Chain of Survival Flashcard 3
Rationale
C. Rationale: After notifying the emergency response team, high-quality CPR, rapid defibrillation, and ACLS support with post-cardiac arrest care are performed appropriately. These are represented by the hand, heart, and hospital bed icons, respectively.
Question
What does the hand icon in the in-hospital cardiac arrest chain of survival represent?
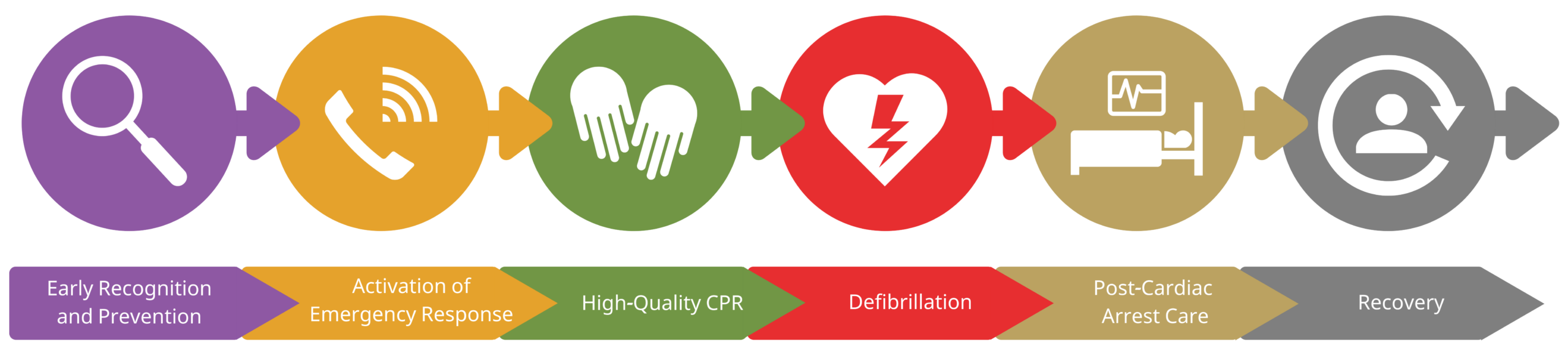
a. Proper handoff from emergency personnel to hospital staff
b. Post cardiac arrest care
c. High-quality CPR
d. Proper hand washing techniques
Answer
c. High-quality CPR
Rationale
C. Rationale: After notifying the emergency response team, high-quality CPR, rapid defibrillation, and ACLS support with post-cardiac arrest care are performed appropriately. These are represented by the hand, heart, and hospital bed icons, respectively.
Question
What does the heart icon in the in-hospital cardiac arrest chain of survival represent?
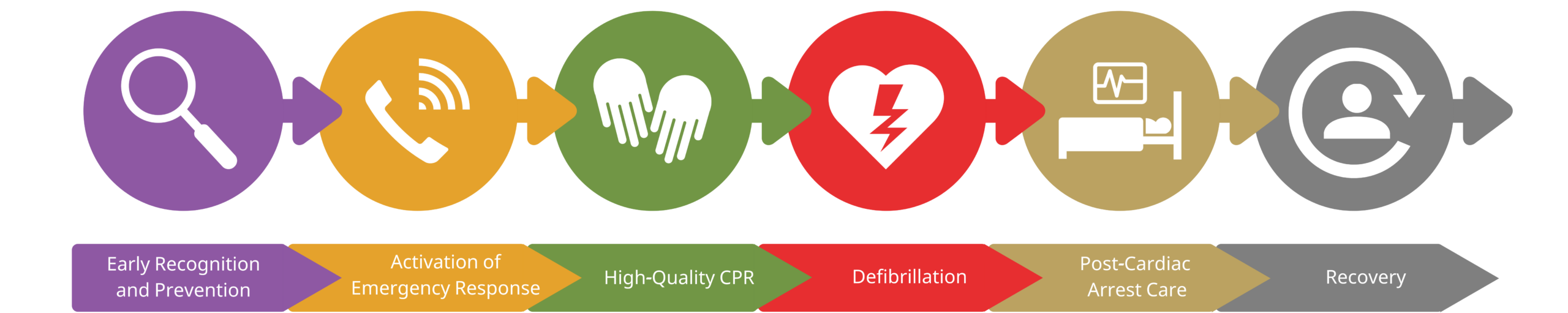
a. Caring for the patient with compassion
b. Chest compressions
c. Rapid defibrillation
d. Administering cardiac medications
Answer
c. Rapid defibrillation
Rationale
D. Rationale: After notifying the emergency response team, high-quality CPR, rapid defibrillation, and ACLS support with post-cardiac arrest care are performed appropriately. These are represented by the hand, heart, and hospital bed icons, respectively.
Question
What does the hospital bed icon in the in-hospital cardiac arrest chain of survival represent?

a. Post resuscitation patients recover in a quiet and comfortable place
b. The EMS team must be well-rested
c. Availability of beds at telemetry ward/critical care
d. ACLS support with post-cardiac arrest care
Answer
d. ACLS support with post-cardiac arrest care
Rationale
A. Rationale: IHCA patients require effective surveillance of the patient to prevent cardiac arrest. This pertains to the magnifying glass on the first link.
Question
What does the magnifying glass in the In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Chain of Survival signify?
a. Effective surveillance of the patient
b. Investigation of the immediate cause of cardiac arrest
c. Attention to detail in administering high-quality CPR
d. Strict monitoring of compliance to protocols by emergency personnel
Answer
a. Effective surveillance of the patient
Rationale
C. Rationale: The telephone receiver icon on the second link represents activating the emergency response team in the event of a cardiac arrest. This team includes multidisciplinary specialists, such as doctors, nurses, respiratory therapists, etc., that are trained and have an immediate response time.
Question
What does the telephone receiver icon in the in-hospital cardiac arrest chain of survival represent?
a. Properly informing the patient’s family
b. Making sure there is a cellphone signal in the hospital
c. Activating the emergency response team
d. Recovery phase after cardiac arrest
Answer
c. Activating the emergency response team
Rationale
B. Rationale: Only trained lay rescuers are certified to perform conventional CPR. Untrained lay rescuers may perform compression-only CPR in the pre-hospital setting with emergency dispatcher assistance.
Question
What is the most appropriate action for UNTRAINED lay rescuers when assisting a patient with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest?
a. Conventional CPR
b. Compression-only CPR
c. Monitor and wait for the paramedics to arrive
d. Perform any of the abovementioned actions to the best of their abilities
Answer
b. Compression-only CPR
Rationale
A. Rationale: Studies have shown that only 2.4% of patients receiving dispatcher-assisted CPR gain some survival benefit, and there is no evidence proving that it improves neurologic outcomes or return of spontaneous circulation. However, since providing CPR is better than no CPR, the AHA still recommends instructions for compression-only CPR to be given to callers.
Question
What is the survival benefit for patients given dispatcher-assisted CPR in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest?
a. 2.4%
b. 10.5%
c. 24.6%
d. 33.3%
Answer
a. 2.4%
Rationale
C. Rationale: The untrained bystander should provide compression-only (hands-only) CPR to adult cardiac arrest patients. They may be guided by the dispatcher. They should continue CPR until an AED or a trained rescuer arrives on the scene. (Systems of Care: OHCA)
Question
What should an untrained bystander do in an adult cardiac arrest situation when no trained provider is present?
a. Contact EMS and avoid the immediate vicinity of the patient
b. Crowd control
c. Hands-only CPR
d. Rescue breathing only
Answer
c. Hands-only CPR
Rationale
B. Rationale: Due to the lack of trained personnel and equipment, the out-of-hospital cardiac arrest chain of survival has poorer survival rates.
Question
Which of the following chains of survival is most difficult due to the limited resources in personnel and equipment?
a. In-hospital cardiac arrest chain of survival
b. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest chain of survival
c. EMS provider chain of survival
d. Lay rescuer provider chain of survival
Answer
b. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest chain of survival
Rationale
C. Rationale: ST elevation myocardial infarction is the most common cause of cardiac arrest in the out-of-hospital setting. Thus, it is prudent to integrate information regarding this condition with a well-organized system of care in the community. Dispatchers may try to elicit information from the caller to help determine if the patient is having a heart attack. When feasible, dispatchers may suggest that the caller give aspirin or other interventions specific for myocardial infarction.
Question
Which of the following disease conditions is the most common cause of cardiac arrest that needs to be included in the systems of care in the out-of-hospital setting?
a. Status asthmaticus
b. Trauma from vehicular crash
c. Myocardial infarction
d. Sepsis
Answer
c. Myocardial infarction