Rhythm Strip Identification Flashcard 2
Rationale
B. Rationale: Ventricular tachycardia.
CLUES – regularity: regular; rate: 300 bpm; P waves: not visible; PR interval: none; QRS: 160 milliseconds, bizarre configuration.
Question
Identify the rhythm. To help you in your identification, clues are provided.

a. Ventricular fibrillation
b. Ventricular tachycardia
c. Trigeminy
d. Atrial flutter
Answer
b. Ventricular tachycardia
Rationale
B. Rationale: Sinus rhythm with bigeminy of PVCs.
CLUES – regularity: regular, but the underlying rhythm is interrupted by PVCs; rate: 50 bpm by visible P waves; P waves: uniform with regular P-P interval; PR interval: 200 milliseconds; QRS: 140 milliseconds.
Question
Identify the rhythm. To help you in your identification, clues are provided.
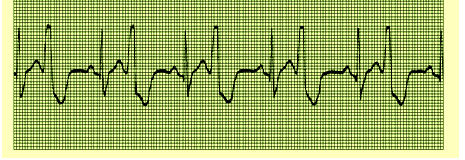
A. Ventricular tachycardia
B. Sinus rhythm with bigeminy of PVCs
C. PVCs with a couplet pattern
D. Supraventricular tachycardia
Answer
B. Sinus rhythm with bigeminy of PVCs
Rationale
A. Rationale: Supraventricular tachycardia.
CLUES – regularity: regular; rate: 188 bpm; P waves: none visible; PR interval: none; QRS: 100 milliseconds
Question
Identify the rhythm. To help you in your identification, clues are provided.
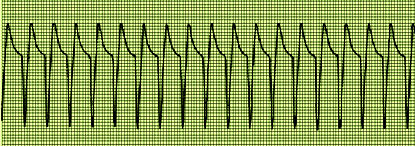
a. Supraventricular tachycardia
b. Sinus tachycardia
c. Atrial tachycardia
d. Ventricular tachycardia
Answer
a. Supraventricular tachycardia
Rationale
D. Rationale: An extremely irritable focus can override higher pacemaker sites to cause a sustained run of PVCs The R-R intervals in VT may have a slightly irregular appearance but they are generally uniform. Like premature ventricular complexes, VT will have a bizarre-appearing QRS complex that is 120 milliseconds or longer; T wave deflection is opposite the R wave; and the P wave, if present, is not seen before the QRS complex. The fact that the patient is in cardiac arrest means the final diagnosis of this case is pulseless VT.
Answer option A: PEA is the absence of all physical contractions of the heart with electrical activity on the ECG tracing.
Answer option B: VF is a deadly dysrhythmia that results in completely erratic, disorganized electrical impulses. It requires immediate defibrillation.
Answer option C: Torsade’s de pointes is a specific type of dysrhythmia that appears as a polymorphic VT. It is usually caused by hypomagnesemia. Torsade’s de pointes
Question
Refer to the image below. A 56-year-old man presents in the emergency department in cardiac arrest after a myocardial infarction. His ECG image appears as below. What is your diagnosis?
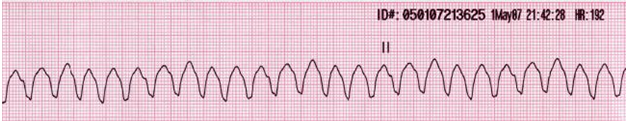
a. Pulseless electrical activity
b. Ventricular fibrillation
c. Torsade’s de pointes
d. Pulseless ventricular tachycardia
Answer
d. Pulseless ventricular tachycardia
Rationale
C. Rationale: The wide, bizarre-looking QRS complexes represent PVCs. A pattern showing one PVC followed by two sinus beats with prolonged QRS complexes is known as trigeminy. If this pattern shows four beats consisting of one premature ventricular complex followed by three sinus rhythms, it is known as quadrigeminy.
Answer option A: VT is a dysrhythmia in which electrical impulses arise from the ventricles as opposed to the SA node. It has a very rapid rate with very wide QRS complexes. A pulse may or may not be present.
Answer option B: SVT is an umbrella term for any dysrhythmia that originates above the ventricles.
Answer option D: PACs are premature complexes that originate from the atria.
Question
Refer to the image below. A patient who reports having palpitations after drinking coffee had a routine checkup with the following ECG tracing. What is your ECG diagnosis?
a. Ventricular tachycardia
b. Supraventricular tachycardia
c. Premature ventricular complex in trigeminy
d. Premature atrial complexes
Answer
c. Premature ventricular complex in trigeminy
Rationale
D. Rationale:
Choice A describes ventricular tachycardia. Choice B describes a sinus tachycardia. Choice C describes atrial flutter.
Question
Tachycardia can come in many forms. Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) can be distinguished from other types of tachycardia because:
a. SVT originates below the bifurcation of the bundle of His. The impulse will spread outside the AV conduction system. Activation of the ventricles is asynchronous, and the QRS complex is widened.
b. SVT is a rhythm that originates from the SA node, causing a rate of > 100 bpm, likely from a physiologic process.
c. SVT is due to a very irritable atrium with an impulse propagated through a cyclic pattern that causes a rate of 300 ± 50 bpm. This is represented by a saw-tooth pattern on an electrocardiogram.
d. SVT originates above the bifurcation of the bundle of His, follows the normal AV conduction system, and activates the ventricles synchronously. An ECG will show narrow QRS complexes measuring < 120 milliseconds.
Answer
d. SVT originates above the bifurcation of the bundle of His, follows the normal AV conduction system, and activates the ventricles synchronously. An ECG will show narrow QRS complexes measuring < 120 milliseconds.
Rationale
C. Rationale: Atrial fibrillation is when the atria are so irritable that they are no longer beating but merely quivering. There are no discernible P waves. The ECG tracing will show barely visible waves along the isoelectric line, and these fibrillatory waves are known as f waves. The quivering atria have impulse rates of > 350 per minute. But this is only an inference since no P waves are produced. The presence of a reasonable ventricular rate exemplified by irregular R-R intervals is due to the AV node blocking the rapid impulses from the irritable atria. The fibrillatory waves are generated in a chaotic manner so that no pattern is produced.
Answer option A: Supraventricular tachycardia is a dysrhythmia originating above the ventricles. It is a regular rhythm with very narrow QRS complexes and an accelerated rate.
Answer option B: Atrial flutter produces a characteristic sawtooth pattern on the ECG tracing.
Answer option D: A bundle branch block is a block in electrical conduction through either the left or right bundle branches that run along the intraventricular septum.
Question
This ECG finding comes from very irritable atria where the heart chamber is merely quivering with an ECG tracing depicting f waves. What is the diagnosis in this case?
a. Supraventricular tachycardia
b. Atrial flutter
c. Atrial fibrillation
d. Bundle branch block
Answer
c. Atrial fibrillation
Rationale
A. Rationale: An SA nodal exit block is an interference of impulse conduction from the regular impulse-generating SA node. The SA node continues to depolarize normally. But in some instances, the impulses are being blocked before they can even leave the SA node, resulting in the absence of P waves on the ECG.
Answer option B: An AV block is a delay in impulse conduction from the AV node.
Answer option C: A right bundle branch block is a delay in impulse conduction through the right bundle branch.
Answer option D: A left bundle branch block is a delay in impulse conduction through the left bundle branch.
Question
What is the ECG diagnosis when impulse conduction is delayed from the sinoatrial node?
a. Sinoatrial exit block
b. Atrioventricular block
c. Right bundle branch block
d. Left bundle branch block
Answer
a. Sinoatrial exit block
Rationale
D. Rationale: In third-degree sinoatrial exit block, the impulses generated from the SA node are totally blocked from reaching the right atrium. An escape rate may be maintained by a junctional rhythm. In some instances, a long pause will lead to cardiac arrest.
Answer option A: Atrial fibrillation is an atrial dysrhythmia that produces fibrillatory waves in the absence of P waves. It is an irregularly irregular rhythm.
Answer option B: Asystole is the complete absence of all electrical activity within the heart.
Answer option C: SVT is a dysrhythmia originating above the ventricles. It is a regular rhythm with very narrow QRS complexes and an accelerated rate.
Question
When the impulse generated from the sinoatrial node is totally blocked from reaching the right atrium, which rhythm will develop in order to maintain the mechanical function of the heart?
a. Atrial fibrillation
b. Asystole
c. Supraventricular tachycardia
d. Junctional rhythm
Answer
d. Junctional rhythm
Rationale
B. Rationale: Atrial fibrillation is a sustained arrhythmia with disorganized electrical activity. It is an irregularly irregular rhythm with no P wave and an absence of an isoelectric line. The fibrillatory waves may be misconstrued as P waves.
Answer option A: A PAC manifests with a premature P wave.
Answer option C: SVT is an umbrella term for any tachycardia that originates above the ventricles, and there may or may not be P waves present.
Answer option D: A second-degree block type II would result in dropped P waves, and there are P waves present on this ECG strip.
Question
Which one of the following dysrhythmias has no P wave?
a. Premature atrial contraction
b. Atrial fibrillation
c. Supraventricular tachycardia
d. Second-degree AV Block Type II
Answer
b. Atrial fibrillation