuous compressions
Rationale
C. Rationale: If an IV or IO line cannot be established, then the last resort is drug delivery through the ET tube.
Question
If an intravenous or intraosseous line cannot be established, the last resort for drug delivery is:
a. intraocular
b. transdermal
c. through the endotracheal tube
d. intramuscular
Answer
c. through the endotracheal tube
Rationale
A. Rationale: Studies have shown that epinephrine given within 1 to 3 minutes after the onset of cardiac arrest improves survival to hospital discharge with good neurologic outcomes when compared to giving it at a later time.
Question
Of the following timeframes, which is the best time to administer epinephrine to a patient in a nonshockable cardiac arrest so that the chance of survival is increased?
a. 1 minute after cardiac arrest
b. 5 minutes after cardiac arrest
c. 10 minutes after cardiac arrest
d. 15 minutes after cardiac arrest
Answer
a. 1 minute after cardiac arrest
Rationale
A. Rationale: Studies have shown that there is an increase in ROSC incidence, greater survival to hospital discharge, and improved neurologic outcomes if epinephrine is given between 1 and 3 minutes after the onset of cardiac arrest as compared to giving epinephrine at a later time.
Question
Studies show that there is an increased incidence of ROSC, a greater chance of survival to hospital discharge, and improved neurologic outcomes if epinephrine is given within how many minutes after the onset of cardiac arrest?
a. 1–3 minutes
b. 2–5 minutes
c. 5 minutes
d. 10 minutes
Answer
a. 1–3 minutes
Rationale
C. Rationale: This rhythm is VF, a shockable rhythm, so the correct action is asynchronous defibrillation.
Question
The patient with this rhythm has no pulse and no respirations. He is attached to a biphasic monitor. The first step in treatment is to:
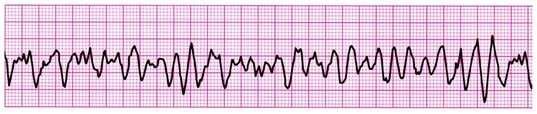
a. give epinephrine
b. give atropine
c. defibrillate
d. do asynchronized cardioversion
Answer
c. defibrillate
Rationale
Rationale: A higher success rate of achieving ROSC is determined by a correct rate of chest compressions at 100–120/min, the appropriate rate of ventilations, and a shorter duration of interruptions in chest compressions.
Question
The chance of reaching successful ROSC is aided greatly by:
a. chest compressions given at a rate of 100–120/minute
b. giving faster ventilations
c. interrupting chest compressions for frequent pulse checks
d. calling 9-1-1 sooner
Answer
a. chest compressions given at a rate of 100–120/minute
Rationale
A. Rationale: Epinephrine to treat cardiac arrest is recommended to be given intravenous or intraosseous with a solution of 1:10,000 dilution, at a dose of 1 mg every 3 to 5 minutes.
Question
What is the dosage of epinephrine given in the treatment of cardiac arrest?
a. 1 mg every 3 to 5 minutes
b. 2 mg every 3 to 5 minutes
c. 1 mg before every pulse check
d. 2 mg single dose before every defibrillator shock
Answer
a. 1 mg every 3 to 5 minutes