Pediatric Bradycardia with a Pulse and Poor Perfusion Algorithm
Algorithm at a Glance
- The provider quickly identifies bradycardia with a pulse.
- The goal is to identify and treat the underlying cause of bradycardia.
- If the child is symptomatic, treatment begins immediately to prevent deterioration.
- If the child is not symptomatic, the team continues close monitoring.
Related Video – Understanding the Pediatric Bradycardia with a Pulse and Poor Perfusion Algorithm
Goals for the Management of Child with Bradycardia
The provider must succeed in the following goals to successfully manage children with bradycardia:
- Recognize and differentiate among several bradyarrhythmias:
- Sinus bradycardia
- First-degree AV block
- Second-degree AV block: Type l (Wenckebach/Mobitz l)
- Second-degree AV block: Type II(Mobitz II)
- Third-degree AV block
- Recognize the signs and symptoms of symptomatic bradycardia.
Pediatric Bradycardia Algorithm Explained
This algorithm outlines the steps for assessing and managing children presenting with symptomatic bradycardia.
Box 0: Ensure Scene Safety
The provider surveys the scene to ensure it is safe for rescuers and the child. If not, the provider carefully moves the child to a safe environment.
Box 1: Determine That the Child Has Bradycardia
A heart rate < 60 bpm is cause for alarm in a child.
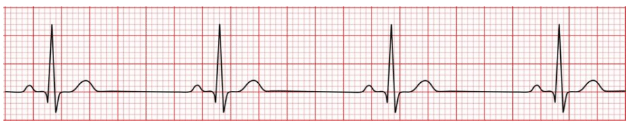
An ECG depicts bradycardia, a heart rate less than 60 beats per minute.
Box 2: Cardiopulmonary Compromise?
If the child has mental status changes, hypotension, or any signs of shock, the team proceeds to Box 3. If the child does NOT have cardiopulmonary compromise, the team proceeds to Box 4a.
Box 3: Assess for and Treat the Underlying Cause
Possible causes of bradycardia in a child include hypothermia, hypoxia, and medications. The team performs a quick assessment and does the following:
- Ensures a patent airway
- Assists breathing as necessary
- Administers oxygen
- Provides a cardiac monitor to identify the rhythm
- Monitors blood pressure and oximetry
- Gains IO/IV access
- Obtains a 12-lead ECG if available but does not delay therapy if unavailable.
Box 4: Initiate CPR
The team evaluates the heart rate and perfusion. If the HR is < 60 bpm despite adequate oxygenation and ventilation, the provider begins high-quality CPR.
Box 5: Bradycardia Persists?
If no, the team proceeds to Box 4a.
If yes, the team proceeds to Box l.
Box 4a: Ongoing Care
If available, the team begins providing oxygen and supports the ABCs while continuously reassessing the child. The team considers expert consultation.
Box 6: Management of Persistent Bradycardia
The team:
- Continues high-quality CPR for a heart rate < 60 bpm
- Administers epinephrine every 3–5 minutes at a dosage of 0.01 mg/kg of the 1:10,000 concentration
- If AV block is noted, administers atropine at a dose of 0.02 mg/kg to a maximum of 0.5 mg and repeats the same atropine dosage if needed
- Considers transthoracic or transvenous pacing
- Continually assesses and treats any underlying causes
Epinephrine helps increase the heart rate to treat bradycardia.
Box 7: Pulse Present?
The team assesses the pulse every 2 minutes.
If a pulse is not present, the team proceeds to Box 8.
If a pulse is present, the team proceeds to Box 5.
Box 8: Pulseless Arrest
The team immediately implements the Pediatric Cardiac Arrest algorithm.
More Free Resources to Keep You at Your Best
Editorial Note
ACLS Certification Association (ACA) uses only high-quality medical resources and peer-reviewed studies to support the facts within our articles. Explore our editorial process to learn how our content reflects clinical accuracy and the latest best practices in medicine. As an ACA Authorized Training Center, all content is reviewed for medical accuracy by the ACA Medical Review Board.