ACLS Principles Flashcard 5
Rationale
D. Rationale: It is important to recognize if a cardiac arrest patient has converted to sinus rhythm in conjunction with assessing the patient’s clinical presentation as a guide to the next treatment options.
Question
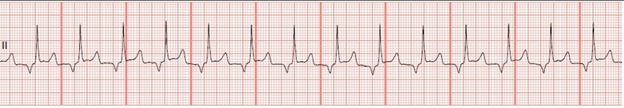
After giving the third shock to a cardiac arrest patient in ventricular fibrillation, you observe the following ECG tracing:

What is your interpretation of this finding?
a. Supraventricular tachycardia
b. Second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II
c. Ventricular fibrillation
d. Sinus tachycardia
Answer
d. Sinus tachycardia
Rationale
B. Rationale: When you are unsure that you feel a pulse, continue high-quality CPR for 2 minutes and give a 1 mg bolus of IV epinephrine every 3 to 5 minutes.
Question
After providing 8 minutes of continuous high-quality CPR to a cardiac arrest patient with asystole, you perform a rhythm check and note the following ECG tracing:

You are unsure if you feel a pulse. What is your next course of action?
a. Defibrillate
b. Continue high-quality CPR for 2 minutes
c. Maintain adequate oxygenation and stabilize blood pressure
d. Apply transcutaneous pacing
Answer
b. Continue high-quality CPR for 2 minutes
Rationale
C. Rationale: Rhythm changes occur often in ACLS. Early ventricular fibrillation will present with coarse waveforms. When ACLS is inadequate or if intervention is delayed, the waveforms become finer and then progress into asystole. Asystole is a non shockable rhythm, and thus rescuers must immediately resume CPR, beginning with chest compressions in this case.
Question
After shocking the patient with ventricular fibrillation, CPR is initiated immediately. After 2 minutes of CPR, a pulse and rhythm check is performed. The rhythm has changed to asystole. What is the next course of action?
a. Shock the patient again with a higher dose
b. Shock the patient again with the same dose
c. Resume CPR
d. Perform post-cardiac arrest care
Answer
c. Resume CPR
Rationale
D. Rationale: Epinephrine 1 mg IV bolus injection is administered after the second shock and every 3 to 5 minutes thereafter.
Question
After the first shock, attempts at resuscitating a patient in cardiac arrest secondary to ventricular fibrillation are restarted. IV access has been established in the left upper extremity. After 2 minutes of high-quality CPR, the patient’s condition does not change. What is the most appropriate next step for treatment?
a. Give epinephrine 1 mg IV bolus
b. Continue high-quality CPR
c. Intubate the patient
d. Defibrillate again
Answer
d. Defibrillate again
Rationale
C. Rationale: The goal of ACLS is to achieve a return of spontaneous circulation. There must be a perfusing rhythm present, and the goal is to achieve a normal sinus rhythm. Before rescuers proceed to post-cardiac arrest care, they must ensure that the patient has a pulse. Otherwise, this can just be pulseless electrical activity, which is also a serious cardiac arrest rhythm. If no pulse is present, CPR must immediately resume.
Question
After two cycles of CPR, a patient with cardiac arrest secondary to asystole has converted into normal sinus rhythm. What is your next course of action?
a. Shock the patient.
b. Proceed to post-cardiac arrest care.
c. Check for a pulse.
d. Resume CPR.
Answer
c. Check for a pulse.
Rationale
D. Rationale: The ECG tracing represents asystole. The flat line is an indication that there is no electrical activity coming from the heart.
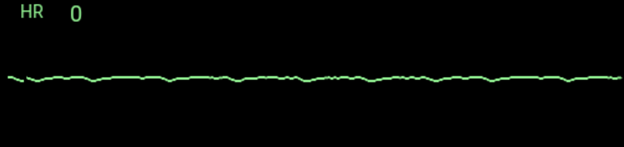
Question
An ECG tracing that shows the following is an indication of:
a. A chaotic firing of impulses throughout the heart, making it quiver
b. An organized rhythm without a pulse
c. An irritable focus somewhere in the atria
d. An absence of electrical activity from the heart
Answer
d. An absence of electrical activity from the heart
Rationale
D. Rationale: The next step would be to send for an AED or other emergency equipment. Assessment of the patient’s pulse and breathing would follow, and treatment would commence, depending on the assessment.
Question
An older man is seen clutching his chest before falling to the ground in a restaurant. His companions call EMS. What should be their next step?
a. Continue trying to elicit a response.
b. Immediately give rescue breaths.
c. Immediately start vigorous chest compressions.
d. Find an AED or instruct someone to do so.
Answer
d. Find an AED or instruct someone to do so.
Rationale
D. Rationale: Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia involves reentrant impulses through the AV node. This causes a narrow-complex and regular tachyarrhythmia, for which adenosine is the drug of choice. Tachyarrhythmias that do not involve the SA or AV nodes are best treated with amiodarone. These tachyarrhythmias include atrial tachycardia or atrial fibrillation, wide-complex ventricular tachycardia, and atrial flutter.
Question
Antiarrhythmic drugs are used to treat stable tachyarrhythmias and shockable cardiac arrest rhythms that are refractory to defibrillation. Which of the following is the first-line antiarrhythmic drug that treats stable tachyarrhythmias involving the AV node?
a. Amiodarone
b. Lidocaine
c. Sotalol
d. Adenosine
Answer
d. Adenosine
Rationale
C. Rationale: When performing high-quality CPR, it is important to avoid excessive ventilation. CPR must be provided at a ratio of 30 chest compressions to 2 ventilations. Excessive ventilations cause increased intrathoracic pressures and adverse hemodynamic effects such as decreased cerebral blood flow.
Question
As the leader of a team, you are assessing a healthcare provider performing high-quality CPR. She is pushing at 2 inches in depth, with a rate of 110 per minute, allowing for complete chest recoil, and ventilating 5 breaths every 30 chest compressions. What will you comment on the provider?
a. Faster chest compressions
b. Push harder
c. Slow ventilations
d. You’re doing great, keep up the good work
Answer
c. Slow ventilations
Rationale
D. Rationale: During the resuscitation of patients with pulseless electrical activity, only epinephrine is the drug of choice.
Question
Aside from epinephrine, which one of the following drugs is necessary for the resuscitation of a patient with pulseless electrical activity?
a. Methylprednisolone 40 mg slow IV injection
b. Adenosine 6 mg rapid IV injection
c. Amiodarone 300 mg IV bolus
d. Only epinephrine is necessary in pulseless electrical activity
Answer
d. Only epinephrine is necessary in pulseless electrical activity