ACLS Principles Flashcard 1
Rationale
B. Rationale: Chest compression rate must be between 100 and 120/min. These chest compression rates have been associated with improved survival.
Question
Your team leader wants you to increase the chest compression rate while performing high-quality CPR to a cardiac arrest patient. What is the recommended chest compression rate for an adult cardiac arrest patient?
a. between 60 and 90 compressions/minute
b. between 100 and 120 compressions/minute
c. between 90 and 110 compressions/minute
d. between 80 and 90 compressions/minute
Answer
b. between 100 and 120 compressions/minute
Rationale
C. Rationale: This woman has persistent ventricular fibrillation after a witnessed arrest. She was given prompt standard therapy with CPR, defibrillation, and epinephrine. In this case, amiodarone is the standard of care following VF refractory to standard management. It has a 40% success rate in nonarrest cases of VT. It has less side effects than other anti-arrhythmic medications. While epinephrine can be tried again, it is appropriate to try another medication since it has failed multiple times already in this patient. It is inappropriate to terminate resuscitation efforts in this patient until all options have been exhausted. Lidocaine is an alternative to amiodarone, but is is considered inferior.
Question
A 37-year-old woman has persistence of cardiac arrest. CPR was started within 1 minute of collapse, and defibrillation was provided at about 4 minutes following arrest. Her initial rhythm is shown below.
She has been treated with increasing doses of biphasic defibrillations without success. Three doses of 1 mg epinephrine have been administered IV. What is the next step in management?
a. Give 1 mg epinephrine IV.
b. Terminate the resuscitation.
c. Give a 300 mg bolus of amiodarone IV.
d. Give 1.5 mg/kg of lidocaine IV.
Answer
c. Give a 300 mg bolus of amiodarone IV.
Rationale
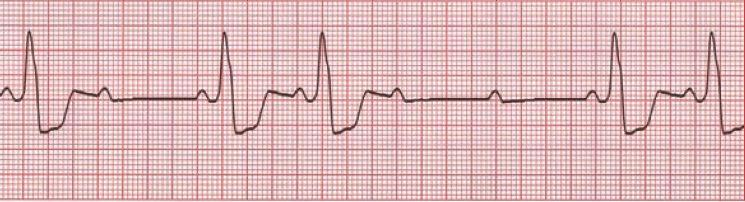
D. Rationale: Atropine is the treatment of choice in symptomatic bradycardia, as it works at the nodal level to oppose vagal stimulation of the node. However, 2nd-degree (Mobitz II) AV block (as in this case) or 3rd-degree AV block are initiated below the node and are unlikely to respond to atropine. Instead, these patients should be managed with beta-adrenergic medications (e.g., epinephrine, dopamine) or transcutaneous pacing as a temporizing measure until transvenous pacing can be accomplished. Dobutamine is generally not recommended in bradycardia due to the high risk of hypotension. Defibrillation is not warranted in this alert patient with a pulse. Note that a new Mobitz type II AV block may be related to ACS with blockage in the left anterior descending artery. Evaluation for ACS with this patient’s classic symptoms is warranted.
Question
A 56-year-old man reports persistent central chest pain and dyspnea. His BP is 94/63 mm Hg. His ECG is shown below:
What of the following is part of the management for this patient?
a. Defibrillation
b. Atropine 0.5 mg IV
c. Dobutamine 10 mcg/kg/min IV infusion
d. Epinephrine 5 mcg/min IV infusion
Answer
d. Epinephrine 5 mcg/min IV infusion
Rationale
A. Rationale: Even though the rhythm looks like sinus bradycardia, the fact that there is no pulse means the patient is in cardiac arrest secondary to pulseless electrical activity. Rescuers must recognize this as soon as possible so that high-quality CPR may be provided immediately.
Question
A 65-year-old man was brought to the emergency department. He is unconscious with no pulse and is not breathing spontaneously. He is hooked up to an ECG machine, and the following tracing is recorded:
What is the interpretation of this ECG finding?

a. pulseless electrical activity
b. sinus bradycardia
c. idioventricular rhythm
d. first-degree AV block
Answer
a. pulseless electrical activity
Rationale
B. Rationale: While performing continuous chest compressions, a provider delivers 1 asynchronous breath every 6 seconds during CPR with an advanced airway such as an endotracheal tube.
Question
A cardiac arrest patient has been successfully intubated. During CPR with an advanced airway, the provider must deliver 1 breath every:
a. 3 seconds
b. 6 seconds
c. 7 seconds
d. 10 seconds
Answer
b. 6 seconds
Rationale
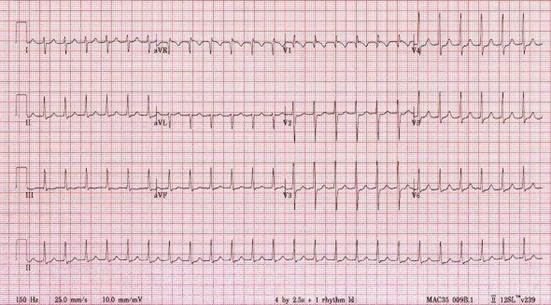
C. Rationale: This is a paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, likely an AV nodal re-entrant tachycardia. The characteristic finding seen on this ECG is a narrow and regular tachyarrhythmia. The presence of unstable symptoms, such as hypotension and chest pain, is an indication for synchronized cardioversion. A precordial thump may be performed, but only if a defibrillator is not available. In this case, the patient is already connected to a defibrillator.
Question
A patient presents to the emergency department with chest pain and hypotension. You obtain the following 12-lead ECG tracing:
You determine that the rhythm is supraventricular tachycardia. The patient is connected to a defibrillator. What is the best treatment for this patient?
a. adenosine 6 mg IV rapid bolus injection
b. precordial thump
c. synchronized cardioversion
d. amiodarone 300 mg IV bolus
Answer
c. synchronized cardioversion
Rationale
B. Rationale: In this scenario, the patient has symptomatic bradycardia. The first choice of medication to be given in this case is atropine.
Question
A patient presents with a palpable pulse of 38 bpm and a decreasing level of consciousness. He has some shortness of breath, and his skin is cool and pale. The first choice for medication to be given to this patient is:
a. epinephrine
b. atropine
c. dopamine
d. rTPA
Answer
b. atropine
Rationale
B. Rationale: In patients with cardiac arrest, regardless of etiology, the first step is CPR, beginning with chest compressions and defibrillation if a shockable rhythm is found. This does not change, even in the case of toxic ingestion. In a patient with clinically symptomatic opiate toxicity, naloxone IV is a good treatment strategy. Advanced airway management is indicated for respiratory distress or arrest that is not responsive to naloxone. Flumazenil is used in cases of benzodiazepine toxicity, not opiate ingestion.
Question
A patient suspected of having opiate toxicity suddenly becomes pulseless and unresponsive. What is the next best step in management?
a. Naloxone IV
b. Chest compressions
c. Advanced airway management
d. Flumazenil IV
Answer
b. Chest compressions
Rationale
A. Rationale: An oxygen saturation of greater than or equal to 94% is in the normal range and will not require any intervention.
Question
A patient with an oxygen saturation of 96% will require what mandatory action?
a. No intervention is necessary
b. Increase in frequency of vital signs monitoring
c. Inform the physician
d. Increase the oxygen flow
Answer
a. No intervention is necessary
Rationale
B. Rationale: One of the important measures to successful advanced cardiac life support is the shortest time to defibrillation. When a shockable rhythm is diagnosed, then defibrillation should not be delayed.
Question
A patient with cardiac arrest secondary to pulseless ventricular tachycardia is being resuscitated, and after 5 cycles of compressions, the biphasic defibrillator is charged and ready to shock. What should the team do next?
a. Continue high-quality CPR for 2 minutes.
b. Defibrillate.
c. Insert an IV line and inject a 1 mg bolus of epinephrine IV every 3–5 minutes.
d. Intubate the patient.
Answer
b. Defibrillate.