ACLS Principles Flashcard 16
Rationale
B. Rationale: It may seem like this patient has sinus bradycardia. However, not feeling a pulse suggests that this is pulseless electrical activity, and thus the patient is in cardiac arrest. ACLS must be initiated immediately, and the first step is to call for help and activate the emergency response team.
Question
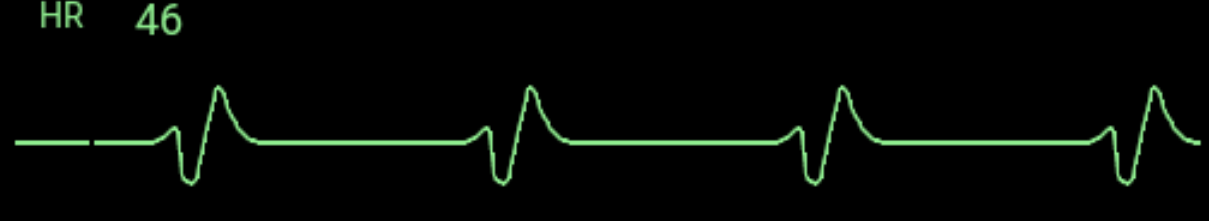
You are monitoring a person in the ICU that has the following ECG tracing:
You check and do not feel a pulse. What is your next appropriate action?
a. Administer atropine 0.5 mg IV bolus
b. Call for help and activate EMS
c. Begin high-quality CPR
d. Defibrillate the patient
Answer
b. Call for help and activate EMS
Rationale
C. Rationale: Recognizing the ECG tracing in cardiac arrest guides the first responder to the proper treatment protocol. Ventricular tachycardia is a shockable rhythm.
Question
You are part of an EMS team resuscitating a 23-year-old man who was drowning. You find him unresponsive with no spontaneous breathing and absent pulses. You connect him to a defibrillator and see the following tracing:

What is your impression of this ECG finding?
a. Ventricular fibrillation
b. Atrial fibrillation
c. Ventricular tachycardia
d. Supraventricular tachycardia
Answer
c. Ventricular tachycardia
Rationale
A. Rationale: AHA guidelines recommend a 1 mg epinephrine 1:10,000 dilution IV bolus injection. A 1:1,000 dilution is too concentrated and is reserved for anaphylactic shock delivered intramuscularly. Defibrillation is not an option for pulseless electrical activity.
Question
You are resuscitating a patient in the ICU. He is in cardiac arrest with pulseless electrical activity. The patient is intubated and has IV access in the left upper extremity. After 2 minutes of high-quality CPR, what is the next treatment of choice?
a. Epinephrine 1 mg 1:10,000 dilution IV
b. Epinephrine 1 mg 1:1,000 dilution IM
c. Epinephrine 2 mg 1:1000 dilution per the ET tube
d. Immediate defibrillation
Answer
a. Epinephrine 1 mg
Rationale
D. Rationale: Intraosseous cannulation allows access to the venous plexus, which has almost the same effect as peripheral venous access.
Question
You are resuscitating an intubated patient in the ED, but intravenous access is not available. What is the next most appropriate access for the pharmacologic treatment of cardiac arrest?
a. Subcutaneous
b. Endotracheal
c. Intramuscular
d. Intraosseous
Answer
d. Intraosseous
Rationale
A. Rationale: AHA guidelines recommend a 1 mg epinephrine (1:10,000 dilution) IV bolus injection as soon as possible for nonshockable rhythms. A 1:1,000 dilution is too concentrated and is reserved for anaphylactic shock delivered intramuscularly. Defibrillation is not an option for pulseless electrical activity. (ACLS Case: Cardiac Arrest algorithm)
Question
You are reviving a cardiac arrest patient with pulseless electrical activity (PEA) in the ICU. The patient is intubated and has intravenous access on the left upper extremity. What is the next treatment of choice after 2 minutes of high-quality CPR?
a. Epinephrine 1 mg 1:10,000 dilution intravenous route
b. Epinephrine 1 mg 1:1,000 dilution intramuscular route
c. Epinephrine 2 mg 1:1,000 dilution endotracheal route
d. Immediate defibrillation at 120 J
Answer
Epinephrine 1 mg 1:10,000 dilution intravenous route
Rationale
B. Rationale: When giving epinephrine or any drugs during resuscitation, do not stop the delivery of high-quality CPR.
Question
You are tasked to administer epinephrine in a 1 mg IV bolus to a patient with asystole. Which one of the following choices is NOT the proper way to administer epinephrine?
a. Elevate the limb with the IV access while injecting
b. Stop CPR for < 10 seconds while injecting epinephrine
c. Follow up epinephrine with an IV bolus of 20 mL normal saline solution
d. Give 1 mg epinephrine 1:10,000 dilution intravenously
Answer
b. Stop CPR for < 10 seconds while injecting epinephrine
Rationale
B. Rationale: The most basic diagnostic finding is the ECG interpretation of a sinus rhythm. An upward P wave deflection is seen in lead II in sinus rhythm, which must be followed promptly by a QRS complex. The P wave represents atrial depolarization with impulses coming from the sinoatrial node. Any rhythm without a P wave is not considered a sinus rhythm. Recognition of the P wave is important.
Question
You are trying to interpret an ECG strip on lead II. What constitutes a normal sinus rhythm in this lead?
a. QRS complex between 0.8 and 0.10 seconds
b. Presence of the P wave
c. Upright T waves
d. Presence of a Q wave
Answer
b. Presence of the P wave
Rationale
B. Rationale: The hypoxic nature of this incident necessitates the traditional airway-breathing-circulation approach. “Patients in respiratory arrest usually respond after a few artificial breaths are given.”
Question
You discover a patient who has drowned in a local public pool. You find him unresponsive and not breathing, and you are unsure if you feel a pulse. What adjustments should be made to perform basic life support appropriately in this patient?
a. Turn the patient prone to expel the fluid in his lungs
b. Provide the airway-breathing-circulation approach
c. An AED is a priority in this situation
d. Perform high-quality CPR for 2 minutes
Answer
b. Provide the airway-breathing-circulation approach
Rationale
B. Rationale: The patient is in pulseless electrical activity. This cardiac arrest rhythm is nonshockable. You must immediately continue high-quality CPR, beginning with chest compressions.
Question
You have defibrillated a cardiac arrest patient with ventricular fibrillation. After 2 minutes of CPR, you perform a rhythm check and observe an organized sinus bradycardia. You check for breathing and pulse but do not observe any. What is the next course of action?
a. Defibrillate with the same dose or higher
b. Continue CPR beginning with chest compressions
c. Perform post-cardiac arrest care because the patient has achieved ROSC
d. You may discontinue CPR and call the time of death
Answer
b. Continue CPR beginning with chest compressions
Rationale
A. Rationale: The best course of action for untrained lay rescuers is to call 9-1-1 and follow dispatcher instructions. Dispatchers are trained to give instructions to lay rescuers for compression-only CPR while EMS is en route.
Question
You want to help a patient with cardiac arrest in an airport, but you are not certified. What should be your actions?
a. Call 9-1-1 and follow dispatcher instructions in providing compression-only CPR.
b. Have someone call 9-1-1, and perform chest compressions with ventilations.
c. Avoid litigation by having someone else rescue the patient.
d. Call the nearest security guard.
Answer
a. Call 9-1-1 and follow dispatcher instructions in providing compression-only CPR.