Ventricular Rhythms Flashcard 2
Rationale
A. Rationale: Ventricular fibrillation is brought about by an extremely irritable ventricular focus characterized as a disorganized or severely chaotic rhythm that causes the ventricles to quiver, presenting with a nonperfusing rhythm. Pulseless ventricular tachycardia is also a nonperfusion rhythm, but it produces organized electrical activity. Pulseless electrical activity is also an organized nonperfusing electrical activity. Asystole is the absence of electrical activity.
Question
Which of the following cardiac arrest rhythms appears as chaotic, disorganized electrical activity?
a. Ventricular fibrillation
b. Pulseless ventricular tachycardia
c. Pulseless electrical activity
d. Asystole
Answer
a. Ventricular fibrillation
Rationale
B. Rationale: A PAC is produced by an ectopic focus ahead of the normal impulse conduction anywhere within the atria. A PAC with an inverted p wave indicates an ectopic focus near the distal portion of the atria. A PAC occurs earlier than the normal sinus p wave, has a different p wave morphology, and has normal PR intervals in most cases. A PVC has a wide QRS complex, occurring earlier than the expected QRS complex during normal impulse conduction.
Answer choice A – Neither PACs nor PVCs are necessarily followed by an rSr complex.
Answer choice C – A prolonged PR interval is indicative of first-degree AV block.
Answer choice D – A PAC may have a p wave, but the morphology will not appear normal.
Question
Which of the following descriptions accurately differentiates a premature atrial contraction (PAC) from a premature ventricular contraction (PVC)?
a. A PAC is followed by an rSr’ complex, while a PVC does not need to have a succeeding rSr’ complex.
b. A PAC has an inverted P wave, while a PVC shows a wide QRS complex.
c. A PAC has a prolonged PR interval, while a PVC has a narrow QRS complex.
d. A PAC does not have a p wave, while a PVC does have a p wave.
Answer
b. A PAC has an inverted P wave, while a PVC shows a wide QRS complex.
Rationale
A. Rationale: The term polymorphic may be attributed to torsade’s de pointes, but there are also disease conditions with polymorphic ventricular tachycardia that are not. Sometimes, polymorphic QRS complexes are observed in nonsustained ventricular tachycardias, particularly if the tachycardia only lasts for several beats. It can also be seen in patients with severe myocardial damage from myocardial infarction. These patients may progress to ventricular fibrillation immediately. It can also be seen in patients with cardiogenic shock just before the patient expires.
Question
Which of the following ECG tracings represents a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia?
a. Torsade’s de pointes
b. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
c. AVNRT
d. Ventricular fibrillation
Answer
a. Torsade’s de pointes
Rationale
B. Rationale: Two successive PVCs occurring one after the other is known as a couplet. The successive PVC did not allow the normal pacemaker to resume. Bigeminy describes a PVC after every two sinus beats. Trigeminy describes a PVC that appears after every three sinus beats. A run of PVCs describes multiples in a row without intervening sinus beats.
Question
Which of the following terms describe two successive premature ventricular contractions that occur one after another and do not allow a normal pacemaker to resume?
a. Bigeminy
b. Couplet
c. Trigeminy
d. Runs
Answer
b. Couplet
Rationale
A. Rationale: A distinct feature of a premature ventricular complex is a T wave with an opposite deflection from the QRS complex. Second-degree AV block Mobitz type 1 has a progressive prolongation of the PR interval. Dropped beats can be a feature of second-degree AV block Mobitz type 2. Prominent Q waves appear with an infarct.
Question
Which one of the following is a feature of a premature ventricular complex?
a. The T wave has an opposite deflection from the QRS complex
b. Progressive prolongation of the PR interval
c. Dropped beats
d. Prominent Q waves
Answer
a. The T wave has an opposite deflection from the QRS complex
Rationale
D. Rationale: The ventricular escape rhythm is the last line of defense in a heart with a severely compromised conduction system. It has an inherent rate of 20–40 bpm.
Question
Which one of the following is the last line of defense when conduction is significantly compromised?
a. Sinoatrial node
b. Atrioventricular node
c. Junctional escape rhythm
d. Ventricular escape rhythm
Answer
d. Ventricular escape rhythm
Rationale
A. Rationale: The most common etiologies of acute pericarditis include viral infections such as Coxsackie A and B and influenza. “Answer choices B, C, and D are all common etiologies of acute pericarditis, but Coxsackie virus is the most common etiology.”
Question
Which one of the following is the most common cause of acute pericarditis?
a. Coxsackie B virus
b. Adenovirus infection
c. Myocardial infarction
d. Chest trauma
Answer
a. Coxsackie B virus
Rationale
A. Rationale: Premature ventricular contractions are differentiated based on their focus of impulse generation: (1) unifocal PVC and (2) multifocal PVC. Unifocal PVCs originate from one irritable focus and have the same morphology throughout the ECG tracing. Multifocal PVCs originate from multiple foci of irritability and present with different morphologies.
Question
Which type of premature ventricular contractions has the same morphology throughout the ECG tracing?
a. Unifocal PVCs
b. Multifocal PVCs
c. Paroxysmal PVCs
d. Ventricular nodal re-entry
Answer
a. Unifocal PVCs
Rationale
B. Rationale: The rhythm represents PVCs in quadrigeminy. The term quadrigeminy refers to a PVC followed by three consecutive normal beats. The most striking morphology in PVCs is the presence of a premature broad QRS complex that is not preceded by a P wave. This means that the origin of the impulse came from the ventricles. When an impulse comes from the interventricular septum, the broad QRS complex is small with a slightly altered configuration.
Answer choice A – PACs are early beats that originate from the atria, so they appear normal in morphology.
Answer choice C – Torsade’s de pointes is a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia.
Answer choice D – Ventricular tachycardia is a wide complex regular tachycardic dysrhythmia.
Question
You are diagnosing an ECG with the following tracing in limb lead II. What is your diagnosis?
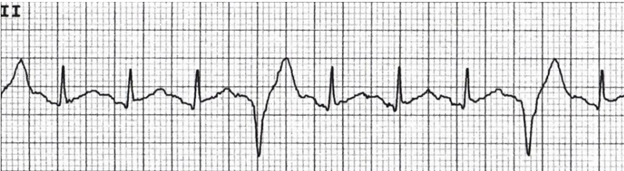
a. Sinus rhythm with PACs
b. Sinus rhythm with PVCs
c. Torsade’s de pointes
d. Ventricular tachycardia
Answer
b. Sinus rhythm with PVCs