ECG Basic Principles Flashcard 1
Rationale
A. Rationale: Measuring an irregular heart rate is possible using an electrocardiogram. Take a 6-second strip and count the number of QRS complexes within the strip. Multiply that number by 10 to calculate the number of beats per minute. In the case of bradycardia, a 12-second strip may be taken to improve accuracy. Count the number of QRS complexes within the 12-second strip, and then multiply that number by 5 to get the heart rate per minute.
Question
A 6-second ECG strip shows the following:
The heart rate for this rhythm is:
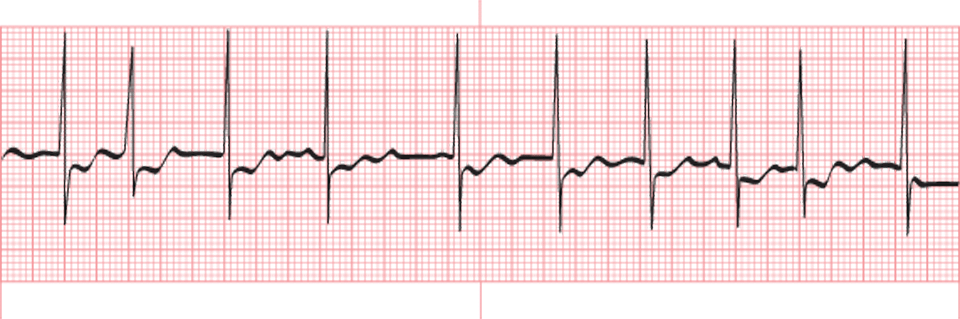
a. 100 bpm
b. 155 bpm
c. 130 bpm
d. 140 bpm
Answer
a. 100 bpm
Rationale
D. Rationale: All myocardial cells are polarized, with the intracellular environment being more negative compared to the extracellular environment. Even if potassium is positively charged, the extracellular environment, which is already rich in sodium, is even more so. The intracellular environment is relatively more negative than the extracellular environment. If we consider the myocyte, its resting potential is –90mV, meaning the cell is more negative than the outside environment by 90mV.
Question
All myocardial cells are capable of being discharged because:
a. All myocardial cells have a positive intracellular environment that allows sodium to leave the cell membrane via the sodium-potassium ATPase pump to cause an action potential.
b. All myocardial cells are rich in ATP, and the process of dissociating a phosphate bond to form ADP produces an electrical current that creates an action potential.
c. All myocardial cells have troponin and myosin capable of producing an electric gradient from the intracellular environment to the extracellular environment in the presence of calcium and ATP.
d. All myocardial cells are polarized, and since they have more intracellular potassium, this causes them to be more negative than the extracellular environment. Thus, an influx of sodium will cause an action potential.
Answer
d. All myocardial cells are polarized, and since they have more intracellular potassium, this causes them to be more negative than the extracellular environment. Thus, an influx of sodium will cause an action potential.
Rationale
C. Rationale: In the normal heart, the SA node is the pacemaker that generates the impulse. It is located high in the right atrium, where the superior vena cava enters the heart. Lead V1 is a right-sided precordial lead placed near the right ventricle in the 4th intercostal space, immediately to the right of the sternum. Therefore, in relation to the SA node, lead V1 is below and to the right. An impulse generated from the SA node will travel away from lead V1. The ECG tracing should register small R waves with deep S waves. Since the ECG tracing showed tall R waves, it can be deduced that lead V1 was not placed on the 4th intercostal space to the right of the sternum but instead somewhere over the left ventricle. This is a common error, and healthcare workers should always be mindful of lead placement.
Question
An electrocardiogram shows small Q waves and tall R waves in lead V1 in a patient with a normal heart. The significance of this finding is:
a. The electrical impulse is measured from the SA downward and toward lead V1 in the right ventricle, making this a normal finding.
b. Lead V1 should have tall R waves because the electrical impulse from the heart starts from the SA node and travels downward and away from lead V1.
c. Lead V1 should have small R waves and deep S waves in the normal heart. Therefore, a misplacement of lead V1 should be considered.
d. Lead V1 should show a downward deflection of the QRS complex because the impulse in the normal heart travels from the AV node toward the SA node. Hence, the impulse generated travels away from lead V1.
Answer
c. Lead V1 should have small R waves and deep S waves in the normal heart. Therefore, a misplacement of lead V1 should be considered.
Rationale
A. Rationale: Sometimes, certain foci within the heart exceed their inherent rates and take over the pacemaker cells. This is known as irritability. Escape is a failsafe mechanism of the heart that allows other areas to take over when higher pacemakers such as the SA node fail.
Torsade’s de pointes is an arrhythmia described as a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia.
Wenckebach phenomenon refers to an atrioventricular block.”
Question
At times, foci within the heart may fire at a rate faster than the SA node rate and take over as the heart’s pacemaker. This is known as:
a. Irritability
b. Escape
c. Torsade’s de pointes
d. Wenckebach phenomenon
Answer
a. Irritability
Rationale
B. Rationale: The PR interval of the normal sinus rhythm is 120 milliseconds to 200 milliseconds. Any interval faster than 120 milliseconds or slower than 200 milliseconds is not considered to be a normal sinus rhythm. Furthermore, a PR interval should be consistent throughout the ECG strip.
Question
Atrioventricular blocks present prolonged PR intervals because there is a delay in the conduction of impulses through the AV node. What is the normal PR interval?
a. 0.06–0.10 seconds
b. 0.12–0.20 seconds
c. 0.30–0.44 seconds
d. 0.40–0.60 seconds
Answer
b. 0.12–0.20 seconds
Rationale
A. Rationale: The normal interval of the QRS complex is 0.06 to 0.10 seconds (60–100 milliseconds). This is approximately 1-½ to 2-½ small squares in the ECG rhythm strip.
Question
How long is a normal QRS interval?
a. 0.10 seconds
b. 0.20 seconds
c. 0.30 seconds
d. 0.40 seconds
Answer
a. 0.10 seconds
Rationale
C. Rationale: Heart rate is established by the autonomic nervous system and the inherent rates of the conduction system. The autonomic nervous system contains two branches: the sympathetic and the parasympathetic. These branches oppose each other to regulate the heart. The sympathetic branch influences the atria and ventricles to increase the rate, increase the conduction velocity through the AV node, and increase irritability. Alpha receptors on the heart regulate vasodilation and vasoconstriction of the vessels. Beta receptors located on the heart increase the strength of cardiac contraction when stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system. The parasympathetic branch counteracts the sympathetic branch by reducing the rate, irritability, and the conduction velocity through the AV node.
Question
The autonomic nervous system regulates the heart rate. Which part of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for increasing the conduction rate of the heart?
a. Alpha receptors
b. Beta receptors
c. Sympathetic branch
d. Parasympathetic branch
Answer
c. Sympathetic branch
Rationale
D. Rationale: The electrical charges of cardiac cells come from the sodium and potassium concentrations inside and outside of the cells. This concentration is regulated by the sodium-potassium channels within the myocyte cell walls. These channels give the electrical cells automaticity, and they can discharge electrical activity without a stimulus by changing the conformation of the sodium-potassium channels.
Question
The heart’s electrical function is regulated by which one of the following cell structures?
a. Mitochondria
b. Endoplasmic reticulum
c. Golgi bodies
d. Sodium-potassium channel
Answer
d. Sodium-potassium channel
Rationale
C. Rationale: The normal PR interval is 120–200 milliseconds.
Question
The normal PR interval is:
a. 40–120 milliseconds
b. 80–200 milliseconds
c. 120–200 milliseconds
d. 200–300 milliseconds
Answer
c. 120–200 milliseconds
Rationale
C. Rationale: The normal QRS interval is 0.06–0.10 seconds. In a standard ECG, one small square is equivalent to 0.04 seconds. Therefore, 4 small squares is equivalent to 0.16 seconds, meaning the QRS complex (ventricular depolarization) in this instance is too slow. There is insufficient information to conclude that this is an irregular rhythm.
Question
The QRS complex of an ECG tracing spans 4 small squares. What can you conclude from this finding?
a. The QRS interval is normal.
b. The QRS interval is too fast.
c. The QRS interval is too slow.
d. There is an irregular rhythm.
Answer
c. The QRS interval is too slow.