Pharmacology Flashcard 1
Rationale
B. Rationale: There is evidence that supports the use of amiodarone following epinephrine to treat shock-refractory cardiac arrest secondary to ventricular fibrillation. Lidocaine is only secondary—if amiodarone has not been effective or is unavailable.
Question
A 24-year-old woman resuscitated after a drowning is transported to the emergency department unconscious, pulseless, and not spontaneously breathing. You record the following ECG:
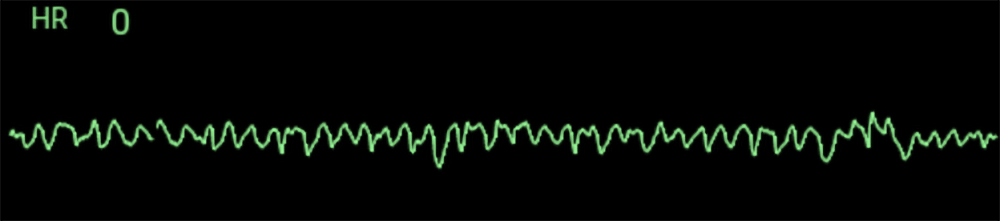
After three rounds of high-quality CPR and three shocks, there is no improvement, and the patient’s ECG tracing remains the same. What first-line pharmacologic treatment can help address this arrhythmia?
a. Sotalol
b. Amiodarone
c. Magnesium
d. Lidocaine
Answer
b. Amiodarone
Rationale
C. Rationale: The correct dose is labetalol 10 mg IV, followed by a continuous IV infusion of 2–8 mg/min. Blood pressure after reperfusion therapy should be monitored every 15 minutes for 2 hours, then every 30 minutes for 6 hours, and then every hour for 16 hours.
Question
A patient is given rtPA for an ischemic stroke, after which he becomes hypertensive. The physician orders labetalol to manage the patient’s blood pressure. What is the correct dosing regimen for labetalol?
A. 2.5 mg IV, may repeat every 3–5 minutes as needed
B. 5 mg IV q 5 minutes until systolic blood pressure is < 160 mm Hg
C. 10 mg IV, followed by a continuous IV infusion of 2–8 mg/min
D. 20 mg IV, followed by a continuous infusion of 5 mg/hour
Answer
C. 10 mg IV, followed by a continuous IV infusion of 2–8 mg/min
Rationale
D. Rationale: Atropine is ineffective in heart transplant patients because they lack vagal innervation.
Question
Atropine is ineffective in heart transplant patients because they:
a. Lack the receptors for atropine
b. Have developed a resistance to atropine
c. Have vagal innervation
d. Lack vagal innervation
Answer
d. Lack vagal innervation
Rationale
A. Rationale: Βeta-blocker administration to patients achieving ROSC after VF or pVT can achieve higher survival rates. But due to some unwanted effects of beta-blockers, such as hemodynamic instability, worsening heart failure, and bradyarrhythmias, their routine use is not warranted. Healthcare providers must consider the use of beta-blockers on a case-by-case basis.
Question
Beta-blocker administration in patients with a return of spontaneous circulation after ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia:
a. Has been shown to correlate with higher survival rates
b. May cause hemodynamic instability and worsening heart failure
c. May cause bradyarrhythmias
d. All of the above
Answer
a. Has been shown to correlate with higher survival rates
Rationale
D. Rationale: Beta-blockers oppose the sympathetic response of the heart. This causes bradyarrhythmia’s. A slow heart rate affects cardiac output. This can worsen heart failure symptoms due to increased preload and cause hemodynamic instability.
Question
Beta-blockers must be used with caution when used in routine post-cardiac arrest treatment because they can cause which unwanted effect(s)?
a. Hemodynamic instability
b. Worsening of heart failure symptoms
c. Bradyarrhythmia’s
d. All of the above
Answer
d. All of the above
Rationale
B. Rationale: Vasoactive drugs impact the cardiovascular system by causing chronotropic effects (increasing heart rate), inotropic effects (myocardial contractility), vasoconstrictive effects (arterial pressure changes), or vasodilator effects (afterload reduction).
Question
Dopamine is a vasoactive drug with positive chronotropic effects and can be used to increase cardiac output. Vasoactive drugs with positive chronotropic effects improve patients’ clinical status in cardiac arrest by:
a. Decreasing the heart rate
b. Increasing the heart rate
c. Increasing myocardial contractility
d. Reducing afterload
Answer
b. Increasing the heart rate
Rationale
C. Rationale: End points for the administration of procainamide include suppression of the arrhythmia, hypotension, maximum dosage reached (17 mg/kg), or widening of the QRS by 50%.
Question
End points for the administration of procainamide include:
A. Duration of QRS increases by 25%
B. Maximum dose of 27 mg/kg is reached
C. Hypotension
D. Increase in heart rate by 30 points
Answer
C. Hypotension
Rationale
D. Rationale: Epinephrine to treat cardiac arrest is recommended to be given as a 1 mg dose of a 1:10,000 dilution IV or IO every 3 to 5 minutes. Studies have shown that this standard dose was responsible for improved survival and ROSC. Epinephrine has α-adrenergic vasoconstrictor effects that can increase coronary and cerebral perfusion during CPR. Epinephrine also has β-adrenergic effects, thought to cause an increase in myocardial workload and depress subendocardial perfusion.
Question
Epinephrine for cardiac arrest is given in what dilution?
a. 1:10
b: 1:100
c. 1:1,000
d. 1:10,000
Answer
d. 1:10,000
Rationale
D. Rationale: Epinephrine has α-adrenergic vasoconstrictor effects that can increase coronary and cerebral perfusion during CPR. Epinephrine also has β-adrenergic effects, thought to cause an increase in myocardial workload and depress subendocardial perfusion.
Question
Epinephrine is used in the treatment of cardiac arrest because:
a. It has α-adrenergic effects
b. It has β-adrenergic effects
c. It increases coronary and cerebral perfusion
d. All of the above
Answer
d. All of the above
Rationale
B. Rationale: The lidocaine dosing regimen is correct. Magnesium sulfate is given as a 1–2 g loading dose diluted as stated over 5 to 20 minutes, not as a rapid IV bolus. Amiodarone 300 mg IV/IO is given initially; a second dose of 150 mg may be given. Atropine is not an antiarrhythmic.
Question
Identify the correct antiarrhythmic dosing regimen:
A. Magnesium sulfate loading dose of 2–3 g IV/IO diluted in 10 mL of D5W and given as a rapid bolus
B. Lidocaine 1–1.5 mg/kg IV/IO, then 0.5–0.75 mg/kg IV/IO given at 5–10 minute intervals to a maximum dose of 3 mg/kg
C. Atropine 1 mg IV/IO; may be repeated to a maximum of 3 mg
D. Amiodarone 300 mg IV/IO bolus; may be repeated once
Answer
B. Lidocaine 1–1.5 mg/kg IV/IO, then 0.5–0.75 mg/kg IV/IO given at 5–10 minute intervals to a maximum dose of 3 mg/kg