Acute Coronary Syndrome Flashcard 1
Rationale
D. Rationale: Intravenous nitroglycerin relieves chest discomfort, pulmonary edema, and hypertension in patients with ischemic syndromes. (ACLS Case: Acute Coronary Syndrome)
Question
In the ED, the attending physician treats a patient with acute coronary syndrome with intravenous nitroglycerin. What is the purpose of this drug in patients with ischemic syndromes?
a. To relieve chest discomfort
b. To treat pulmonary edema
c. To treat hypertension
d. All of the above
Answer
d. All of the above
Rationale
A. Rationale: ACLS providers must be able to recognize STEMI based on an ECG tracing. ST elevation is seen in leads V1–V4 (anteroseptal leads) with Q waves in the septal leads.
Question
A 12-lead ECG is presented to you at the emergency department by a first responder with the following recorded tracing:
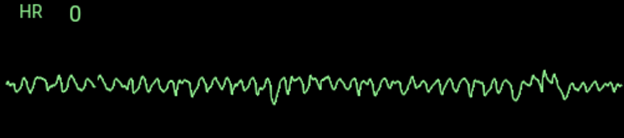
What is your interpretation of this ECG finding?
a. ST elevation myocardial infarction
b. Myocardial ischemia
c. Hyperkalemia
d. Left bundle branch block
Answer
a. ST elevation myocardial infarction
Rationale
A. Rationale: Obtaining a 12-lead ECG is a priority. If not performed by EMS, a 12-lead ECG should be obtained within 10 minutes of the patient’s arrival in the ED.
Question
A 12-lead ECG should be obtained and analyzed within how many minutes of the patient’s arrival in the emergency department?
A. 10
B. 20
C. 30
D. 60
Answer
A. 10
Rationale
C. Rationale: ACLS providers must learn to diagnose low- or intermediate-risk acute coronary syndrome.
Question
A 12-lead ECG shows 0.5 mm ST segment depression in the anterior leads. What is your interpretation of this ECG finding?
a. ST segment elevation MI
b. Non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome
c. Low-/intermediate-risk acute coronary syndrome
d. Normal sinus rhythm
Answer
c. Low-/intermediate-risk acute coronary syndrome
Rationale
B. Rationale: Patients with low or intermediate risk for acute coronary syndrome must be admitted and monitored for possible invasive treatments.
Question
A 39-year-old man with dyslipidemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus presents to the emergency department with retrosternal chest pain. A 12-lead ECG shows nonspecific ST-T wave changes. What is the best course of action for the management of this patient’s chest pain?
a. Patient may be discharged with follow-up in the out-patient department
b. Admit patient to the cardiac unit for further monitoring and possible intervention
c. Prepare patient for percutaneous coronary intervention
d. Start adjunctive therapies
Answer
b. Admit patient to the cardiac unit for further monitoring and possible intervention
Rationale
B. Rationale: The ECG tracing exhibits a wide complex polymorphic irregular tachycardia, which is likely torsades de pointes. The tracing seems to twist around an isoelectric point, a characteristic finding of this rhythm.
Question
A 43-year-old woman comes to the emergency department with reports of palpitations, chest pain, and feeling faint. You request an ECG and are presented with the following tracing:

What is your interpretation of this ECG finding?
a. Ventricular tachycardia
b. Torsades de pointes
c. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
d. Ventricular fibrillation
Answer
b. Torsades de pointes
Rationale
B. Rationale: When STEMI is confirmed, there must be no delay in initiating reperfusion therapies such as percutaneous coronary intervention. The door-to-balloon time is significant in this case.
Question
A 45-year-old man with cardiac arrest secondary to STEMI is revived after two cycles of CPR. What is the immediate intervention recommended in this case?
a. Post-cardiac arrest care
b. Percutaneous coronary intervention
c. Mechanical CPR device
d. Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Answer
b. Percutaneous coronary intervention
Rationale
D. Rationale: Patients with chest pains signifying ACS will have severe retrosternal chest discomfort (pressure or chest tightness) that can radiate to the shoulders, neck, and jaw. It can be accompanied by other symptoms such as fainting spells, dizziness, cold sweats, vomiting, and shortness of breath.
Question
A 54-year-old man who is obese and a heavy smoker suddenly complains of retrosternal chest pain, grade 8 out of 10, dizziness, cold sweats, and vomiting. You suspect an acute coronary syndrome. Which of the following signs and symptoms represents an acute coronary syndrome?
a. Retrosternal chest pain
b. Dizziness
c. Vomiting
d. All of the above
Answer
d. All of the above
Rationale
B. Rationale: Recognizing ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is required for healthcare providers. Early recognition of STEMI allows for prompt, definitive treatment for patients with myocardial infarction.
Question
A 55-year-old man comes to the emergency department with a report of crushing retrosternal chest pain. He has a history of dyslipidemia and is a 20 pack-year smoker. A 12-lead ECG shows the following tracing:

What ECG morphology is seen in leads I, aVL, and V2–V5?
a. Prolonged PR interval
b. ST segment elevation
c. Wide QRS complex
d. Peak T waves
Answer
b. ST segment elevation
Rationale
A. Rationale: This is a new-onset left bundle branch block, and the patient can be treated as a STEMI. In LBBB, the QRS complex is prolonged (> 120 milliseconds) with broad notched R waves in leads I, AVL, and V6. Q waves are absent. Leads V1 to V4 have an rS-complex with appropriate discordance (ST elevation and upright T wave). ¹⁴
Question
A 62-year-old man with a history of GERD presents to the emergency department with acute-onset chest pain. On arrival, he has the following ECG tracing:
 This ECG pattern is new. What is your next course of action?
This ECG pattern is new. What is your next course of action?
a. Start adjunctive therapies and prepare patient for percutaneous coronary intervention
b. Give proton pump inhibitors to decrease acid production in the stomach
c. Request serum troponin levels and start adjunctive therapies as indicated
d. Admit patient for further monitoring
Answer
a. Start adjunctive therapies and prepare patient for percutaneous coronary intervention