Electrolyte and Toxicology Disturbances Flashcard
Rationale
B. Rationale: Patients with severe hypokalemia will present with TU infusion. Since the end of the T wave is not delimited due to the TU infusion, the QT interval cannot be measured in these patients. ST depression may also be present in these patients. Other causes of TU fusion include congenital long QT syndrome and polymorphic ventricular tachycardia.
Answer choice A – A prolonged PR interval is representative of a first-degree atrioventricular block.
Answer choice C – Peaked T waves are indicative of hyperkalemia.
Answer choice D – ST elevation is indicative of acute myocardial infarction.
Question
A patient with severe hypokalemia will present with which one of the following ECG changes?
a. Prolonged PR-interval
b. TU infusion
c. Peaked T waves
d. ST elevation
Answer
b. TU infusion
Rationale
C. Rationale: Digitalis toxicity leads to arrhythmias that affect the sinoatrial and atrioventricular conduction systems. Toxicity in patients with atrial fibrillation impairs the AV conduction of impulses and cause bradycardia in these patients. A patient with first-degree AV block will develop second-degree AV block. When left untreated, it will further progress into a 2:1 AV block and complete AV block.
Question
Which of the following is the effect of digitalis toxicity in the presence of atrial fibrillation?
a. Supraventricular tachycardia
b. Torsade’s de pointes
c. Bradycardia
d. Pulseless electrical activity
Answer
c. Bradycardia
Rationale
D. Rationale: Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is the most striking sign of severe hypomagnesemia.
Answer choice A – This ECG has a sinus rhythm.
Answer choice B – This ECG represents a third-degree AV block. Notice that the atrial rate is independent of the ventricular rate.
Answer choice C – This ECG represents significant ST elevation that may indicate myocardial infarction.
Question
Which one of the following ECGs shows changes most likely to be seen in patients with severe hypomagnesemia?
a. 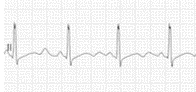
b.
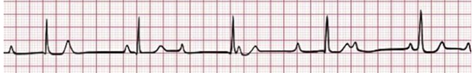
c.
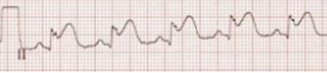
d.
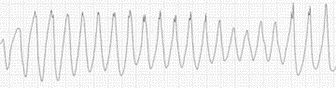
Answer
d.
